Clostridia [1] ( lat. Clostridium ) is a genus of gram-positive , obligate anaerobic bacteria capable of producing endospores [2] .
| Clostridia | |||||||||||||
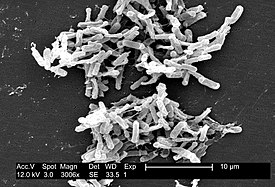 Clostridium difficile | |||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||
| International scientific name | |||||||||||||
Clostridium Prazmowski 1880 | |||||||||||||
| Kinds | |||||||||||||
numerous, including:
| |||||||||||||
Clostridia are part of the normoflora of the gastrointestinal tract and female genital tract. Sometimes they are found in the oral cavity and on the skin.
Bacteria of the clostridium genus produce the strongest known poisons - botulinum toxin ( C. botulinum ), tetanospasmin ( C. tetani ), ε-toxin C. perfringens and others.
Content
The form of bacteria
Individual cells are elongated sticks , the name of the genus comes from other Greek. κλωστήρ "spindle". Many species that were attributed to clostridia on this morphological basis were later reclassified. Endospores can be located centrally, eccentrically and terminally. The diameter of the endospores often exceeds the diameter of the cell.
Clostridia is also a form of bacterial cells in which the centrally located spore has a diameter larger than the diameter of the cell itself, which is why the cell “swells” and takes on a spindle-shaped shape.
Representatives
The genus includes both free-living species (for example, Clostridium pasteurianum ) and pathogenic, for example, causative agents of tetanus , gas gangrene and botulism [3] , pseudomembranous colitis .
The species Clostridium chauvoei is the causative agent of emphysematous carbuncle in livestock.
Notes
- ↑ Atlas of Medical Microbiology, Virology, and Immunology: A Textbook for Medical Students / Ed. A.A. Vorobyev , A.S. Bykov . - M .: Medical News Agency, 2003. - P. 66. - 236 p. - ISBN 5-89481-136-8 .
- ↑ Ryan KJ, Ray CG (editors). Sherris Medical Microbiology. - 4th ed. - McGraw Hill, 2004 .-- ISBN 0-8385-8529-9 .
- ↑ Wells CL, Wilkins TD. Clostridia: Sporeforming Anaerobic Bacilli in: Baron's Medical Microbiology (Baron S et al , eds.) . - 4th ed. - Univ of Texas Medical Branch, 1996. - ISBN 0-9631172-1-1 .