Trimipramin is one of the representatives of the class of tricyclic antidepressants , a subclass of tertiary amines. Used as hydrochloride.
| Trimipramine | |
|---|---|
| Trimipraminum | |
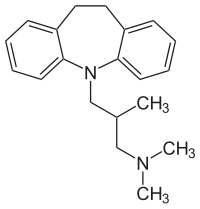 | |
| Chemical compound | |
| IUPAC | ( RS ) -3- (10,11-Dihydro-5 H -dibenzo [ b, f ] azepin-5-yl) - N, N , 2-trimethylpropan-1-amine |
| Gross formula | C 20 H 26 N 2 |
| Molar mass | 294.434 g / mol |
| CAS | |
| Pubchem | |
| Drugbank | |
| Classification | |
| ATH | |
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Bioavailable | 40% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| The period is half out. | from 11 to 23 hours, depending on the type of metabolism (fast or slow) |
| Excretion | Bud |
| Dosage Forms | |
| tablets (or capsules) of 10, 12.5, 25, 50, 75, 100, 150 mg; 1.25% solution in 25 mg ampoules. | |
| Mode of administration | |
| inside , intramuscular , intravenous | |
| Other names | |
| Gerfonal, Surmontil, etc. | |
In Russia it is withdrawn from the circulation of medicines (in Norway it is limited in circulation) due to the high toxicity of the drug, the risk of overdose and the appearance of suicidal intentions when using high doses of the medicine .
Content
Pharmacological action
Trimipramine is an inhibitor of reverse neuronal uptake of mediator monoamines, including norepinephrine , dopamine , serotonin, and others. MAO does not cause inhibition.
It has strong antihistamine activity (stronger than amitriptyline), as well as significant M-cholinolytic (anticholinergic) and alpha-adrenolytic activity.
The antidepressant (thymoanaleptic) effect is combined with trimipramine with a pronounced sedative, hypnotic, and anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) effect.
Trimipramine, unlike amitriptyline, does not have metabolites with a stimulating effect and itself has practically no stimulating properties, therefore it has an advantage in treating depressions that occur with pronounced psychomotor agitation, anxiety or severe insomnia (anxious and agitated depressions).
By the strength of the sedative, hypnotic and anti-anxiety effect, trimipramine in the tricyclic class is the absolute champion and is superior to amitriptyline.
Clinical use and indications
Trimipramin is used mainly in endogenous depressions . It is especially effective in anxiety-depressive states; reduces anxiety, psychomotor agitation ( agitation ), internal tension and fear, insomnia and depressive manifestations proper.
Trimipramin usually does not cause exacerbation of delirium, hallucinations and other productive symptoms, which is possible with the use of antidepressants with a predominantly stimulating effect (imipramine, etc.) and rarely even with amitriptyline.
Contraindications
Trimipramin as a drug with pronounced anticholinergic activity is contraindicated in glaucoma, prostatic hypertrophy, and atony of the bladder.
Complications and side effects
Trimipramine is usually well tolerated (but worse than many other tricyclics and than modern selective antidepressants) with certain precautions, sufficiently smooth dosage increases at the start of therapy, and timely prevention or correction of side effects that occur. Due to the presence of pronounced sedative effect does not disturb sleep, and it is prescribed throughout the day, including at bedtime.
The main side effects are associated with a pronounced anticholinergic effect. Often (especially at the beginning of therapy and with increasing doses) dry mouth, dilated pupils, disturbed accommodation of the eyes (blurred and blurred vision near, inability to focus eyes at close range - for example, reading and embroidering), constipation, sometimes severe, up to development of paresis or complete atony (paralysis) of the intestine, fecal blockages and acute dynamic obstruction of the intestine. At higher doses, there may be difficulty and delay of urination up to complete atony of the bladder. Hand tremor also appears at higher doses and is associated with stimulation of the peripheral beta-adrenergic system (removed by beta-blockers). Also often observed (especially at the beginning of therapy) is a feeling of intoxication (the so-called "anticholinergic intoxication", similar to intoxication from cyclodol or atropine), drowsiness, lethargy, apathy due to excessive sedation, dizziness.
Due to the pronounced alpha-adrenolytic effect of trimipramine, there are often observed (especially at the beginning of therapy and with a rapid increase in doses) hypotensive action (reduction in blood pressure), orthostatic hypotension when getting up to fainting and collaptoid states, tachycardia, weakness.
There may be increased depersonalization (sometimes), ataxia , drug parkinsonism , weight gain, decreased libido , paroxysmal effects, allergic reactions (rarely) [1] , paresthesias .
The most dangerous complication of therapy with trimipramine is a heart rhythm disorder, in particular a conduction disorder and a prolongation of the QT interval. The appearance of these cardiac arrhythmias dictates the need to either reduce the dose or very carefully monitor the patient's condition with frequent ECG.
Epileptiform convulsions are also sometimes observed (usually at high and very high doses or when intravenous drip is too fast). In patients with epilepsy and other convulsive states or with organic brain damage, a history of cranial trauma, even small doses of trimipramine can cause convulsions or their equivalents. The appearance of epileptiform convulsions during treatment with amitriptyline dictates the need to reduce the dose of trimipramine or administer an anticonvulsant at the same time.
It is often observed (especially in patients with concomitant thyroid function deficiency, with bipolar affective disorder, bipolar form of schizoaffective disorder, but can also be observed in a patient who was assumed to be monopolar depressed before treatment) inversion of the sign of the phase from depression to mania or hypomania, or development mixed "dysphorically irritable state, or an increase and acceleration of the cycle with the formation of the disease with rapid phase change (rapid cycling). At the same time, depending on the clinical situation, it may be necessary to either reduce the dose or even completely cancel trimipramine and other antidepressants, or add normottimik, thyroid hormones, neuroleptics, or both measures together.
Interactions
The drug should not be administered simultaneously with irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitors or with reserpine . Potentiates the effect of sedatives , alcohol , barbiturates , neuroleptics . It is not recommended to combine with SSRI antidepressant citalopram . Trimipramin increases the concentration of SSRIs [1] .
Special instructions
Trimipramin is a drug that poses a greater risk of death with a relatively small overdose. Admission 1000-1500 mg leads to the development of deadly poisoning. At the same time, with the improvement of the patient's condition under the influence of treatment, suicidal ideas often disappear and the mood returns to normal much later than the increase in energy and physical strength. As a result, the patient may have more energy and strength to commit suicide against the background of still lingering melancholy and bad mood.
Therefore, patients with severe endogenous depression and high suicidal risk can receive treatment with trimipramine only in a psychiatric hospital (preferably with placement in a supervisory ward), or at least provided that it is possible to ensure strict supervision of the patient’s family or relatives for regular medication and the amount remaining drug packaging. Patients should not be prescribed with endogenous depression, just starting outpatient treatment, for one prescription (for one visit to the doctor) quantities of the drug that are more than one to two weeks of therapy.
After improving the patient's condition and the disappearance of suicidal risk, the severity of supervision can be gradually reduced up to the prescription of one-month or even 2-3-month amount of the drug for one prescription.
Storage: List B.
Notes
- ↑ 1 2 Podkorytov V.S., Chaika Yu. Yu. Depression. Modern therapy. - Kharkov: Tornado, 2003. - 352 p. - ISBN 966-635-495-0 .