Glipizid (Latin: Glipizidum) is an antidiabetic drug , 2nd generation sulfanylurea drug. The drug stimulates insulin secretion in specialized pancreatic cells, which leads to an increase in its secretion. Glipizid is an organic compound containing 21 carbon atoms and having a molecular weight of 445.535 Da . Effects usually begin within half an hour and can last up to a day.
| Glipizid | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Chemical compound | |
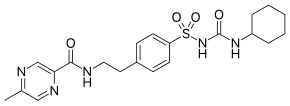
| IUPAC | N - (4- [ N - (cyclohexylcarbamoyl) sulfamoyl] phenethyl) -5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxamide |
| Gross formula | C 21 H 27 N 5 O 4 S |
| Molar mass | 445.536 g / mol |
| CAS | |
| Pubchem | |
| Drugbank | |
| Classification | |
| ATH | |
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Bioavailable | 100% (regular formulation) 90% (extended release) |
| Plasma Protein Binding | 98 to 99% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic hydroxylation |
| The period is half out. | 2 to 5 hours |
| Excretion | Renal and fecal |
| Mode of administration | |
| Oral | |
Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, low blood sugar and headache. Other side effects include drowsiness, skin rashes and tremors. Dosage adjustment may be required for patients with liver or kidney disease. Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding is not recommended. It works by stimulating the pancreas to release insulin and increases the sensitivity of tissues to insulin.
Glipizid was approved for medical use in the United States in 1984.
Content
Mechanism of Action
Glipizid sensitizes beta cells of the pancreatic islets by insulin Langerhans reaction, which means that more insulin is released in response to glucose than it would be without taking glipizid. Glipizid acts by partially blocking potassium channels among the beta cells of the pancreatic islets of Langerhans. By blocking potassium channels, the cell is depolarized, which leads to the discovery of voltage-controlled calcium channels. As a result, the influx of calcium contributes to the release of insulin from beta cells.
Pharmacokinetics
Glipizid is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The maximum concentration in the blood plasma reaches approximately 1 hour. It is associated with plasma proteins by 98%. The biological half-life is about 7 hours.
Indications
- Type 2 diabetes
Contraindications
- hypersensitivity to the drug
- type 1 diabetes
- diabetic coma
- ketonuria
- diabetic acidosis
- acute infectious diseases
- past injuries
- abnormal liver or kidney function
Side Effects
- hypoglycemia
- stomachache
- nausea
- vomiting
- lack of appetite ( anorexia )
- headache
- skin allergies
- jaundice
Preparations
- Antidiab - 0.005 g tablets
- Glibenese GITS - Extended Release Tablets 0.005 g, 0.01 g
- Glipizide BP - 0.005 g tablets
- Minidiab - 0.005 g tablets
- Glucotrol HL 0.0007
- Glibenez retard 0.0002
- Glibenez 0.0002
- Antidiab 0.0001
- Minidiab® 0.0001
- Мовоглекен® 0.0001
Dosing
Inside The dose and frequency of use of the drug are determined by the doctor depending on the course of the disease. The daily dose is 2.5-20 mg, usually in a single dose before breakfast. Assign sulfonylurea derivatives inside for 30 minutes before eating.
Notes
The drug can not be used in pregnant or lactating women. During treatment, blood glucose and urine levels should be monitored.