
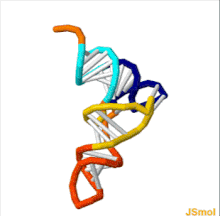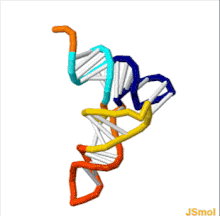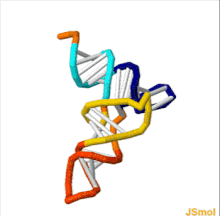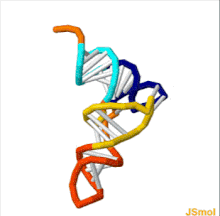
An anticodon is a triplet ( trinucleotide ), a region in the transport ribonucleic acid ( tRNA ), which, during translation, mates with a codon of messenger RNA (mRNA) and ensures that the corresponding amino acid residue is incorporated into the protein. Since each transport RNA is designed to bind only one specific amino acid, it contains only one corresponding anticodon. However, the correspondence between a codon and an anticodon is not always unambiguous: while the third and second nucleotides of the anticodon are always strictly complementary to the first and second nucleotides of the codon, the first nucleotide of the anticodon can be linked to different codon nucleotides. For example, uracil , located in the anticodone in the first position, can be associated with either adenine or guanine [2] .
Notes
- ↑ Transfer RNA (tRNA) . Proteopedia.org . The appeal date is November 7, 2018.
- ↑ Glaser .
Literature
- Antikodon // Big Encyclopedic Dictionary / Ch. ed. A. M. Prokhorov . - 1st ed. - M .: The Great Russian Encyclopedia , 1991. - ISBN 5-85270-160-2 .