Reaction Kriege :
1) The reaction of oxidative cleavage of β-glycols with lead tetraacetate to form carbonyl compounds. Proceeds quantitatively. High stereospecificity is characteristic. Α-glycols break down most quickly. Oxalic acid α-hydroxyaldehydes, α-hydroxyketones, α-hydroxy acids are similarly decomposed.

2) The reaction of cis- hydroxylation of olefins using osmium tetroxide OsO 4 .
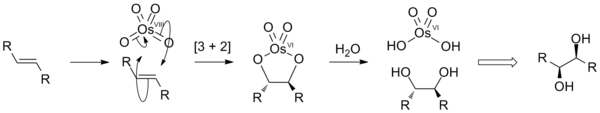
3) Thermal rearrangement of tertiary peroxoethers to form carbonyl compounds:

For example, in the case of the thermal rearrangement of the esters of 9-hydroperoxide alkaline, 1-hydroxy-1,6-epoxycyclodecane esters are formed:

Literature
- R. Criegee, Ber. 64, 260 (1931).
- R. Criegee in Newer Methods of Preparative Organic Chemistry (Interscience, New York, 1948), p.12.