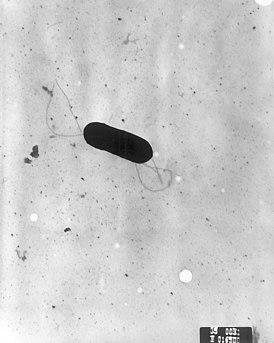
Listeriosis is a bacterial infection that is mainly caused by the bacterium Listeria monocytogenes [3] . This is a gram-positive bacillus with rounded ends, does not form spores and capsules, is an optional anaerobic, grows on ordinary nutrient media [4] . At the same time, there is a case when listeriosis was caused by another type of listeria - L. ivanovii [5] .
| Listeriosis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| ICD-10 | A 32 |
| ICD-10-KM | , , , , and |
| ICD-9 | 027.0 |
| ICD-9-KM | |
| Diseasesdb | 7503 |
| Medlineplus | 001380 |
| eMedicine | med / 1312 ped / 1319 |
| Mesh | and |
Listeriosis is considered a typical sapronosis , while the primary natural reservoir of listeria is the soil from which they can enter plant organisms. The source of infection of farm animals is feed, in particular, silage, where listeria reproduce. Infection of people is associated with the consumption of vegetables and animal products [6] .
Thermo-tolerance, psychrophilicity and other features of Listeria biology determine their ability to infect food products and propagate in them, which leads to numerous epidemic outbreaks and sporadic cases of food listeriosis [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [ 13] .
The role of listeria as a causative agent of human diseases can be described as: they are causative agents of foodborne infection ; causative agents of a wide range of opportunistic infections ; the cause of perinatal and neonatal human pathology. Specialists at the beginning of treatment prescribe antibacterial medications. Effective drugs remain under the names chloramphenicol, erythromycin and tetracycline. [fourteen]
Content
- 1 Treatment
- 2 Epidemiology
- 3 Listeria infection in food production
- 4 Forecast
- 5 Listeriosis in animals
- 6 notes
Treatment
Etiotropic therapy for listeriosis according to the literature is more often empirical . Treatment recommendations are based on a study of the sensitivity of Listeria to in vitro antibiotics , animal experiments, and clinical experience in the treatment of small groups of patients.
L. monocytogenes is known to be sensitive. [ specify ] to a wide range of antibiotics, with the exception of new cephalosporins and fosfomycin . Listeria are sensitive to penicillin derivatives (especially aminopenicillins), most macrolides (except azithromycin and spiramycin), aminoglycosides , and tetracycline . The causative agent is sensitive to representatives of glycopeptides (vancomycin) and lipopeptides (daptomycin), oxazolidinones. There are reports that most drugs from the quinolone group have moderate activity against listeria . At the same time, some researchers report that new fluoroquinolones ( levofloxacin , moxifloxacin , etc.) were active against more than 99% of L. monocytogenes strains.
Epidemiology
Listeria infects the central nervous system and can cause meningitis and encephalitis [3] . Listeriosis can be fatal [3] [15] [7] [8] . The disease is most susceptible to certain groups of people. These are pregnant women, newborns, the elderly and people with weakened immune systems.
According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in the United States, about 1,600 cases of listeriosis are recorded per year. Moreover, the number of deaths due to listeriosis is about 260 [16] .
Published on February 21, 2017, a study by the School of Veterinary Medicine Madison (USA) showed that listeriosis can also lead to miscarriage already in the early stages of pregnancy (first trimester) [17] . Previously, listeriosis was recognized only in the late stage of pregnancy (third trimester), and its effect in the early stage has not been studied.
The main method of infection with listeriosis is food. The bacterium enters the human body along with food, which, in turn, become infected during production and storage.
At the same time, faced with frequent cases of infections with listeria at a food enterprise, in most cases we still don’t know what caused the contamination. At the same time, there are a number of studies showing which zones Listeria is distributed in the production workshop.
Listeria infection in food production
In 1990, the British Research Institute Campden BRI conducted a study of food production for the possibility of infection with monocytogenic listeria [18] . About 10,000 samples were taken from various food enterprises. Speaking about the distribution of positive samples in different zones, the distribution of Listeria was as follows: 53% of the samples were taken from cleaning equipment, 28% from the gangways and 19% from the floors (Fig. 1). Listeria was practically not present on the food equipment.
Moreover, 25% of all samples taken from the ladders were positive for listeria.
A similar study, but already focused only on the dairy sphere, was conducted by the Foggia Institute (Italy) in 2012 [19] . 34 dairy enterprises in southern Italy were investigated. Different strains of listeria were detected at 19 enterprises (56%). Speaking about the distribution of positive samples in different zones, the distribution of listeria was as follows: 19% of the samples were taken from equipment, 69% from the ramps , 12% from the products. At the same time, monocytogenic listeria was found at 7 enterprises: 19% of positive samples were taken from equipment, 73% from traps , 8% from products (Fig. 2).
Another interesting study is a 1997 study by the Norwegian College of Veterinary Medicine. The study included 40 smoked fish factories [20] . Samples were taken from the final product and from the ladders. Listeria monocytogenes was found in the final product in 13 plants out of 40 (33%), and in the ladders in 25 plants out of 40 (63%). Different strains of listeria were found in the final product at 16 plants from 40 (40%), and in the ladders at 30 plants from 40 (75%) (Fig. 3).
In 2018, as a result of the epidemic in South Africa, about 1000 people fell ill and 180 people died [21] .
Forecast
With a nervous form of the disease in 98-100% of cases, the prognosis is hopeless, treatment is successful only in the very initial stage of the disease, and with a septic form, the prognosis is cautious [4] .
Animal Listeriosis
This is a widespread disease from the group of zooanthroponoses. It is found in animals of almost all species. The most commonly affected sheep. The disease is characterized by damage to the nervous system, septic effects, abortion and mastitis. [4] In vivo, there is a nervous, septic, genital, mixed, subclinical and latent forms of the disease. The main one is considered nervous. Infection usually occurs by an alimentary route. The pathogenic effect of the pathogen is associated with the release of exo- and endotoxins [22] . The incubation period for listeriosis in animals is 7-30 days [4] .
Notes
- ↑ Disease Ontology release 2019-05-13 - 2019-05-13 - 2019.
- ↑ Monarch Disease Ontology release 2018-06-29sonu - 2018-06-29 - 2018.
- ↑ 1 2 3 Questions and Answers | Listeria | CDC (neopr.) . www.cdc.gov. Date of treatment May 6, 2017.
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 R.F.Sosov et al. Epizootology. - M .: Kolos, 1969 .-- 400 p.
- ↑ Christelle Guillet, Olivier Join-Lambert, Alban Le Monnier, Alexandre Leclercq, Frédéric Mechaï. Human Listeriosis Caused by Listeria ivanovii (en-us) // Emerging Infectious Diseases. - T. 16 , no. 1 . - S. 136–138 . - DOI : 10.3201 / eid1601.091155 . - PMID 20031061 .
- ↑ Tartakovsky I.S., Maleev V.V., Ermolaeva S.A. Listeria: role in human infectious pathology and laboratory diagnostics. // "Medicine for all." - M. , 2002.
- ↑ 1 2 Listeria Outbreak Traced To Meat Plant Outside Philadelphia . Date of treatment May 6, 2017.
- ↑ 1 2 Blue Bell Tracks Down Source of Its Deadly Listeria Outbreak . Eater (April 4, 2016). Date of treatment May 6, 2017.
- ↑ CB Dalton, CC Austin, J. Sobel, PS Hayes, WF Bibb, LM Graves, B. Swaminathan, ME Proctor and PM Griffin ,. “An Outbreak of Gastroenteritis and Fever Due to L. monocytogenes in Milk” // New England Journal of Medicine. - 1997 .-- T. 336 . - S. 100-105 . - DOI : 10.1056 / NEJM199701093360204 . - PMID 8988887 .
- ↑ Multistate Outbreak of Listeriosis Linked to Soft Raw Milk Cheese Made by Vulto Creamery | Listeria | CDC (neopr.) . www.cdc.gov. Date of treatment May 6, 2017.
- ↑ 2008 Canada listeriosis outbreak (English) // Wikipedia. - 2016-10-16.
- ↑ 2011 United States listeriosis outbreak (English) // Wikipedia. - 2017-02-26.
- ↑ Fruit Processing Plant Linked to Deadly Listeria Outbreak , Scientific American . Date of treatment May 6, 2017.
- ↑ Listeriosis: symptoms in humans, during pregnancy, listeria, what is analysis . zemed.ru. Date of treatment January 11, 2018.
- ↑ CNN Library. Listeria Fast Facts . CNN Date of treatment May 6, 2017.
- ↑ Listeria (Listeriosis) | Listeria | CDC (neopr.) . www.cdc.gov. Date of treatment May 6, 2017.
- ↑ Bryce Wolfe, Gregory J. Wiepz, Michele Schotzko, Gennadiy I. Bondarenko, Maureen Durning. Acute Fetal Demise with First Trimester Maternal Infection Resulting from Listeria monocytogenes in a Nonhuman Primate Model (English) // mBio. - 2017-03-08. - Vol. 8 , iss. 1 . - P. e01938-16 . - ISSN 2150-7511 . - DOI : 10.1128 / mBio.01938-16 .
- ↑ Holah, JT Effective microbiological sampling of food processing areas. // Guideline No. 20, Campden & Chorleywood Food Research Association. - 1999.
- ↑ A. Parisi, L. Latorre, R. Fraccalvieri, A. Miccolupo, G. Normanno, M. Caruso, G. Santagada. Occurrence of Listeria spp. in dairy plants in Southern Italy and molecular subtyping of isolates using AFLP. // Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale della Puglia e della Basilicata, Foggia, Italy. Food Control. - 2013 .-- T. 29 . - S. 91-97 . - DOI : 10.1016 / j.foodcont.2012.05.05.036 .
- ↑ Rorvik, LM, Skjerve, E., Knudsen, BR, & Yndestad, M. Risk factors for contamination of smoked salmon with Listeria monocytogenes during processing. // International Journal of Food Microbiology. - 1997 .-- S. 215-219 . - PMID 9310857 .
- ↑ Meat sausages caused mass deaths
- ↑ A.V. Zharov, V.P. Shishkov et al. Pathological anatomy of farm animals. - M .: Kolos, 1995 .-- 543 p.