Doxycycline is a semi-synthetic antibiotic of the tetracycline group with a wide spectrum of action.
| Doxycycline | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Chemical compound | |
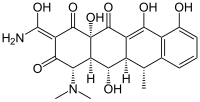
| IUPAC | (4 S , 4a R , 5 S , 5a R , 6 R , 12a S ) -4-dimethylamino-3,5,10,12,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-1,11-dioxo-1,4, 4a, 5.5a, 6,11,12a-octahydrotetracene-2-carboxamide |
| Gross formula | C 22 H 24 N 2 O 8 |
| Molar mass | 444.435 g / mol |
| Cas | |
| PubChem | |
| Drugbank | |
| Classification | |
| ATX | |
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Bioavailable | 100% |
| Metabolism | hepatic, minimal |
| The half-life. | 18-22 hours |
| Excretion | urine, feces |
| Dosage Forms | |
| capsules, lyophilisate for solution, intravenous solution, tablets | |
| Route of administration | |
| orally, buccally, intramuscularly, intravenously | |
| Other names | |
| Vidoktsin, Xedocin, Unidox Solutab | |
Content
Pharmacological action
It has a bacteriostatic effect due to the suppression of protein synthesis of pathogens. Active against aerobic gram-positive bacteria: Staphylococcus spp. (including penicillinase producing strains), Streptococcus spp. (including Streptococcus pneumoniae ), Bacillus anthracis , Listeria monocytogenes ; anaerobic bacteria: Clostridium spp. Doxycycline is also active against aerobic gram-negative bacteria: Neisseria gonorrhoeae , Escherichia coli , Shigella spp., Salmonella spp., Enterobacter spp., Klebsiella spp ., Bordetella pertussis , as well as against Rickettsia spp., Treponema slasppm., Mypp . and Chlamydia spp. Pseudomonas aeruginosa , Proteus spp., Serratia spp ., Most strains of Bacteroides fragilis are resistant to doxycycline .
Pharmacokinetics
After ingestion, it is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the digestive tract . Eating slightly affects the absorption of doxycycline. It is widely distributed in tissues and body fluids. Binding to plasma proteins is 80-95%. T 1/2 is 12-22 hours. It is excreted unchanged in the urine (40%), however, the main part of the dose is excreted unchanged with feces due to the secretion of bile.
Indications
Infectious and inflammatory diseases caused by microorganisms sensitive to doxycycline, including infections of the respiratory system and ENT organs; gastrointestinal tract infections; purulent infections of the skin and soft tissues (including acne); infections of the genitourinary system: gonococcal and non-gonococcal urethritis (gonorrhea), primary and secondary syphilis ; typhus , brucellosis , rickettsiosis , osteomyelitis , trachoma , chlamydia , as well as the initial stage of Lyme disease (tick-borne borreliosis).
Side effect
From the digestive system: nausea , vomiting , anorexia , abdominal pain, diarrhea , constipation , dysphagia, glossitis, esophagitis , transient increase in the blood level of hepatic transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin. From the hemopoietic system: neutropenia , thrombocytopenia , hemolytic anemia . Allergic reactions: skin rash, itching, eosinophilia , rarely - Quincke's edema , photosensitivity . Other: increased residual nitrogen, candidiasis , intestinal dysbiosis , discoloration of teeth in children. In some cases, blood pressure drops.
Contraindications
Pregnancy, children under 8 years of age (the possibility of the formation of insoluble complexes with calcium in the skeleton, tooth enamel and dentin), hypersensitivity to tetracyclines, porphyria, severe liver failure, leukopenia, lactation, myasthenia gravis (for iv administration). Allergy to tetracyclines. Tetracyclines used during the formation and development of teeth can lead to violations of their development, which can vary from a persistent change in their color even (in extremely severe cases) to a complete delay in their growth. Therefore, with the exception of vital indications, the use of tetracyclines in the second half of pregnancy, during breastfeeding, as well as in children earlier than the 8th year of life, is not allowed. Pharma Handbook
- Pregnancy and lactation
Doxycycline is contraindicated in pregnancy and lactation . Doxycycline crosses the placental barrier. It can cause irreversible discoloration of teeth, enamel hypoplasia , inhibition of bone growth and fragility of the skeleton of the fetus , as well as the development of fatty liver. If necessary, use during lactation should stop breastfeeding. Frequent pain in the stomach.
Special instructions
Doxycycline is used with caution in case of impaired liver function. In case of impaired renal function, dose adjustment is not required. To prevent local irritating effects ( esophagitis , gastritis , gastrointestinal ulceration), it is recommended to take it during the daytime with plenty of fluids and food. In connection with the possible development of photosensitization, it is necessary to limit insolation during treatment and within 4-5 days after it.
Doxycycline is not used in children under 8 years of age, since tetracyclines (including doxycycline) cause a long-term change in tooth color, enamel hypoplasia and a slowdown in the longitudinal growth of skeleton bones in this category of patients.
A solution of doxycycline for iv administration should be used no later than 72 hours after its preparation.
Doxycycline in the form of tablets, capsules, powder for injection is included in the List of Essential Drugs .
Drug Interactions
Preparations containing metal ions ( antacids , preparations containing iron, magnesium, calcium) form inactive chelates with doxycycline, and therefore, their simultaneous administration should be avoided. With simultaneous use with barbiturates, carbamazepine, phenytoin, the concentration of doxycycline in blood plasma decreases due to the induction of microsomal liver enzymes, which may cause a decrease in its antibacterial effect.
Combinations with penicillins, cephalosporins that have a bactericidal effect and are antagonists of bacteriostatic antibiotics (including doxycycline) should be avoided. The absorption of doxycycline is reduced by antacids containing aluminum, magnesium and calcium, foods containing calcium ( milk, cottage cheese ), iron preparations, sodium bicarbonate, magnesium-containing laxatives, colestyramine and colestipol, so their use should be divided by an interval of 3 hours! Due to the suppression of intestinal microflora, doxycycline reduces the prothrombin index, which requires dose adjustment of indirect anticoagulants. Reception of doxycycline reduces the reliability of contraception and increases the frequency of breakthrough bleeding while taking estrogen-containing oral contraceptives. The simultaneous use of retinol contributes to an increase in intracranial pressure.