The wild donkey [1] ( lat. Equus asinus ) is a species of the genus Equus of the equidae family of equidae . Its domesticated form played an important historical role in the development of the economy and human culture.
| Wild donkey |
 |
| Scientific classification |
|---|
| No rank : | Bilateral symmetrical |
|
| International scientific name |
|---|
Equus asinus Linnaeus , 1758 |
| Synonyms |
|---|
|
| Area |
|---|
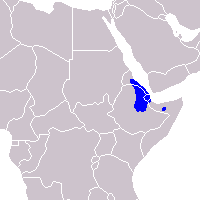
|
| Security status |
|---|
Endangered SpeciesIUCN 3.1 Critically Endangered : 7949 |
|
About 4.4-4.5 million years ago, according to geneticists, the Equus line appeared, giving birth to all modern horses, zebras and donkeys [2] .
Content
Unlike a horse, a donkey has hooves adapted to a rocky and uneven surface. They help to move more safely, but are not suitable for a quick jump. However, in some cases, a donkey can reach speeds of up to 70 km / h. Donkeys come from countries with arid climates . Their hooves do not tolerate the humid European climate and often form deep-going cracks and holes in which foci of decay are hidden. Caring for donkey hooves is therefore crucial. True, they shoe them less often than horses.
Donkeys can have a gray, brown, or black coat ; occasionally white breeds are found. The abdomen is usually light, the same applies to the front of the muzzle and the area around the eyes. Donkeys have a stiff mane and tail ending in a tassel. Ears are much longer than equine. A narrow dark stripe runs along the back. Some subspecies sometimes still have stripes - one on the shoulders and several on the legs.
Depending on the breed, they reach a height of 90 to 160 cm, and acquire sexual maturity at the age of 2-2.5 years. In principle, mating is possible year-round, but usually occurs in the spring . After a period of 12 to 14 months of gestation, one or two cubs are born, which at the age of 6 to 9 months become independent.
In addition to external differences from horses, there are some more features that are not noticeable at first glance. One of them is a different number of vertebrae . In addition, donkeys have only 31 pairs of chromosomes , while horses have 32 chromosomes . Donkeys have a slightly lower body temperature, averaging 37 ° C rather than 38 ° C. Donkeys also have a longer gestation period.
As in the case of horses, it is necessary to distinguish between wild and feral donkeys. The once different subspecies of wild donkeys lived in northern Africa and Western Asia , but as a result of domestication they almost disappeared in the era of the ancient Romans. In our time, they are preserved only in Ethiopia , Eritrea , Djibouti , Somalia and Sudan ; a small population managed to take root in a nature reserve in Israel . In the 1980s, the total number of wild donkeys was estimated at one thousand individuals and has since declined even further. In Somalia, wild donkeys as a result of civil war and anarchy are probably already completely exterminated; in Ethiopia and Sudan, the same fate is likely to await them in the near future. Eritrea is the only country with a relatively stable population of wild donkeys, where their number is about 400 individuals.
Unlike native wild donkeys, feral former domestic donkeys exist in many regions of the world. Their range also includes those countries in which there are still wild donkeys, which, according to the fears of zoologists, can lead to the fact that both groups mix and destroy the “genetic purity” of the wild donkey. About 1.5 million feral donkeys roam the steppes of Australia . In the southwestern United States , approximately 6,000 feral donkeys, called burros , are under guard. One of the few European populations of feral donkey is found in Cyprus on the Karpas Peninsula . They are dark brown or black and are noticeably larger than other donkeys. Often they have zebra-like stripes on their legs.
- Somali donkey
- Kulan
- Onager
- Donkey penguin
- Donkey Albino


