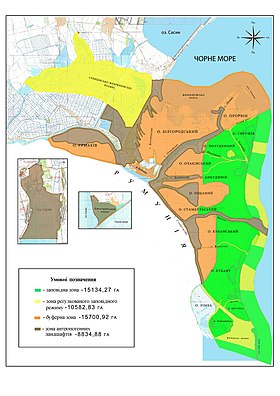
The Danube Biosphere Reserve (until 1998, the Danube Plavni Reserve) is an independent nature conservation and research organization. Most of the territory of the Danube Biosphere Reserve (hereinafter DBZ) is located in the north-eastern part of the Danube Delta within Ukraine in the vicinity of the city of Vilkovo , Kiliysky district of Odessa region. In the east, DBZ borders on the Black Sea, and in the south - with Romania. The constituent natural and territorial parts of the DBZ are the secondary (sea) delta of the Kiliysky arm , the Zhebriyanskaya ridge , the Stentsovo-Zhebriyansk plains (SZHP) and the island of Ermakov . In addition, Decree of the President of Ukraine No. 117/2004 of February 2, 2004 included rather autonomous territories in the DBZ — the headwaters of Lake. Sasyk and Dzhantsheysky estuary . The total area of DBZ along with channels, inland water bodies, a 2-kilometer strip of the Black Sea and the sites included in 2004 is 50,252.9 ha. By the decision of the International Coordinating Committee of the UNESCO Program “Man and the Biosphere” of December 9, 1998, the reserve was included in the global network of biosphere reserves as part of the bilateral Romanian-Ukrainian biosphere reserve “Danube Delta”.
| Danube Biosphere Reserve | |
|---|---|
| Ukrainian Danube Biosphere Reserve | |
 | |
| IUCN Category - Ia (Strict Nature Reserve) | |
| basic information | |
| Area | 50,252.9 ha |
| Established | 1998 year |
| Location | |
| A country |
|
| Region | Odessa region |
| Nearest town | Vilkovo |
dbr.org.ua | |
On the Romanian side of the Danube Delta, a reserve was also created, which was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1991 [1]
Content
- 1 Territory and history of creation
- 2 Nature reserve
- 2.1 Fauna
- 3 References
- 4 notes
Territory and History
The creation of the reserve in the Ukrainian part of the Danube Delta began in the 60s of the last century. Scientists of the Institute of Hydrobiology (Kiev.) And the Institute of Zoology. Shmalgauzena (Kiev.) NAS of Ukraine was proposed to create a zoological reserve in the Danube Delta.
In 1964, the Interdepartmental Meeting on the Integrated Use of Natural Resources of the Danube Delta, which was held under the auspices of the Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, it was recommended to create a reserve in the Ukrainian part of the Danube Delta. And already in 1967, by Decree of the Council of Ministers of the Ukrainian SSR No. 490 of July 24, a nature protection zone was created in the Danube River Delta with the regime of a natural monument of national significance. It included a strip of smooth lands along the coastal part of the Black Sea 1 km wide inland (total 3 thousand hectares) and a kilometer strip of sea water. In the years 1973-1978. The Council of Ministers of the USSR creates the Danube branch of the Black Sea State Reserve in the system of the Academy of Sciences of Ukraine on an area of 7758 hectares, and subsequently the reserve territory expands to 14851 hectares. By the government decision, the Danube Delta is classified as an Ramsar wetland of international importance, mainly as a habitat for waterfowl. On April 23, 1981, the Council of Ministers of the Ukrainian SSR adopted a resolution “On the organization of the Danube Plavnyi State Reserve” subordinate to the Ukrainian Academy of Sciences. The structural reserve was subordinated to the Odessa branch of the Institute of Biology of the South Seas named after A. O. Kovalevsky.In 1994, the Danube Plavny Nature Reserve reports to the Presidium of the National Academy Sciences of Ukraine and becomes an independent legal entity.In the same year, the Government of Ukraine signed an agreement with the World Bank "Preservation of biological diversity in the Ukrainian part of the Danube Delta", which provided for the allocation of funds for the creation of the Danube Biosphere Reserve. More than 60 participated in the implementation of this project Researchers from many scientific institutions of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, universities and others, including the reserve. The results of these studies on the project are covered in numerous scientific publications and, above all, in the monograph “Biodiversity of the Danube Biosphere Reserve, Conservation and Management” (1999). The project was exhibited by Ukraine at the world exhibition in Hanover (2000) among the most successful environmental projects. The Danube Biosphere Reserve was created by Decree of the President of Ukraine "On the Creation of the Danube Biosphere Reserve" No. 861 dated August 10, 1998 on the basis of the Danube Plavnyi Nature Reserve with a total area of 46402.9 ha. By a UNESCO decision of February 2, 1999, DBZ was included in the global network of biosphere reserves as part of the bilateral Romanian-Ukrainian biosphere reserve “Danube Delta”, due to which one of the largest deltas in the world has become almost completely protected. In 2004, in accordance with the Decree of the President of Ukraine “On Expanding the Territory of the Danube Biosphere Reserve” No. 117 of February 2, the area of land transferred to DBZ for permanent use was increased by 1295 hectares (due to the land of the Kiliysky district) and the total territory was expanded by 3850 hectares ( land of the Tatarbunar district) provided without exemption from land users. In accordance with the above decrees, as well as taking into account the results of land management, the total area of DBZ is 50,252.9 ha. Taking into account the processes of continuous delta formation, all the neoplasms (islands, spits, etc.) of the forewells are automatically included in the DBZ territory. This unique natural process of forming the new land of Ukraine and Europe in the Danube Delta, which from the very beginning receives the status of a reserve, is a hallmark of DBZ.
Nature Reserve
The primary Danube delta was formed in the postglacial period from a solid river flow at the site of the Ancient Danube Estuary. The secondary (marine) delta of the Kiliysky arm, below the town of Vilkovo, is geologically quite young. Her age is only about 400 years. It was created on the shallows mainly by deposits of solid river runoff with admixtures of sand of marine origin. The remnant of the ancient ridge of sea dunes is the modern sand Zhebriyanovsky ridge. The soils of the delta were formed on the basis of river aluminum and sea sandy substrate as a result of a sod-meadow process under conditions of strong and prolonged wetting. For delta lands, characteristic meadow, meadow-bog, bog soils and salt marshes. According to the mechanical composition, they are mainly heavy loamy and clayey. Marsh soils in the delta naturally account for the largest areas. They are formed in almost all understated areas. Significant areas in the delta are deposits of coastal braids and coastal stripes of the islands. They are usually humus-poor and have a low moisture capacity. On alluvial deposits of the Danube floodplain, soddy soils of various types were formed. Saline soils are represented by salt marshes, in which readily soluble salts are located on the surface.
Flora
Flora of the Danube Biosphere Reserve totals about 950 species of vascular plants belonging to 371 genera and 97 families. Among them, herbaceous species predominate (96.7%). The main core of the plant species composition is formed by the littoral floristic complex. The most diverse is the flora of the Zhebriyanovsky sand ridge. The vast majority of plant species of the reserve belongs to the entomophilous group.
In the environmental aspect, the mesophytes (23.3%), xeromesophytes (21.0%), mesoxerophytes (17.0%) and hygrophytes (13.2%) predominate in the flora of the reserve. They make up the vegetation of grassy marshes and marshy meadows, occupy the largest areas in the reserve.
The flora of the reserve includes 65 endemic species of the Black Sea-Caspian endemic complex. They belong to 44 births and 21 families. 16 species of plants are listed in the Red Book of Ukraine. The reserve contains the largest in Ukraine thickets of floating water hazelnuts and swamp grass.
A significant number are represented by adventitious species - 13.3%. They are mainly associated with land reclamation, as well as in a significant amount found in alluvial sections of the coastal ridge.
The vegetation of the reserve is a territorially integral, but genetically heterogeneous set of its various types: marsh, water, meadow, halophytic, forest and psammophytic. The leading factor determining the territorial division and the ratio of groups of various types is the hydrological regime and the intensity of the alluvial process.
The main component of the vegetation cover of the biosphere reserve is marsh vegetation, which occupies more than half of its territory. The second place belongs to aquatic vegetation. It is represented by unrooted free-floating, rooted submerged, rooted with floating leaves and airy forms. Meadow vegetation occupies the flat sections of riverbed and floodplain ridges and is represented by groups of marshy, saline, real and steppe meadows. Significant areas are occupied by psammophytic vegetation. Its main massifs are confined to the sand arenas of the Zhebriyanovsk ridge.
Forest vegetation of the reserve is a characteristic element of the Danube Delta floodplains, although it does not occupy significant areas in it. Its composition is dominated by various species of willows. Among them, the usual white willow and brittle willow. Shrub vegetation, like forest, is a characteristic element of the delta. It is divided into shrub floodplain and shrub coastal. A characteristic type of shrubby coastal vegetation is buckthorn. Its thickets in the reserve are the largest among natural in Ukraine. Saline and saline vegetation is not a characteristic element of the Danube floodplains and is represented by insignificant areas.
For the territory of the reserve today, 39 species of mushrooms belonging to 21 genera are known. This is not a complete list of them, because detailed mycological examinations of this territory were practically not carried out.
Fauna
By the number of species of fauna, the Danube Delta is perhaps the richest place in modern Europe. The animal kingdom is represented quite fully on the territory of the Danube Biosphere Reserve.
Insects
For the reserve 1937 species of insects are known, among which 40 are listed in the European Red List and the Red Book of Ukraine. Moreover, according to experts, this is only less than half of all types of insects that actually live on its territory. The total number of the latter is estimated at 5500. It is interesting that among the insect species identified for the protected area, 7 are new to science.
Amphibians and reptiles
The fauna of the amphibian reserve and the surrounding areas includes 11 species and 11 subspecies belonging to 2 rows, 6 families and 6 genera.
6 species and 6 subspecies belonging to 2 rows, 3 families and 5 genera are known to be reptiles for protected areas.
Among amphibians, the most numerous are lake and edible frogs, common tree frog and Danube newt, and among reptiles - swamp turtle and common already. Among this group of animals, species listed in the European Red List and the Red Book of Ukraine are absent in the reserve.
Birds
In the entire delta of the river. Danube recorded stay of more than 350 species of birds. From 1983—2017 on the territory of the DBZ 297 species were recorded, which is about 70% of the avifauna of Ukraine. Based on the fact that in the territories adjacent to the DBZ (about Zmeiny Island, the Romanian part of the Danube Delta), about 70 species were noted that were not recorded on the DBZ territory, it can be assumed that the number of species on the DBZ territory is much larger and further with ornithological monitoring, their number in the Annotated list of DBZ birds may increase.
As of 2017, the total list of birds listed in the Red Book of Ukraine is 68 species. The European Red List includes 11 species, 287 species are protected by the Berne, 153 - by the Bonn, 44 - by the Washington Convention.
Among the colonial birds, the territory of the Danube Biosphere Reserve is important for the small cormorant - up to 1000 pairs and spoonbills - up to 360 pairs. The cormorant, gray, red, small and large white herons, heron, river and variegated terns are quite numerous in the reserve; flocks of pink pelicans up to several thousand individuals that feed here are also frequent in the reserve. There is also a curly pelican.
Fish
The fish fauna of the reserve totals 107 species belonging to 39 families. Moreover, all 7 species of fish from the European Red List are found in protected waters. And among 32 species of fish listed in the Red Book of Ukraine, 15 live here. Among them, beluga is the largest among fish living in fresh waters. The Danube, including the reserved water area, plays a special role in preserving the Black Sea herds of migratory sturgeons. Among all the rivers of the Black Sea basin, only in the Danube their natural spawning has been preserved.
Mammals
Mammals in the reserve are represented by 45 species. Among them, 7 are on the European Red List and 19 are in the Red Book of Ukraine. For some of them, like the European mink and the forest cat, the lands of the Danube Delta are very important for survival on a European scale.
Educational and sightseeing work
The tourist information center of the reserve is located in the central part of Vilkovo on Nakhimova Street. The center has informational, environmental education, natural, local history expositions. The hall of the Tourist Information Center, with a capacity of about 35 people, is equipped with modern television and video equipment. There is a video library of environmental films. The center is open both for local residents, primarily schoolchildren, and for guests of the reserve and the city.
In addition to the Tourist Information Center, visitors to the reserve are offered several permanent excursion routes: “Zero Kilometer” and “Path to the Birds”.