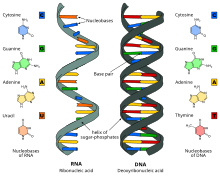
RNA with its nucleic bases (left) and DNA (right).
Nucleic acid analogs (xenonucleic acid, KNK) are clusters that are structurally similar to natural RNA and DNA molecules. Xenonucleic acids are used in medicine and molecular biology. Used in medicine and in research in the field of molecular biology.
Nucleic acids are nucleotide chains consisting of three parts: phosphate base, pentose sugar, ribose or deoxyribose and four nucleic bases. An analogue may contain changes in any of these parts.
Artificial nucleic acids are peptide nucleic acids (PNA), Morpholine oligonucleotides and Closed nucleic acid (ZNA), as well as Glycol-nucleic acid (GNA) and Treoso-nucleic acid (TNC). Each of them differs from natural DNA and RNA by a change in the foundations of the molecules.