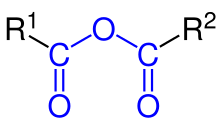
Carboxylic acid anhydrides are compounds of the general formula R 1 CO – O – COR 2 in which two acyl groups are attached to the same oxygen atom [1] . Depending on the nature of the acyl groups, the anhydrides can be “simple” (R 1 = R 2 , for example, acetic anhydride (CH 3 CO) 2 O, mixed (various acyl residues) or cyclic (R 1 and R 2 are parts of the same molecule) [2] .
Formic anhydride with the formula H − CO − O − CO − H (C 2 H 2 O 3 ) does not exist in free form.
Anhydrides can be formally considered as a condensation product of two −COOH groups:
Synthesis
Some cyclic anhydrides, such as phthalic anhydride , are formed by heating the corresponding acids. In the case of the synthesis of anhydrides from aliphatic acids, dehydrating agents are used - in particular, phosphoric anhydride in the synthesis of acetic anhydride from acetic acid:
or carbodiimides , which react with carboxylic acids with the formation of O-acylisoureas, highly reactive compounds capable of acylating carboxylic acids:
In most cases, anhydrides are synthesized by acylation of carboxylic acids or their salts. For example, by acylation of sodium formate with formyl fluoride, unstable formic acid anhydride can be obtained [3] :
When acylating carboxylic acids in laboratory practice, complexes of carboxylic acid halides with pyridine [4] or ketenes formally internal carboxylic acid anhydrides are usually used as acylating agents:
Acetylation of acetic acid with ketene is an industrial method for the synthesis of acetic anhydride.
Reactivity
Anhydrides are acylating agents and react with various nucleophiles:
forming esters (Nu = OR), amides (Nu = NR 1 R 2 ), hydrazides (Nu = HNNR 1 R 2 ), etc.
See also
- Carboxylic Chlorides
Notes
- ↑ acid anhydrides // IUPAC Gold Book.
- ↑ cyclic acid anhydrides (cyclic anhydrides) // IUPAC Gold Book.
- ↑ George A. Olah, Yashwant D. Vankar; Massoud Arvanaghi; Jean Sommer (1979), Formic Anhydride . Angewandte Chemie Int. Ed. Engl., Volume 18, issue 8, page 614. DOI : 10.1002 / anie.197906141 .
- ↑ ACID ANHYDRIDES (Eng.) // Organic Syntheses : journal. - 1946. - Vol. 26 . - P. 1 . - ISSN 2333-3553 . - DOI : 10.15227 / orgsyn.026.0001 .
