The genus was named in 1971 by Alexander Grigorievich Sharov [3] . The only species is Sordes pilosus . The genus name means “evil spirits” in Latin , and the species name means “hairy”. Despite the grammatical word sordes being feminine, the species name was not corrected for pilosa .
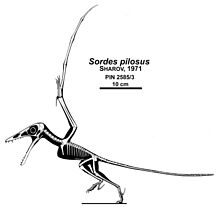
Reconstruction of the skeleton of
S. pilosus ,
holotype PIN 2585/3
Sordes had a wingspan of 0.63 meters. The wings were relatively short. According to Sharov and Anvin, sordes had leathery membranes extending from the wings to the legs, and the same membranes between the legs. The neck is short. The tail is long, more than twice as long as the body, with an elongated lobe at the tip.
Skull and Teeth
Sordes had a thin, not round head with moderately long pointed jaws. Unlike many pterosaurs, he did not have a crest. The teeth in the front of the jaw were large, adapted to capture prey. In the depths of the mouth, the teeth were smaller and more numerous, adapted to crush the solid parts of food. Two different types of teeth indicate a specialization for catching prey, which was difficult not only to catch, but also to eat. Sordes probably hunted invertebrates with a solid exoskeleton or slippery amphibians that needed to be nibbled before being swallowed [4] .
Hairline
Fossil samples contain the remains of soft tissues, such as leathery membranes and hair filaments. The presence of hair indicates the warm-bloodedness of the animal, as well as the greater streamlining of the body during flight. The hair strands were of two types: long on the far side of the wings and short near the body. In the 1990s, David Anvin claimed that both types were essentially not hairs, but reinforced fibers on leathery membranes. He later emphasized that the “hair” was indeed present on the body of the Sordes, as later findings clearly indicated this.
The genus is based on the holotype PIN 2585/3, an almost complete damaged skeleton on a stone slab. It was found in the 1960s in the foothills of Karatau in Kazakhstan .
Sharov attributed to the Sordes family the paratype , or the second sample, PIN 2470/1 - again, a fairly complete skeleton on the plate. By 2003, six more specimens were discovered.
Sordes was assigned to the Rhamphorhynchidae family. These were one of the earliest pterosaurs that developed in the Late Triassic and survived to the end of the Jurassic period . According to Anvin, sordes, within the family Rhamphorhynchidae belonged to the subfamily Scaphognathinae . Other researchers, such as Alexander Kellner, after conducting a cladistic analysis, classify sordes as more basal (primitive) pterosaurs.

