Metronidazole is an antiprotozoal and antimicrobial drug. Metronidazole is on the list of vital and essential drugs .
| Metronidazole | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Chemical compound | |
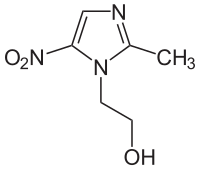
| IUPAC | 2- (2-methyl-5-nitro-1 H- imidazol-1-yl) ethanol |
| Gross formula | C 6 H 9 N 3 O 3 |
| Molar mass | 171.15 g / mol |
| Cas | |
| PubChem | |
| Drugbank | |
| Classification | |
| ATX | , , , , , QP51AA01 |
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Bioavailable | 100% (oral) 59–94% (rectally) |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| The half-life. | 6-7 hours |
| Excretion | Kidneys (60-80%), liver (6-15%) |
| Route of administration | |
| orally, topically , rectally , intravenously, intravaginally | |
| Other names | |
| “Batsimeks”, “Klion”, “Metrovagin”, “Metrovit”, “Metrogil”, “Metrolaker”, “Metron” | |
Content
History
Metronidazole was synthesized in France by Rhone-Poulenc (currently part of Sanofi ) and marketed under the name Flagyl as the first drug in the nitroimidazole group. In the USA, licensed and manufactured by Searle , hereinafter Pfizer . It is a synthetic derivative of the natural substance azomycin produced by Streptomyces spp. The substance was considered as an antiprotozoal agent for the treatment of trichomoniasis . The antibacterial effect was discovered by accident when, in 1962, a patient with trichomoniasis colpitis was cured of bacterial gingivitis . After the patent expires, a large number of generics are issued: Bacimex, Klion, Merinal-B, Metrid, Metrovagin, Metrovit, Metrogil Denta , Metromed, Metron, Metronidazole, Metroseptol, Orvagil, Rosamet, Roseks, Tricho-PIN, Trichobrol, Trichopol, Trichosept Efloran, Anaerobex, Atrivyl, Clont, Efloran, Entizol, Flagesol, Gineflavir
Pharmacodynamics
The mechanism of action is the biochemical reduction of the 5-nitro group of metronidazole by intracellular transport proteins of anaerobic microorganisms and protozoa. The reduced 5-nitro group of metronidazole interacts with the DNA of the cell of microorganisms, inhibiting the synthesis of their nucleic acids, which leads to the death of microorganisms.
The drug is active against Trichomonas vaginalis , Gardnerella vaginalis , Giardia intestinalis , Entamoeba histolytica , obligate anaerobic bacteria: Bacteroides spp. (including Bacteroides fragilis , Bacteroides distasonis , Bacteroides ovatus , Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron , Bacteroides vulgatus ), Fusobacterium spp., Veillonela spp. ; some gram-positive bacteria: Eubacterium spp., Clostridium spp., Peptococcus spp ., Peptostreptococcus spp , as well as Helicobacter pylori (gram-negative) .
Pharmacokinetics
- Suction
After oral administration, it is well absorbed from the digestive tract .
- Distribution
After iv drip for 1 h at a dose of 15 mg / kg body weight and subsequent injections every 6 h at a dose of 7.5 mg / kg, Cssmax of metronidazole is 26 μg / ml and Cssmin is 18 μg / ml. Metronidazole is distributed in many tissues and body fluids, such as bile, saliva, pleural fluid, peritoneal fluid, vaginal secretion, cerebrospinal fluid (about 43% of the concentration in blood plasma), bone tissue, liver, and red blood cells. Plasma protein binding is less than 20%. Metronidazole crosses the BBB and the placental barrier, excreted in breast milk.
- Metabolism
About 30-60% of metronidazole is metabolized in the liver by hydroxylation, oxidation and binding to hyaluronic acid. The main metabolite (2-hydroxymetronidazole) also has an antiprotozoal and antibacterial effect.
- Breeding
T1 / 2 is 8 hours. Excreted in urine (60-80%) and feces (6-15%).
Indications
- trichomoniasis (including chronic complicated);
- giardiasis ;
- gardnerellosis (bacterial vaginosis), Gardnerella vaginalis
- amoebiasis and amoebic liver abscess;
- infections caused by anaerobic bacteria (including peritonitis , abscesses of the abdominal cavity and liver; endometritis, abscesses of the ovaries and fallopian tubes, postoperative complications; pneumonia , pleural empyema, lung abscess ; meningitis , brain abscess; skin infections; bone infections; sepsis ; endocarditis);
- prevention of complications during surgical interventions on the colon, during appendectomy, gynecological operations (in patients from high-risk groups - in combination with iv or iv administration of cefazolin );
- mixed bacterial infections (aerobic and anaerobic), usually in combination with an appropriately selected antibiotic;
- Helicobacter pylori eradication for peptic ulcer or duodenal ulcer in combination with proton pump inhibitors , bismuth preparations and antibiotics (e.g. amoxicillin ). However, there are suggestions of its negative combination with other components of the treatment. [one]
Dosage
With trichomoniasis , adults are prescribed a single dose of 250 mg in the morning and evening for 10 days. After the course of treatment, several control laboratory tests should be carried out (every 3-4 weeks).
With amoebiasis, adults are prescribed 250 mg 3 times / day. The course of treatment is 5-10 days; for children, the dose is set at the rate of 35-50 mg / kg / day. The daily dose should be divided into 3 doses. The course of treatment is 10 days.
With giardiasis , adults and children over 10 years of age are prescribed 500 mg / day; children aged 6-10 years - 375 mg / day; 2-5 years - 250 mg / day. The daily dose should be divided into 2 doses. The course of treatment is 5-10 days. After the course of treatment, several control laboratory tests should be carried out. If necessary, treatment can be repeated after 4-6 weeks.
For the treatment of infectious diseases caused by anaerobic bacteria , adults and children over 12 years of age are prescribed iv in every 8 hours with 100 ml of a 0.5% solution (500 mg). The infusion is carried out at a rate of 5 ml / min. The maximum daily dose for iv administration is 4 g. The course of infusion therapy is 7-10 days, if necessary - 2-3 weeks. For children under 12 years of age, the dose for iv administration is determined at the rate of 7.5 mg / kg body weight (1.5 ml of 0.5% metronidazole solution) every 8 hours. The drug is administered iv drip slowly. Metronidazole is also prescribed orally in a single dose of 250-500 mg.
For the prevention of infections caused by anaerobic bacteria (before surgical operations in the abdominal cavity, in obstetric and gynecological practice), the use of metronidazole infusion solution should be started 5-10 minutes before surgery. For adults and children over 12 years of age, the drug is administered at a dose of 500 mg (100 ml of a 0.5% solution) iv slowly, the infusion is repeated after 8 hours. The drug is prophylactically used no more than 12 hours after surgery. For children under 12 years of age, the dose for iv administration is set at the rate of 7.5 mg / kg body weight (1.5 ml of a 0.5% solution of metronidazole). metronidazole is also prescribed orally. Adults and children over 12 years of age, the first single dose is 1 g (4 tablets of 250 mg), then 250 mg 3 times / day during or after meals, before the onset of preoperative fasting; for children from 5 to 12 years old, 125 mg every 8 hours for 2 days. For newborns and children under 5 years of age, a single dose of the drug for oral administration is established at the rate of 5 mg / kg body weight, every 8 hours for 2 days.
Patients with severe hepatic impairment need to adjust the dosage regimen under the control of serum metronidazole concentration.
- Rules for the introduction of infusion solution
Metronidazole 0.5% solution for iv administration in 100 ml plastic bottles is ready for use. The solution that remains after administration should not be reused. If there are visible changes in the solution, the drug should not be used.
Side effect
- From the digestive system: nausea , vomiting , lack of appetite, an unpleasant metallic taste in the mouth, a change in taste, spastic abdominal pain, constipation or diarrhea .
- From the side of the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system: headache , increased irritability, sleep disturbances, dizziness, ataxia, depression , peripheral neuropathy, cramps , tinnitus, hearing loss, disorientation, fainting .
- From the hemopoietic system: transient leukopenia and thrombocytopenia; a case of bone marrow aplasia has been described.
- Local reactions: with on / in the introduction - thrombophlebitis .
- Allergic reactions: skin rash , itching , urticaria .
- Other: arthralgia , burning sensation in the urethra.
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to metronidazole or other nitroimidazole derivatives.
- If it is necessary to use metronidazole during lactation , breastfeeding should be discontinued, since the substance is excreted along with breast milk.
- Metronidazole quickly penetrates the placental barrier, therefore it is contraindicated for use in the first trimester of pregnancy. The use of the drug in the II and III trimesters is possible only in cases where the intended benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus.
- In combination with amoxicillin is not recommended for patients under 18 years of age.
Special instructions
Patients with a history of side effects from the central nervous system and the hematopoietic system during treatment with metronidazole, if necessary, re-use it should be under close medical supervision.
When prescribing metronidazole to patients with impaired liver function, a correction of the dosage regimen of the drug should be carried out due to the possible cumulation of metronidazole in the body.
With caution, the drug should be prescribed to patients predisposed to the appearance of edema or to patients receiving corticosteroids due to the high sodium content in the solution.
During the use of metronidazole, darker urine staining is observed.
Against the background of drug therapy, it is possible to obtain false results in determining the activity of liver transaminases , LDH, the level of triglycerides and glucose in blood plasma .
Metronidazole can immobilize treponema , which leads to a false positive TPI test (Nelson test).
The simultaneous use of metronidazole and indirect anticoagulants should be avoided. If necessary, their joint appointment should carefully monitor the prothrombin time and establish the appropriate dose of anticoagulant.
With caution, metronidazole should be used simultaneously with lithium preparations, while monitoring the concentration of lithium and creatinine in blood plasma is necessary.
Metronidazole should not be used concurrently with astemizole and terfenadine.
Metronidazole can be used no earlier than 2 weeks after the end of taking disulfiram .
During the treatment with metronidazole, alcohol should be avoided, plus 48 hours after the last dose, since acetaldehyde may accumulate due to a violation of ethanol oxidation. As a result, the development of antabuse-like reactions is possible.
- Pediatric Use
The safety of the use of metronidazole infusion solution in children under 5 years of age has not been established.
- Influence on the ability to drive vehicles and control mechanisms
In connection with the possibility of dizziness while taking the drug, caution should be exercised in patients whose activities require increased attention and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Overdose
Symptoms: convulsions , peripheral neuropathy ; after a single oral administration of 15 g of metronidazole, nausea, vomiting and impaired coordination of movements were observed.
Treatment: conduct symptomatic therapy.
Drug Interactions
- With the simultaneous use of metronidazole potentiates the action of warfarin and other indirect anticoagulants and increases prothrombin time.
- With the simultaneous use of disulfiram and metronidazole, the development of acute psychoses , disorientation is possible.
- With the short-term use of metronidazole against the background of treatment with high-dose lithium salts, it is possible to increase the concentration of lithium in the blood plasma, increase its toxicity and the appearance of symptoms of impaired renal function.
- With the simultaneous use of metronidazole with astemizole and terfenadine , ECG changes, arrhythmias, heart block, fainting are possible.
- With the simultaneous use of metronidazole with cimetidine, the metabolism of metronidazole in the liver can be reduced, which can lead to delayed excretion and an increase in the concentration of metronidazole in the blood plasma.
- With the simultaneous use of metronidazole and phenobarbital, the metabolism of metronidazole is accelerated by the induction of microsomal liver enzymes, as a result of which T1 / 2 and plasma concentrations of metronidazole are reduced.
- With the simultaneous use of metronidazole and phenytoin, there is a decrease in clearance and an increase in the concentration of phenytoin in the blood plasma.
- With the simultaneous use of metronidazole with bismuth salts and proton pump inhibitors, a stronger increase in the pH of the stomach environment is observed. [one]
Synthesis
2-methylimidazole ( 1 ) can be obtained by the imidazole synthesis of Debus-Radzizhevsky or from ethylenediamine and acetic acid , further cyclization of the diamide into dihydroimidazole by exposure to calcium oxide followed by dehydrogenation under the action of Raney nickel . 2-methylimidazole is nitrated to produce 2-methyl-4 (5) -nitroimidazole ( 2 ), which is alkylated with ethylene oxide or 2-chloroethanol to produce metronidazole ( 3 ): [2] [3] [4]
Links
Notes
- ↑ 1 2 Logunov A.V., Lyutin D.S., Lopina N.P., Bordina G.E. “A VIEW OF CHEMISTRY ORGANIC ON THE PROCESS OF INTERACTION OF MEDICINES:“ DE-NOL ”,“ OMEPRAZOL ”,“ METRONIDAZOLE ” . Practical experiment . http://www.eduherald.ru/+( January 15 , 2016).
- ↑ Ebel, K .; Koehler, H .; Gamer, AO; Jäckh, R. Imidazole and Derivatives (Neopr.) . - DOI : 10.1002 / 14356007.a13_661 .
- ↑ Actor, P .; Chow, AW; Dutko, FJ; McKinlay, MA Chemotherapeutics (neopr.) . - DOI : 10.1002 / 14356007.a06_173 .
- ↑ Kraft, M. Ya .; Kochergin, PM; Tsyganova, AM; Shlikhunova, VS Synthesis of metronidazole from ethylenediamine (neopr.) // Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal. - 1989. - T. 23 , No. 10 . - S. 861-863 . - DOI : 10.1007 / BF00764821 .