Ovoid pine , or male pine ( lat. Pinus oocarpa ), ( Spanish: pino Amarillo, pino avellano ) - a species of conifers of the genus Pine ( Pinus ) of the family Pine ( Pinaceae ).
| Ovoid pine | |||||||||||||||||||
 General view of the tree | |||||||||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||
| International scientific name | |||||||||||||||||||
Pinus oocarpa Schiede (1838) | |||||||||||||||||||
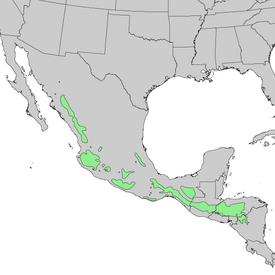
| Area | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Security status | |||||||||||||||||||


Distribution and Ecology
Distributed in Central and North America: Guatemala , Honduras , Mexico , Nicaragua , El Salvador . The species range extends from the northwest to the southeast for a distance of about 3,000 km, gravitating to the Pacific coast, and includes a diverse range of environmental conditions. This is a different range of heights: from 200-500 m to 2300-2700 m above sea level, and a fluctuating average annual rainfall: from 700 to 3000 mm.
Egg-bearing pine makes up about 45% of the pine forest in the Mexican state of Chiapas , 50% in Guatemala, 66% in Honduras, 90% in Nicaragua and 60% in El Salvador. It grows at an altitude of 350-2500 m above sea level, but feels best at an altitude of 1200-1800 m. The most optimal conditions for the growth of this species of pine have developed in the eastern part of Guatemala, Honduras and in the north of Nicaragua, where the average annual rainfall exceeds 1200 mm. In northern Mexico, where the climate is drier, it grows slowly and reaches a smaller size.
Botanical Description
An evergreen tree with a height, depending on natural conditions, from 10 m to 35 m, with an average trunk diameter of 45–80 cm.
The bark is thick, rough, lamellar, from dark brown to gray-brown.
Young shoots are reddish-brown, rough, bare and scaly.
The needles are yellowish-green, in bundles of 3, 4, 5 needles, 15-25 cm long.
Ripe cones vary in shape from broad-to-spherical to almost spherical; open buds are often wider than long; length 3–8, rarely up to 10 cm, diameter 3–9 rarely 12 cm. Seeds are ovoid, slightly flattened, 4–8 mm long and 3 to 4.5 mm wide, blackish-gray.
Usage
It is an important source of wood in Central America. This type of pine was introduced for commercial wood production and further use in the pulp and paper industry in Ecuador , Kenya , Zambia , Colombia , Bolivia , Queensland ( Australia ), Brazil and the Republic of South Africa .
Links
- Pinus oocarpa // The Gymnosperm Database. Edited by Christopher J. Earle. (eng.)
Literature
- Eguiluz, T. 1982. Clima y Distribución del género pinus en México. Distrito Federal. Mexico
- Rzedowski, J. 1983. Vegetación de México. Distrito Federal, Mexico.
- Dvorak, WS, GR Hodge, EA Gutiérrez, LF Osorio, FS Malan and TK Stanger. * 2000. Conservation and Testing of Tropical and Subtropical Forest Species by the CAMCORE Cooperative. College of Natural Resources, NCSU. Raleigh, NC. USA
- Martínez, Maximinio. 1978. Catálogo de nombres vulgares y científicos de plantas mexicanas.