Dwarf African viper [1] ( lat. Bitis peringueyi ) - a poisonous snake from the genus of African vipers .
| Dwarf african viper |
 |
| Scientific classification |
|---|
| No rank : | Bilateral symmetrical |
| Infraclass : | Lepidosauromorphs |
| Infrastructure : | Caenophidia |
|
| International scientific name |
|---|
Bitis peringueyi Boulenger , 1888 |
| Area |
|---|
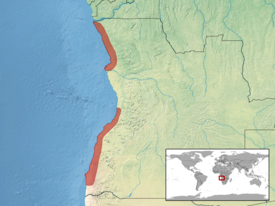
|
| Security status |
|---|
Least ConcernedIUCN 3.1 Least Concern : 178627 |
|
The total length reaches an average of 20-25 cm, the maximum length of 32 cm. Females are longer and heavier than males. The head is wide, flat. The body is thick. There is not a single protruding scale above the eyes. Coloring is gray or reddish-yellow with three longitudinal rows of small dark spots. The tip of the tail is usually black.
He likes sand deserts. It is moved by means of "sideways", and in case of danger it quickly "drowns" in the sand with the help of vibrating movements of the body. Active at dusk and at night. Hides during the day, buried in the sand, usually in the shade of a bush. In this case, the eyes, nasal openings and the tip of the tail protrude from the sand. It feeds on small lizards ( Meroles and Aporosaurus ) and geckos from the genus Ptenopus , as well as invertebrates.
The amount of poison injected with a bite is very small, so lizards die only 10-20 minutes after a bite. A person has only local pain and swelling, without fatal outcome.
Oviparous snake. The female gives birth to 10 cubs 10-13 cm long.
The species is common in Angola and Namibia. It lives in the Namib desert and surrounding areas.


