The pink pelican [1] ( lat. Pelecanus onocrotalus ) is a large waterfowl of the pelican family. The popular Russian name is Baba-Babura, Baba-Bird.
| Pink Pelican |
 |
| Scientific classification |
|---|
| No rank : | Bilateral symmetric |
| Family: | Pelican ( Pelecanidae Rafinesque , 1815 ) |
|
| International Scientific Name |
|---|
Pelecanus onocrotalus Linnaeus , 1758 |
| Area |
|---|
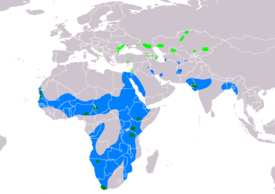 - Only nest
- Year round
- Migration areas
|
| Security status |
|---|
Least concernIUCN 3.1 Least Concern : 22697590 |
|
The Red Book of Russia
view disappears |
|
Content
- Body length of males up to 185 cm.
- Wingspan - up to 380 cm.
- The length of the wing in males is 66.5-77 cm, in females 58.6-78 cm. [2]
- Males weigh 5.5–15 kg, females 5.1–10 kg. [2]
- Primary primary feathers - 11.
- The tail is almost straight, from 24 tail feathers. The tail length of males is 15.5–23 cm, females 13.8–20.5 cm. [2]
- The plumage is rare, tight to the body.
- The beak is long, flattened, ending hook hooked down. The length of the beak of males 35–47.1 cm, females 28.9–46 cm. [2]
- The length of the male cocks is 12–18.5 cm, females 10–16.5 cm. [2]
- The neck is long.
- The throat sac is large, strongly stretched.
- The forehead, bridle, ring around the eye, space behind the eye and the base of the mandible are not feathered. The plumage of the head with a sharp cape protrudes on the bare forehead. On the head there is a crest of elongated, pointed feathers.
- Legs are short.
Coloring
- Brown downy chick . The legs and beak are blackish, the throat sac is darkish lead in color.
- Nest outfit . The head and neck are greyish-brown, lighter towards the back. The back is light blue; humeral, medium and large covering wings are gray-brown with lighter tops, small covering wings are light brown with an ocher tinge. Fly blackish-brown with lighter edging on primary primary and silver-gray patina on secondary ones. Steering light gray. The abdominal side of the body is white with brown patina.
- Adult bird The plumage is white with a pale pink tinge, somewhat more intensely developed on the ventral side of the body. On the chest there is an ocher-yellow spot. Fly black with a light brownish bloom, with white rods and ash-silver outer webs of secondary flywheels. Internal secondary flywheel brighter outdoor. The bare areas around the eyes are yellow, the throat sac is yellowish with translucent red blood vessels. The mandible is greyish-blue with reddish spots, pink edges and whitish top hook, the mandible at the base of greyish-blue gradually yellowing towards the top of the beak. The iris is light red. Legs are yellow, orange on the folds.
- Marital attire : the front, non-perpendicular part of the forehead forms bloating. Bare parts are painted more brightly - red with a yellowish tinge; throat sac yellow-ocher. The iris is dark red. Legs are yellowish-red. The color of the beak is also getting brighter. Males and females are colored the same and differ only in size.
Shedding is poorly understood. The change of primary flywheel and helmsman goes from inner to outer feathers. Young birds put on an adult outfit in the 3rd year of life.
Voice
The voice is indistinguishable from the Curly Pelican .
Range : Southeast Europe , Africa , Front , Middle and South-West Asia .
The pink pelican nests from southeastern Europe ( the Danube Delta ) to western Mongolia . Winters in northeast Africa , partly in southern Asia - from the Persian Gulf to northern India . In Europe, at the beginning of the 20th century, it nested in Hungary and the Czech Republic . In Moldova - in the Dniester plains . In Ukraine - in the Dnieper estuary , in the Karkinitsky Bay , in the Tendrovsky Bay . In Russia , on the islands in the southeastern part of the Sea of Azov between Yeysk and Krivoy Spit , in the Volga delta . In Asia, on the northeastern coast of the Caspian Sea , south to Dead Kultuk ; on the Aral Sea and from the Syr Darya delta to Amu Darya ; along the Syr-Darya and on the adjacent lakes; in the lower reaches of Chu , on Balkhash , in the estuary area of Ili , Karatal , Aksu ; in the Zaisan depression ; in Dzungaria . In Iran on Lake Urmia ; in the southern part of Khorassan , near the Persian Gulf , in Seistan , in Mesopotamia , Syria on the lake of Antioch , in the north-west of India to Sind . There are local, non-migratory populations in northeast Africa from Senegal to Lake Nyasa , in the north-west of India and in the south of Vietnam . In the Caucasus and China does not nest. Since 1999, attempts have been made in the Crimea to nest the pink pelican on the Swan Islands [3] .
Strength
The number of all over the world is estimated at 290 thousand individuals. Of these, 6,660 to 11,550 pairs nest in the Palaearctic , and of this number, 46–55% are within the former USSR . In Europe, the largest nesting site is the Danube Delta ( Romania ), 3–3.5 thousand pairs. The total number of pink pelicans in the XX century has decreased, but in general, this species does not belong to the endangered.
It feeds on the pink pelican, like all pelicans, mainly fish. In Europe, he prefers carps , in Africa - cichlids . Large fish makes up to 90% of its feed; the remaining 10% are small fish, and in Africa, the eggs and chicks of the Cape cormorant ( Phalacrocorax capensis ). Daily need for food - 900-1,200 g (or 2-4 large fish).
Pelicans cannot dive and, fishing for fish, submerge the neck or the front part of the body. Most often, pelicans fish together (which is rare among birds): they drive it to the shore, flapping their wings heavily on the water and making a lot of noise. Previously known joint hunting of pelicans with cormorants . Fishing takes only a small part of the pelican day - usually from 8-9 o'clock in the morning.
Nesting in the temperate zone occurs in the spring; in Africa - year-round. The pink pelican nests in shallow inland waters with dense reed beds on the shore, lakes and rivers, especially in the last deltas, less often on sandy and stony, slightly overgrown islands. Sometimes it settles on saline water bodies without surface vegetation. It forms very dense, sometimes joint with a curly pelican , colonies up to many hundreds of pairs. The location of the colonies is more or less permanent. The first 2-3 years of life pelicans do not start nesting and spend this time, probably near the wintering grounds.
The female builds a nest very quickly - in 2-3 days. The male helps the female: gathers grass, stuffing her throat bag, and brings this material to the female. On occasion, pelicans steal building material from their neighbors, especially often from their relative, the curly pelican . The female is sitting on the nest, when the laying of eggs has not yet begun, and it is hard to go, only in the morning and evening to feed. She usually lays only 2 eggs. The female hatches almost exclusively, the male occasionally helps her. Hatching lasts 29-36 days. At first, the parents feed the chicks with their semi-digested burped food; later they bring small fishes in their beaks, and the chicks reach them, thrusting their beaks deep into the parent's beaks. The chicks fledge on the 65-75 day.
In Russia, pink pelicans appear in spring, in March-April. Since the end of the 19th – beginning of the 20th centuries, the habitat of this species declined significantly: before, the pink pelican was common in nesting in the East Azov region , it nested in large numbers in the Manych and Kuma valleys, in the Terek and Volga deltas . At present, it nests only in the Manych valley, on the Manych-Gudilo lake, irregularly and in small numbers - on the Chogray reservoir. In the Terek delta, the last nesting event was noted in 1961. In the Volga delta in recent years, only in 1980, nesting of two pairs was noted. The current abundance of the species in Russia ranges from 54 to 125 breeding pairs and reaches, after reproduction, 230–400 individuals. The main factor leading to a sharp decline in the number of the species was the reduction in the area of their habitats as a result of irrigation and drainage activities and the use of pesticides .
In the fall of 2010, a flock of pink pelicans, having lost their course due to an abnormally warm autumn, flew to the village of Suslovo of the Republic of Bashkortostan. A small colony of these birds, up to 10 pairs, for several years arrive in the spring in the vicinity of the city of Karasuk, Novosibirsk region.
The pink pelican is listed in the Red Book of Russia , as a species that is in danger of extinction.
egg Pelecanus onocrotalus - Museum of Toulouse
- ↑ Boehme RL , Flint V. Ye. The five-language dictionary of animal names. Birds. Latin, Russian, English, German, French / Under total. ed. Acad. V.E. Sokolova . - M .: Rus. lang, "RUSSO", 1994. - p. 20. - 2030 copies. - ISBN 5-200-00643-0 .
- 2 1 2 3 4 5 Pelicans, Cormorants, and Their Relatives: The Pelecaniformes J. Bryan Nelson Oxford University Press, 2006 p. 677
- ↑ Kostin S.Yu., Tarina N.A. Distribution and reproduction biology of copepods and ankle birds on Lebyazh islands and adjacent territories // Brant: Collection of scientific papers of the Azov-Black Sea Ornithological Station. - 2004.


