Lintakh [1] ( indon. Selat Lintah ) - a strait in the waters of Indonesia in the group of the Lesser Sunda Islands between the islands of Komodo and Rincha . Connects the Sea of Flores with the Sumba Strait . There are many small islands and rocks in the strait.
| Lintah | |
|---|---|
| indone. Selat lintah | |
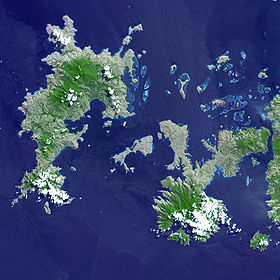 Lintach Strait satellite image | |
| Characteristics | |
| Width | 4.7 km |
| Length | about 40 km |
| Deepest | no more than 100 m |
| Location | |
| Connects | Sea Flores , Sumba |
| Separates | Komodo Island and Rincha Island |
| A country |
|
| Provinces | Eastern Sunda Islands |
| Area | West Mangarai County |
The water area of the strait, as well as the territory of the islands washed by it, are located within the borders of Komodo National Park , which is included in the UNESCO World Heritage List . The shores of the strait are growing in popularity among tourists , including diving enthusiasts.
Content
- 1 Geographical location
- 2 Natural conditions
- 3 Economic and transport importance
- 4 notes
- 5 Literature
Geographical position
Lintah Strait is located in the central part of the Lesser Sunda Range. It runs between Komodo Island (on the west side) and Rincha Island (on the east). Connects the Sea of Flores of the Pacific Ocean with the Sumba Strait, belonging to the Indian Ocean . The length of the strait from northeast to southwest is about 40 km [2] [3] .
The width of the strait is very uneven. In both its southwestern and northeastern inlets, it reaches almost 20 km, but in the center of the water area it narrows sharply: the distance between the nearest points of Komodo and Rinchi is Cape Kuning ( indon. Tanjung Kuning ) and Ngikok ( indon. Tanjung Nggikok ) - does not exceed 4.8 km. The shores of the strait have extremely complex shapes, form many bays and bays , deeply protruding into the land. There are dozens of small islands and cliffs in the strait, and there are long coral reefs . The largest of the islands, Padar ( indon. Pulau Padar ), divides the central part of the strait into two branches - western and eastern. The first of them is about three times wider than the second, which, in turn, is divided by the smaller island of Serai ( indon. Pulau Serai ) into two channels with a width of about 1 km and 0.3 km, respectively. In its northern part, the strait actually splits into several channels passing between many small islands and reefs [4] .
Komodo, Rincha, and all the islands lying in the Lintah Strait belong to the territory of the Western Mangaray okrug of the Indonesian province of the Lesser Sunda Islands . The shores of the strait are very slightly populated, there are only a few small rural settlements [5] .
Natural conditions
Lintach is one of the least deep-sea straits of the Lesser Sunda Islands: its maximum depth does not reach 100 meters. In general, the depths in its water area are uneven, there are many shallows . The surface of the bottom is heterogeneous - there are both rocky and sandy areas. The shores are mostly rocky, in many places steep. Some sections of the coast are covered with mangroves [4] [6] .
In addition, Lintah is one of the most cold-water straits of the Lesser Sunda ridge: the water temperature in it is about 26–27 ° C and is almost not subject to seasonal fluctuations (in most other straits, seasonal fluctuations range from 2 to 4 ° C, and the average annual temperature indicator 1.5-2 ° C lower). The salinity level of local water is also quite stable: all year round it is at about 34 ‰ , while, for example, in the Lombok Strait or Badung Strait, this indicator during the north-western monsoons blowing from January to March is no more than 33 ‰, and during the southeastern period, characteristic for the period from July to September, it rises to 35 ‰ [7] .
In the strait, very intense sea currents are observed, the configuration of which is very complicated and has not yet been fully studied. Tidal currents have a semidiurnal amplitude. Their speed in the central, narrow part of the strait - about 9 km / h - is much higher than in the wider southwest and northeast. The multidirectional movement of sea waters between small islands, rocks, reefs and shallows leads to the formation of numerous whirlpools and rips [4] .
Lintah waters are characterized by a large variety of species of ichthyofauna and coral . The water area of the strait is part of the Komodo National Park , included in the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1991, and forms the bulk of the park’s water area. The land component of the park is formed by the Lintah islands of Komodo and Rincha, as well as all the islands lying in the strait [6] [8] .
Economic and Transport Significance
The national park, covering the shores of the strait and its waters, is the main tourist attraction of this part of Indonesia. Attendance at this facility is growing at a very high pace: for example, in 2008 21,726 people visited here, in 2013, 63,801 people visited the park, 85% of whom were foreign nationals [9] . Most of the visits are on the ground part of the park, in particular on the islands of Komodo, Rincha and Gili Motang , on which the Komodo monitor lizard lives - a rare species for the protection of which the national park was originally created in 1980 (only later protective measures were extended to other local biological species - both terrestrial and marine) [10] . At the same time, the waters of the Lintah Strait are growing in popularity among lovers of sea holidays, especially among divers [6] [11] .
Due to the very difficult navigation conditions associated with shallow depths, the presence of strong multidirectional sea currents, whirlpools, shallows, rocks and reefs, Lintah is rarely used for transport communication between the waters of the oceans connected to it. Only small vessels go in the strait, in particular, ensuring the delivery of passengers and goods to Komodo National Park from Sumbawa and Flores: it is on this strait that the main harbors of the islands of Komodo and Rincha go, respectively, Liang Loh ( indon. Liang Loh ) and Liang -Buaya ( indon. Liang Buaya ), in which the majority of tourists visiting the park arrive [12] [13] .
Due to the nature conservation status extended to the land and water parts of the national park, economic activity in the water area of the Lintah Strait and on its shores is significantly limited. This applies, in particular, to fishing , previously actively practiced here. The accelerated development of the tourism industry and, at the same time, the folding of traditional local branches of the economy cause certain socio-economic problems among the local population [14] .
Notes
- ↑ Large Indonesian-Russian Dictionary, 1990 , p. 534.
- ↑ Great Atlas of the World, 2012 , p. 99.
- ↑ Sailing Directions, 2015 , p. 154.
- ↑ 1 2 3 Sailing Directions, 2015 , p. 155.
- ↑ Wilayah Administrasi Provinsi Nusa Tenggara Timur (indon.) (Unavailable link) . Pemerintah Daerah Provinsi Nusa Tenggara Timur. - The official website of the administration of the province of East Sunda Islands. Date of treatment April 19, 2016. Archived March 31, 2016.
- ↑ 1 2 3 Andi Oktami Dewi Artha Ayu Purnama, 2015 , p. 66.
- ↑ Introduction to the Jawa Sea, 2007 , p. 5.
- ↑ Komodo National Park . UNESCO - Information about Komodo National Park on the official website of UNESCO. Date of treatment April 19, 2016.
- ↑ Andi Oktami Dewi Artha Ayu Purnama, 2015 , p. 5.
- ↑ Komodo National Park (English) (unavailable link) . - The official website of Komodo National Park. Date of treatment April 19, 2016. Archived on September 6, 2017.
- ↑ Diving in Komodo - the World Heritage Site . Dive-the-world. Date of treatment April 19, 2016.
- ↑ Andi Oktami Dewi Artha Ayu Purnama, 2015 , p. 69.
- ↑ How to Get to Komodo National Park . - The official website of Komodo National Park. Date of treatment April 19, 2016.
- ↑ Andi Oktami Dewi Artha Ayu Purnama, 2015 , p. 177.
Literature
- Korigodsky R.N., Kondrashkin O.N., Zinoviev B.I., Loshchagin V.N. Large Indonesian-Russian Dictionary. - M. , 1990 .-- T. 1.
- Great Atlas of the world. - M .: Readers Digest, 2012 .-- ISBN 978-5-89355-169-3 .
- Sailing Directions (enroute) Borneo, Jawa, Sulawesi and Nusa Tenggara . - 13th edition. - Springfield: National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency, 2015.
- Genia Atma Nagara, Nugroho Adi Sasongko, Olubenga Johnson Olakunle. Introduction to the Jawa Sea // Oceanography - University of Stavanger. - 2007 .-- P. 1-14.
- Andi Oktami Dewi Artha Ayu Purnama. Resistensi Masyarakat Lokal Terhadap Pengelolaan Pariwisata di Taman Nasional Komodo (Studi Kasus Desa Komodo, Kecamatan Komodo, Manggarai Barat, Nusa Tenggara Timur) (indon.) // Universitas Hasanuddin. - 2015. - P. 1-205. Archived on May 30, 2016.
