| Dodecahedral honeycombs of order 4 | |
|---|---|
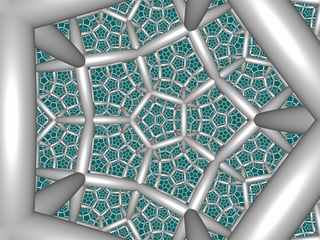 | |
| Type of | Hyperbolic regular cells |
| Schläfli Symbol | {5.3,4} {5.3 1.1 } |
| Charts Coxeter - Dynkin | |
| Cells | {5.3} |
| Verge of | Pentagons {5} |
| Rib figure | squares {4} |
| Vertex figure |  Octahedron |
| Dual Honeycombs | |
| Coxeter group | BH 3 , [5,3,4] DH 3 , [5.3 1.1 ] |
| Properties | Regular, quasi-right honeycomb |
In a hyperbolic three-dimensional space, dodecahedral cells of order 4 are one of the four compact regular space-filling mosaics (or cells ). Having a Schlefli {5,3,4} symbol , the cells have four dodecahedrons around each edge and 8 dodecahedrons around each vertex in an octahedral arrangement. The tops of the cells are built on 3 orthogonal axes. The dual body of honeycombs are .
Geometric cells are multi - faceted cells that fill the space in such a way that there are no free spaces left. Honeycombs are an example of a more general mathematical concept of paving in spaces of any dimension.
Honeycombs are usually built in the usual Euclidean ("flat") space like . They can also be constructed in non-Euclidean spaces , such as . Any finite can be projected onto its described sphere in order to form homogeneous cells on a spherical space.
Content
Description
The dihedral angle of the dodecahedron is ~ 116.6 °, so it is impossible to place 4 dodecahedrons on an edge in a Euclidean 3-dimensional space. However, in a hyperbolic space for a dodecahedron, one can choose the size so that its dihedral angles are reduced to 90 degrees, and then four dodecahedrons precisely fill the space around each edge.
Symmetry
Honeycombs are constructed with half symmetry, {5.3 1.1 }, with two types (colors) of hexagonal mosaics in the Witthoff structure . ↔ .
Drawings
Beltrami - Klein Model
Related polyhedra and honeycombs
There are four types of regular compact cells in a hyperbolic 3D space: Template: Regular compact H3 cells
There are in the family [5, 3, 4] of the Coxeter groups , including these regular forms.
| {5.3,4} | r {5,3,4} | t {5,3,4} | rr {5.3,4} | t 0,3 {5,3,4} | tr {5.3,4} | t 0,1,3 {5,3,4} | t 0,1,2,3 {5,3,4} |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| {4.3,5} | r {4,3,5} | t {4,3,5} | rr {4,3,5} | 2t {4,3,5} | tr {4,3,5} | t 0,1,3 {4,3,5} | t 0,1,2,3 {4,3,5} |
There are in an extensive family [5,3 1,1 ] of Coxeter groups, including cells in alternating form. This construction can be represented by alternation (as on a chessboard) with two colors of dodecahedral cells.
These cells are also connected to the 16-cell , cubic cells and , all have octahedral vertex shapes: Template: Tiles with octahedral vertex shapes
These cells are part of a sequence of four-dimensional polyhedra and cells with dodecahedral cells:
| Space | S 3 | H 3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| View | Finite | Compact | Paracompact | Non-compact | |||
| Title | {5.3,3} | {5.3,4} | {5.3,5} | {5.3,6} | {5.3,7} | {5,3,8} | ... {5,3, ∞} |
| Picture | |||||||
| Vertex figure | {3.3} | {3,4} | {3,5} | {3.6} | {3.7} | {3.8} | {3, ∞} |
Full-length dodecahedral cells of order 4
| Full-length dodecahedral cells of order 4 | |
|---|---|
| Type of | |
| Schläfli Symbol | r {5,3,4} r {5.3 1.1 } |
| Charts Coxeter - Dynkin | ↔ |
| Cells | r {5.3} {3,4} |
| Verge of | Triangles {3} pentagons {5} |
| Vertex figure | cube |
| Coxeter group | BH 3 , [5,3,4] DH 3 , [5.3 1.1 ] |
| Properties | Vertex transitive, edge transitive |
Full-length dodecahedral cells of order 4 ' , , have alternating octahedral and icosododecahedral cells with a cube as a vertex figure .
Associated Honeycomb
There are four types of full-cut compact regular cells:
| Picture | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Designation | r {5,3,4} | r {4,3,5} | r {3,5,3} | r {5,3,5} |
| Vertex figure |
Truncated dodecahedral cells of order 4
| Truncated dodecahedral cells of order 4 | |
|---|---|
| Type of | |
| Schläfli Symbol | t {5,3,4} t {5.3 1.1 } |
| Charts Coxeter - Dynkin | ↔ |
| Cells | t {5.3} {3,4} |
| Verge of | Triangles {3} Decagons {10} |
| Vertex figure | Square pyramid |
| Coxeter group | BH 3 , [5,3,4] DH 3 , [5.3 1.1 ] |
| Properties | Vertex transitive |
Truncated dodecahedral cells of order 4 , , have octahedral and truncated dodecahedral cells with a cube as a vertex shape .
Honeycombs can be considered as an analogue of two-dimensional hyperbolic t {5,4} with faces in the form of truncated pentagons and squares:
Associated Honeycomb
| Picture | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Designation | t {5,3,4} | t {4,3,5} | t {3,5,3} | t {5,3,5} |
| Vertex figure |
Shapeless dodecahedral cells of order 4
| Bi-sectional dodecahedral cells of order 4 Chiselled cubic honeycombs of order 5 | |
|---|---|
| Type of | |
| Schläfli Symbol | 2t {5.3,4} 2t {5.3 1.1 } |
| Charts Coxeter - Dynkin | ↔ |
| Cells | t {3,5} t {3,4} |
| Verge of | Triangles {3} squares {4} hexagons {6} |
| Vertex figure | Tetrahedron |
| Coxeter group | BH 3 , [5,3,4] DH 3 , [5.3 1.1 ] |
| Properties | Vertex transitive |
Bi-sectioned dodecahedral cells of order 4 or bi-cut cubic cells of order 5 , , have truncated octahedra and truncated icosahedra as cells and a tetrahedron as a vertex figure .
Associated Honeycomb
| Picture | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Designation | 2t {4,3,5} | 2t {3,5,3} | 2t {5,3,5} |
| Vertex figure |
Oblique dodecahedral cells of order 4
| Oblique dodecahedral honeycombs of order 4 | |
|---|---|
| Type of | |
| Schläfli Symbol | rr {5.3,4} rr {5.3 1.1 } |
| Charts Coxeter - Dynkin | ↔ |
| Cells | rr {3,5} r {3,4} {} x {4} cube |
| Verge of | Triangles {3} squares {4} pentagons {5} |
| Vertex figure | Triangular prism |
| Coxeter group | BH 3 , [5,3,4] DH 3 , [5.3 1.1 ] |
| Properties | Vertex transitive |
Oblique dodecahedral cells of order 4 , , have rhomboicosododecahedral , cubooctahedral and cubic cells and a triangular prism as a vertex figure .
Associated Honeycomb
| Four kinds of canted regular compact honeycombs in H 3 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Bevel-truncated dodecahedral cells of order 4
| Skewed-truncated dodecahedral cells of order 4 | |
|---|---|
| Type of | |
| Schläfli Symbol | tr {5.3,4} tr {5.3 1.1 } |
| Charts Coxeter - Dynkin | ↔ |
| Cells | tr {3,5} t {3,4} {} x {4} Cubes |
| Verge of | squares {4} hexagons {6} Decagons {10} |
| Vertex figure | mirror sphenoid |
| Coxeter group | BH 3 , [5,3,4] DH 3 , [5.3 1.1 ] |
| Properties | Vertex transitive |
Bevel-truncated dodecahedral cells of order 4 are homogeneous cells with a Coxeter-Dynkin diagram and having a mirror sphenoid as a vertex figure .
Associated Honeycomb
| Picture | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Designation | tr {5.3,4} | tr {4,3,5} | tr {3,5,3} | tr {5,3,5} |
| Vertex figure |
Strug-truncated dodecahedral cells of order 4
| Strug-truncated dodecahedral cells of order 4 | |
|---|---|
| Type of | |
| Schläfli Symbol | t 0,1,3 {5,3,4} |
| Charts Coxeter - Dynkin | |
| Cells | t {5.3} rr {3,4} {} x {10} {} x {4} |
| Verge of | Triangles {3} squares {4} Decagons {10} |
| Vertex figure | quad pyramid |
| Coxeter group | BH 3 , [5,3,4] |
| Properties | Vertex transitive |
Structural-truncated dodecahedral cells of order 4 are homogeneous cells with a Coxeter-Dynkin diagram and a quadrilateral pyramid as a vertex shape .
Associated Honeycomb
| Four types of strug-truncated regular compact cells in H 3 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
See also
- Poincaré homology sphere Poincaré dodecahedral space
- Seifert-Weber space Seifert – Weber dodecahedral space
- List of valid multidimensional polyhedra and compounds
Notes
Literature
- Coxeter . Tables I and II: Regular polytopes and honeycombs // . - 3rd. ed .. - Dover Publications, 1973. - p. 294–296. - ISBN 0-486-61480-8 .
- Coxeter . Chapter 10: Regular Honeycombs in Hyperbolic Space; Summary Tables II, III, IV, V // The Beauty of Geometry: Twelve Essays. - Dover Publications, 1999. - p. 212-213. - ISBN 0-486-40919-8 .
- Jeffrey R. Weeks. Chapter 16-17: Geometries on Three-manifolds I, II // The Shape of Space. - 2nd. - ISBN 0-8247-0709-5 .
- Uniform Polytopes. - 1991. - (Manuscript).
- The Theory of Uniform Polytopes and Honeycombs. - University of Toronto, 1966. - (Ph.D. Dissertation).
- Chapter 13: Hyperbolic Coxeter groups // Geometries and Transformations. - 2015.