Spotted bonito or Indian king mackerel [1] ( lat. Scomberomorus guttatus ) is a species of mackerel fish. They live in the tropical waters of the Indian and in the central-western and north-western Pacific Ocean between 38 ° C. w. and 7 ° s. w. and between 49 ° c. d. and 134 ° c. e. Oceanodromic fish are found at a depth of up to 200 m. The maximum body length is 76 cm. Valuable commercial fish [2] [3] .
| Spotted bonito |
 |
| Scientific classification |
|---|
| No rank : | Bilateral symmetrical |
|
| International scientific name |
|---|
Scomberomorus guttatus ( Bloch & JG Schneider , 1801) |
| Synonyms |
|---|
- Cybium crookewitii Bleeker 1851
- Cybium guttatum (Bloch & Schneider 1801)
- Cybium interruptum Cuvier 1832
- Cybium kuhlii Cuvier 1832
- Indocybium guttatum (Bloch & Schneider 1801)
- Scomber guttatus Bloch & Schneider 1801
- Scomber leopardus shaw 1803
- Scomberomorus crookewiti (Bleeker 1851)
- Scomberomorus guttatum (Bloch & Schneider 1801)
- Scomberomorus interruptus (Cuvier 1832)
- Scomberomorus kuhlii (Cuvier 1832)
- Scomberomous guttatum (Bloch & Schneider 1801)
|
| Security status |
|---|
Not enough data IUCN Data Deficient : 170311 |
|
Content
Spotted bonito lives in the coastal waters of the Indian and Pacific Oceans, in the Indo-Malayan archipelago up to the islands of Java and Sulawesi , in the southern part of the Sea of Japan , the Persian Gulf . Caught in estuaries of rivers [4] . These pelagic non-heretical fish are kept at a depth of 15 to 200 m, usually between 20 and 90 m [2] . They make seasonal migrations , but to a lesser extent compared with narrow-band mackerel [5] .
Ancient image of a spotted bonito
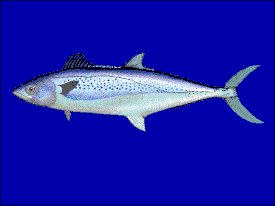
Spotted pelamids have an elongated fusiform body, a thin caudal stem with a simple keel. Knife-shaped teeth. The head is short. Snout length shorter than remaining head length. There are opener and palatine teeth. The maxillary bone is not hidden under the preorbital. 2 dorsal fins separated by a small gap. The lateral line is not wavy, sharply bends under the second dorsal fin. The ventral fins are small. The abdominal inter fin fin is small and bifurcated. No teeth on tongue [6] . The swim bladder is absent. The lateral line has several branches [1] . The height of the trunk is smaller compared to the Korean mackerel , is 22.8-25.2% of the length to the fork of the tail, against 24.4-26.7%. The head is also larger - 20.2-21.5% versus 19.7-20.4%. The number of branchial stamens on the first branchial arch is 8-14. Vertebrae 47-52. In the first dorsal fin there are 15-18 spiny rays, in the second dorsal fin 18-24 and in the anal fin 19-23 soft rays. Behind the second dorsal and anal fins lies a series of 7-10 smaller fins, helping to avoid the formation of whirlpools during rapid movement. Small pectoral fins are formed by 20-23 rays [5] . The back is dark. The sides are silvery with several rows of almost round spots. The anterior half of the first dorsal fin is colored black, at the base in the posterior third the fin is white. The second dorsal, pectoral and caudal fins are dark brown, the ventral and anal are silver-white. The maximum recorded length is 76 cm [4] .
Epipelagic schooling fish, kept mainly in coastal waters.
Spawning is long. In the Indian Ocean off the coast of Madras, spawning occurs from July to January, and in the Strait of Polk between India and Sri Lanka from April to July. The eggs have a diameter of about 1.2 mm, the yolk is not segmented, the fat drop is large. The prelarvae are 2.8 mm long. On the first day of life, they grow to 4 mm [4] . Fertility grows with age, ranging from 400,000 eggs at the age of 2 years to 2 million at the age of four. Males and females reach puberty with a length of 48-52 cm at the age of 1-2 years. Life expectancy is estimated at 16 years [3] .
Spotted bonito feeds mainly on small fish, as well as cephalopods [4] and crustaceans [2] .
Local fishing facility in Thailand , Kampuchea , Malaysia , India and Indonesia . Fishing is carried out by drift nets, spinners, trolls. The meat is white, of dense consistency, tasty [4] . Caloric content per 100 g is 109 kcal, protein content is 16 g, and fat is 7.5 g [7] . It enters the market mainly in fresh form, as well as in ice cream, smoked and salted. A small amount of frozen spotted bonito enters the markets of Europe and North America [2] . The International Union for Conservation of Nature has assigned the conservation status of “Least Concern” [3] .
- ↑ 1 2 Reshetnikov Yu.S. , Kotlyar A.N. , Russ T.S. , Shatunovsky M.I. Pentate-linguistic dictionary of animal names. Fish. Latin, Russian, English, German, French. / edited by Acad. V. E. Sokolova . - M .: Rus. Yaz., 1989 .-- S. 364. - 12,500 copies. - ISBN 5-200-00237-0 .
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 Spotted bonito in the FishBase database.
- ↑ 1 2 3 Scomberomorus guttatus (English) . The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species .
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 5 Commercial fish of Russia. In two volumes / Ed. O.F. Gritsenko, A.N. Kotlyar and B.N. Kotenev. - M .: publishing house of VNIRO, 2006. - T. 2. - S. 871-872. - 624 p. - ISBN 5-85382-229-2 .
- ↑ 1 2 Bruce B. Collette, Cornelia E. Nauen. Scombrids of the world. An annotated and illustrated catalog of tunas, mackerels, bonitos and related species known to date. - FAO species catalog. - Rome, 1983. - Vol. 2. - P. 59-68.
- ↑ G. Lindberg, Z. Krasyukova. 4 // Fishes of the Sea of Japan and adjacent parts of the Sea of Okhotsk and the Yellow Sea. - Keys to the fauna of the USSR, published by the Zoological Institute of the USSR Academy of Sciences. - Leningrad: Nauka, 1975 .-- S. 285-293. - 451 p. - ISBN 9785458519892 .
- ↑ Ramasamy Santhanam. Nutritional Marine Life. - CRC Press ;, 2014. - P. 199-200. - ISBN 1482262053 .
- Species of Spotted bonito (English) in the World Register of Marine Species .
