Picrates - a group of chemical compounds - salts of picric acid (2,4,6-trinitrophenol C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 OH). Traditionally, this group also includes compounds of picric acid with some organic substances, which, as a rule, are not salts. Picric acid forms picrates with almost all metals , with the exception of tin . Picrates are most often used as initiating explosives or components of compounds that increase their sensitivity .
History
Presumably, salts of picric acid (picrates of lead and potassium) were discovered by Glauber by exposing them to the coat and horn with nitric acid (the manufacturing methods of which he developed). It is believed that the first printed messages about picrates were published in 1795 , but for a long time their composition and properties were not precisely defined. The first use of a mixture of potassium picrate, potassium nitrate and coal as an explosive was proposed by Desoligne (Designolle) in 1869 . In the same year, Fountaine proposed a mixture of potassium picrate and potassium chlorate, and Abel proposed a mixture of ammonium picrate and potassium nitrate. The first systematic studies of metal picrates were carried out in 1901 by Dupre, continued by Will in 1906 , Silberrad and Phillips in 1908 , and Kast in 1911 .
Explosive properties
A common property of all picrates is to form crystalline hydrates with a different number of water molecules. Sensitivity largely depends on the amount of residual water, the more it is, the less sensitive the materials.
In the series of picrates with various cations, the sensitivity decreases in the series: Pb> Fe> Co> Ni> Ba> Cu> Mn> Zn> Ca, Na, NH 4
Getting
Picrates can be obtained by treating picric acid with hydroxides or carbonates of the corresponding metals, as well as by other methods.
Selected Inorganic Picrates
Aluminum picrate
The chemical formula of [C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 O] 3 Al, molecular weight 711.31 a. e. m. The nitrogen content of 17.73%. Melts above 100 ° C, explodes upon further heating. It can be obtained by continuous heating from its hydrates (for example, di-, tetra-, deca- or hexadecahydrate) at a temperature below 100 ° C. Sensitivity to shock when tested by the Arsenal Picattini method with a load of 2 kg - 40.6 cm (for TNT - 35.6 cm).
Aluminum picrate dihydrate [C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 O] 3 Al * 2H 2 O is obtained from decahydrate when heated to +80 ° C. In sensitivity, it is comparable to anhydrous salt, and decahydrate has a low sensitivity. Aluminum picrate dihydrate explodes at a temperature of about 360 ° C.
The main aluminum picrate [C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 O] 2 AlOH · 7H 2 O, molecular weight 530.35 a. e. m. Reddish or pale yellow needle crystals, when heated to +80 ° C, turn into yellow tetrahydrate, which explodes upon further heating.
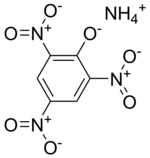
Ammonium picrate
Other names: ammonium trinitrophenolate , explosive D and dannite ( en: dunnite ) (for military use in the USA).
The chemical formula is C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 ONH 4 , molecular weight 246.14. The nitrogen content is 22.77%. Oxygen balance with oxidation to CO 2 : −52%. Two forms: stable yellow and metastable red. Obtained by the reaction of neutralization in an aqueous solution of picric acid with ammonia in the form of a gas or an aqueous solution.
Ammonium picrate is one of the first blasting explosives that began to be used in the 19th century to equip ammunition; the name dannite was given from the surname of the US Army major Dunn, who suggested using it in shells. Under the name Explosive D ( Explosive D ) has been widely used and is used in the United States. It is part of several explosive mixtures (for example, picratol ).
In terms of explosive characteristics, it is slightly inferior to TNT, the sensitivity is less than that of TNT.
Barium picrate
The chemical formula is [C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 O] 2 Ba, molecular weight 594.64 a. e. m. The nitrogen content of 14.14%. Yellow crystalline powder explodes at 333–337 ° C with moderate power. Can be obtained by heating the [C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 O] Ba · 5H 2 O pentahydrate. Pentahydrate - yellow prismatic needle crystals, obtained from a concentrated aqueous solution. Anhydrous salt explodes at 403 ° C, but is insensitive to shock and friction.
Cadmium Picrate
The chemical formula is [C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 O] 2 Cd, molecular weight 569.70 a. e. m. The nitrogen content of 14.76%. Yellow crystalline powder. Explodes at 336–341 ° C. It is obtained by heating crystalline hydrates at 80-150 ° C. (penta-, hepta- or octohydrate). The sensitivity to shock of anhydrous salt according to the Arsenal Picatinny method with a load of 2 kg is 30.5 cm (TNT - 35.6 cm). The sensitivity of octahydrate is 88.9 cm, it is less sensitive than smoky powder .
Calcium Picrate
The chemical formula is [C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 O] 2 Ca, a molecular weight of 497.38 a. e. m. The nitrogen content of 16.90%. Yellow crystalline powder. Explodes at 323–328 ° C. It is obtained by heating decahydrate at +80 ° C.
Picrate Cerium
The chemical formula of [C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 O] 2 Ce, molecular weight 824.45 a. e. m. The nitrogen content of 15.29%. Brown crystalline powder. Explodes at 306-313 ° C. It is obtained by heating crystalline hydrates (tri- or undecahydrate).
Cesium Picrate
The chemical formula is C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 OCs, molecular weight 361.01 a. e. m. The nitrogen content of 11.64%. Yellow needle-shaped crystals. Explodes at 277–287 ° C. It was used in the USA to initiate an explosion in hexogen charges in magnetohydrodynamic generators (MHD generators).
Chromium Picrate
The chemical formula is [C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 O] 5 Cr · 27H 2 0, molecular weight 1695.09 a. e. m. The nitrogen content of 12.04%. Green crystalline powder. Obtained by the interaction of equivalent amounts of barium picrate and the violet modification of chromium sulfate (the green modification does not completely react with barium picrate). Anhydrous salt is obtained by dehydration at 150 ° C. Tridecahydrate and monohydrate explode at 330 ° C. Sensitivity to shock when tested according to the Arsenal Picattini method with a load of 2 kg for tride hydrate 91.4 cm, for monohydrate 20.3 cm (for TNT - 35.6 cm).
Cobalt Picrate
The chemical formula is [C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 O] 2 Co, molecular weight 371.03 a. e. m. The nitrogen content of 22.66%. Brown crystalline powder. Explodes at 320–325 ° C. It is obtained by heating crystalline hydrates at 150 ° C.
Copper picrate
The chemical formula is [C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 O] 2 Cu, molecular weight 520.85 a. e. m. The nitrogen content of 16.14%. Yellow-green crystalline powder, very hygroscopic. Explodes at 282–287 ° C, according to other sources at 373 ° C. It is obtained by heating crystalline hydrates at 80-150 ° C. Sensitivity to shock when tested by the Arsenal Picattini method with a load of 2 kg - 30.5 (for TNT - 35.6 cm). The trihydrate explodes at 300 ° C; its shock sensitivity is 48.3 cm.
Iron (III) picrate
The chemical formula is [C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 O] 3 Fe · 11H 2 O, molecular weight 938.4 a. e. m. The nitrogen content of 13.44%. Red-yellow needle-shaped crystalline powder. Obtained by Custom in 1911 by treatment of a hot saturated solution of iron sulfate with barium picrate. It has several crystalline hydrates that explode at 295 ° C. Sensitivity to shock when tested according to the Arsenal Picattini method with a load of 2 kg - from 15.2 cm for a material dried at 150 ° C to 91.4 cm for a material dried at +25 ° C.
Iron picrate II
The chemical formula of [C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 O] 2 Fe, molecular weight 513.15 a. e. m. The nitrogen content of 16.38%. Dark green crystalline powder. Explodes at 315-320 ° C. It is obtained by drying octahydrate in a vacuum desiccator over sulfuric acid. Octahydrate was obtained by treating a hot saturated solution of iron (II) sulfate with barium picrate. The yellow hexagonal prisms of the octahydrate become brown when stored. Sensitivity to shock when tested according to the Arsenal Picattini method with a load of 2 kg - 91.4 cm.
Lead Picrate
The chemical formula is [C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 O] 2 Pb, molecular weight 663.41 a. e. m. The nitrogen content of 12.67%. Yellow crystalline powder. Explodes at 270–281 ° C. Obtained by drying the monohydrate or tetrahydrate at 150 ° C. Tetrahydrate was obtained by treating a solution of picric acid with lead carbonate. Sensitivity to shock of anhydrous salt when tested with a load of 500 g - 4 cm (for explosive mercury - 24 cm). Sensitivity to shock when tested by the Arsenal Picattini method with a load of 2 kg - 5 cm. The sensitivity to friction is also high.
Lead picrate monohydrate was patented in France in 1872 for use in capsules and detonators. Used in Germany for the production of incendiary mixtures.
Lithium picrate
The chemical formula is C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 OLi, molecular weight 235.05 a. e. m. The nitrogen content of 17.88%. Yellow crystalline powder. Very hygroscopic, with the formation of monohydrate. Explodes at 318–323 ° C. It turns out by drying hydrates. Density 1.724 - 1.740 g / cm3.
Magnesium Picrate
The chemical formula of [C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 O] 2 Mg, a molecular weight of 481.60 a. e. m. The nitrogen content of 17.45%. Explodes at 367–372 ° C. It is obtained by drying hydrates at 150 ° C.
Manganese Picrate
The chemical formula is [C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 O] 2 Mn, molecular weight 512.23 a. e. m. The nitrogen content of 16.41%. Yellow crystalline powder. Explodes at 325-330 ° C. It is obtained by drying hydrates at 150 ° C.
Nickel Picrate
The chemical formula of [C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 O] 2 Ni, molecular weight 516.01 a. e. m. The nitrogen content of 16.29%. Green crystalline powder. Explodes at 335–340 ° C; hexahydrate explodes at 390 ° C. It turns out by drying hydrates. Sensitivity to shock when tested according to the Arsenal Picattini method with a load of 2 kg for anhydrous salt - 10.1 cm.
Platinum
Platinum forms complex compounds containing picric acid ion:
- [Pt (CH 3 SCH 3 ) 4 ] · [C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 O] 2 , nitrogen content 9.32%, yellow crystals, explode upon heating.
- [Pt (C 2 H 5 SCH 2 CH 2 SC 2 H 5 ) 2 ] · [C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 O] 2 , nitrogen content 8.8%, yellow crystals, explodes upon heating.
Potassium Picrate
The chemical formula is C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 OK, molecular weight 267.20 a. e. m. The nitrogen content of 15.73%. Reddish-yellow or green rhombic crystals. Explodes at 310-316 ° C. Presumably, it was first obtained by Glauber in the 17th century by dissolving wood in nitric acid and neutralizing potash K2CO3. It is obtained in the reaction of neutralizing a hot aqueous solution of potassium carbonate with a hot solution of picric acid and separating crystals while cooling the solution. Solubility in water at +15 ° C 0.5 g / 100 g of water, at 100 ° C 25 g / 100 g of water. Solubility in ethyl alcohol 0.2 g / 100 g. Heat of explosive decomposition with a constant volume of 621.8 kcal / mol. Explodes at 370 ° C.
Sensitivity to shock 2 inches. Stability is close to ammonium picrate (Explosive D), but brisance is less. Upon contact with fire, detonates. Under any blasting conditions, black smoke of non-oxidized carbon is released. Mixtures with oxidizing agents (for example, potassium nitrate ) can burn without detonation, but are sensitive to shock and are dangerous to handle.
In 1869 , Designol developed an explosive composition (a mixture of potassium picrate, potassium nitrate and charcoal ) ( Designol powder ), as well as Fountain powder (a mixture of potassium picrate and potassium chlorate ). Potassium picrate was used in pyrotechnic compositions for signal whistles (using the characteristic sound arising from the burning of some picrates). It was used in ballistic solid rocket fuels , in various initiating compositions (for example, in mixtures of potassium picrate, lead picrate and potassium chlorate).
A mixture of finely divided potassium picrate and potassium nitrate in a ratio of 60:40 by weight, tightly packed in paper or bamboo tubes with a diameter of ¼ to ¾ inch, burns with a loud whistling sound. During World War II, the German army used such whistles as additional devices for bombs to enhance psychological impact. Whistles were used as a signal in a gas attack. This mixture has a high sensitivity and is dangerous to handle, so it was replaced by a mixture of gallic acid and potassium chlorate.
Rubidium Picrate
The chemical formula is C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 ORb, molecular weight 313.58 a. e. m. The nitrogen content of 13.40%. Yellow needle-shaped crystalline powder. Explodes at 300-315 ° C. Explodes on impact.
Silver Picrate
Silver forms complex ammonia salts [Ag (NH 3 ) 2 ] · [C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 O] 2 , molecular weight 682.23. The nitrogen content is 28.75%. Yellow crystals explode when heated.
Sodium Picrate
Chemical formula C 6 H 2 (NO2 ) 3 ONa, molecular weight 251.10 a. e. m. The nitrogen content of 16.74%. Yellowish needle-shaped crystalline powder. Explodes at 310-315 ° C. It is obtained by drying the monohydrate at 150 ° C. The monohydrate was obtained by neutralizing an aqueous solution of picric acid with sodium carbonate. Monohydrate explodes at 360 ° C. Sensitivity to shock when tested according to the Arsenal Picattini method with a load of 2 kg for monohydrate 43.2 cm, for anhydrous salt 38.1 cm (for trotyl 35.6 cm).
Sodium picrate burns on contact with a flame and imparts these properties to mixtures with other materials. Used in explosive and pyrotechnic compositions, including instead of potassium picrate.
Double picrates (for example, obtained together with sodium picrate and lead picrate) show less sensitivity to shock than these salts individually.
Picrate Thallium
The chemical formula is C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 OTl, molecular weight 432.48 a. e. m. The nitrogen content of 9.72%. Yellow needle-shaped crystalline powder. Explodes at 273-275 ° C. Obtained by treating a solution of picric acid with thallium carbonate. Explodes on heat and shock.
Thorium Picrate
The chemical formula is [C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 O] 4 Th, molecular weight 1324.68 a. e. m. The nitrogen content of 12.69%. Yellow needle-shaped crystalline powder. Melting point + 52— +53 ° C. Explodes on contact with flame.
Zinc Picrate
The chemical formula is [C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 O] 2 Zn, molecular weight 522.67 a. e. m. The nitrogen content of 16.08%. A tan crystalline powder. Explodes at 350–355 ° C. It is obtained by drying hydrates at 150 ° C. Shock sensitivity 60 cm for a load of 2 kg, which is close to picric acid.
Zirconium Picrate
The chemical formula is [C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 O] 4 Zr, molecular weight 1032.66 a. e. m. The nitrogen content of 16.75%. Yellow needle-shaped crystalline powder. Explodes at 317–322 ° C. It can be obtained by the action of zirconium carbonate on a solution of picric acid.
Organic Picrates
Picric acid forms compounds similar to picrates with many organic substances: hydrocarbons, nitro compounds, amines, phenols, etc. As a rule, they can be obtained by boiling alcohol solutions, followed by cooling and precipitation of picrate crystals. Specific examples of such compounds:
- acenaphthenic picrate (acenaphthen) C 12 H 1 0 + C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 OH. Orange-red prismatic crystals, melting point 161–162 ° C, explodes at 412 ° C.
- allylamine picrate C 3 H 7 N + C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 OH. Lemon-yellow needle crystals, melting point 140–141 ° C, explodes at 270 ° C.
- aniline picrate C 6 H 5 NH 2 + C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 OH. Yellow crystals, melting point with decomposition of 165 ° C, explodes at 398 ° C.
- atropine picrate, melting point 173-175 ° C, explodes at 460 ° C.
- azratoguanidine picrate N 3 CNHNH 2 + C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 OH. Explodes when heated, insensitive to shock.
- cinchonidine picrate 2C 19 H 22 ON 2 + 3C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 OH. Yellow crystals, melting point 194-195 ° C, explodes at 260-268 ° C.
- guanidine picrate CH 5 N 3 + C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 OH. Yellow crystals explode at 498 ° C.
- hexamethylenetetramine picrate C 6 H 12 N 4 + C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 OH. Yellow needle, explodes at 360 ° C.
- пикрат гидразина N 2 H 4 +C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 OH. Жёлтые игольчатые кристаллы, температура плавления 201 °C, взрывается при 385 °C.
- пикрат индена C 9 H 8 +C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 OH. Золотисто-жёлтые кристаллы, температура плавления 98 °C, высокая чувствительность в сухом состоянии, на воздухе медленно разлагается.
- пикрат нафталина C 10 H 8 +C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 OH. Золотисто-жёлтые игольчатые кристаллы, температура плавления 149—151 °C, взрывается при 484 °C. Образует с пикриновой кислотой эвтектическую смесь.
- пикрат альфа- нафтола C 10 H 7 OH+C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 OH. Оранжево-жёлтые игольчатые кристаллы, температура плавления 189—190 °C, взрывается при 458 °C.
- пикрат бета-нафтола C 10 H 7 OH+C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 OH. Оранжево-красные игольчатые кристаллы, температура плавления 155—157 °C, взрывается при 469 °C.
- пикрат фенантрена C 14 H 10 +C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 OH. Золотисто-жёлтые игольчатые кристаллы, температура плавления 143—145 °C, взрывается при 478 °C.
- пикрат пиридина C 5 H 5 N+C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 OH. Золотисто-жёлтые игольчатые кристаллы, температура плавления 165—166 °C, взрывается при 432 °C.
- Пикрат карбамида (мочевины) CH 4 ON 2 +C 6 H 2 (NO 2 ) 3 OH. Жёлтые игольчатые кристаллы, температура плавления 142 °C с разложением, взрывается при 489 °C.
See also
- Тринитрофенол
Literature
- Fedoroff, Basil T. et al Enciclopedia of Explosives and Related Items, vol.1—7. — Dover, New Jersey: Picatinny Arsenal. — 1960—1975. — P274-P285.