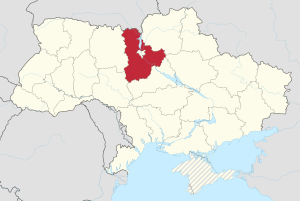
Kiev region ( Ukrainian, Kyiv region ) is a region in the north of Ukraine . Kiev is the administrative center of the region, but formally is not part of it, being a separate administrative-territorial unit within Ukraine.
| Region | |||||
| Kiev region | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ukrainian Kiev region | |||||
| |||||
| A country | |||||
| Includes | 25 districts, 26 cities, 30 urban settlements, 1127 villages | ||||
| Adm. Centre | Kiev (is the administrative center of the region, but is not included in its structure) | ||||
| Head of the regional state administration | Mikhail Karenovich Bno-Airiyan | ||||
| Head of the Regional Council | Nikolay Anatolyevich Starichenko | ||||
| History and Geography | |||||
| Date of formation | February 27, 1932 | ||||
| Square | 28 121 [1] km² (4.66%, 8th place ) | ||||
Height
|
| ||||
| Timezone | , in the summer | ||||
| The largest city | White church | ||||
| Dr. big cities | Brovary , Fastov , Boryspil , Vasilkov | ||||
| Population | |||||
| Population | ▲ 1,732,200 people ( 2016 ) (3.79%, 9th place ) | ||||
| Density | 62.24 people / km² | ||||
| Nationalities | Ukrainians, Russians, Belarusians, Poles, Jews and others | ||||
| Official language | Ukrainian | ||||
| Digital identifiers | |||||
| ISO 3166-2 Code | UA-32 | ||||
| Telephone code | +380 45 | ||||
| Postal codes | 07xxx, 08xxx, 09xxx | ||||
| Internet domain | kiev.ua; kv.ua | ||||
| Auto Code numbers | 10, AI (old KX, MI) | ||||
| |||||
| Official site | |||||
 | |||||
 | |||||
| Notes: Awarded the Order | |||||
Content
Physico-geographical characteristics
Kiev region is part of Ukraine. Area - 28 121 km². Population - 1,722,875 (July 1, 2013), including the urban population of 1,066,812 people (61.92%), the rural 656,063 people (38.08%). Center - Kiev , the capital of Ukraine (city of national importance).
Geography
It is located in the middle reaches of the Dnieper , mostly on its right bank. The northern part of the region is located in the Polesskaya lowland . The eastern (left-bank) part is on the Dnieper lowland (absolute altitudes of 100-140 m above sea level within the region). Central and southwestern - on the gentle undulating Dnieper Upland , cut by river valleys and ravines (up to 273 m above sea level).
The entire territory of the region belongs to the Dnieper basin, which is the most important water artery of the region. Within the region, the Dnieper flows for 246 km and has the following largest tributaries: Pripyat (with a tributary of Uzh or Usha), Teterev , Irpen , Stugna , Ros (right), Desna , Trubezh , Supoy (left). Ros and Supoy flow into the Dnieper beyond the borders of the region. In total, there are 177 rivers in the region. There are few lakes; they are concentrated mainly in the north. On the territory of the region there is a large part of the upper reservoir of the Dnieper cascade - the Kiev (“ Kiev Sea ”, as it is often called (1964-1966); length 110 km, width up to 12 km, area - 922 km²; average depth up to 4 m (the largest - 14.5 m), the total volume is 3.73 thousand km³), as well as the Kanevsky reservoir (1978). In total, the region has 13 reservoirs, over 2000 ponds, almost 750 small lakes.
The soil and climatic conditions of the region are favorable for growing winter wheat, sugar beets, corn, vegetables and other agricultural crops, as well as orchards and berry plants. For the successes achieved in the development of agriculture, Kiev region was awarded the Order of Lenin on February 26, 1958 . [2]
The northern part of the Kiev region lies within the mixed forest zone ( Ukrainian Polesie ; Polesie lowland, 183 m), most of it is in the forest-steppe . The natural vegetation of the northern part of the region is represented by large arrays of coniferous and mixed forests (forests are mainly distributed from pine with an admixture of birch and oak, as well as alder, etc.), grass and meadow meadows and wetlands; southern part - broad-leaved forests (small forests of oak, hornbeam, linden), shrubs and meadows.
In the Kiev region there are state farms: Yagotinsky hunting - waterfowl and marsh wild birds; Belozerskoye (now the Beloozersk NPP , Pereyaslav-Khmelnitsky district , Kanevskoe vkhr.) - hares, roe deer, wild pigs, badgers, martens, beaver, swamp and waterfowl; Sukholeskoye ( Belotserkovsky and Rakitnyansky districts) - hares, roe deer, fallow deer, fallow deer; Dnieper-Teterevsky State Forest Hunting Reserve, Zalessky Forestry Reserve Hunting (now Zalesye (National Park) ), etc .; reserves - Zhornovsky , Dzvonkovsky , Dnieper-Desnyansky (Verkhnedudechansky hunting farm; Pirnovo), state. Zhukov Khutor reserve (near Vorzel); numerous state protected areas. On the territory of the region (mostly in Polesie) there are also: elk, wolf, fox, hares, squirrels, ground squirrel, hamster, field and forest mouse, etc.
The Nature Reserve Fund of the city of Kiev and the urban green zone: of national importance - the Forestry Reserve (1110.2 hectares; NPP Goloseevsky (all of which [at the last] in 2001 [3] have 6165 hectares), Koncha-Zaspovskoe lesnichestvo ), The Romanovskoye swamp (30 ha; Svyatoshinsky LPH , the vicinity of Irpen); of local significance - Koncha-Zaspa (landscape - waterfowl and swamp wild birds), Dachnoe , Zhukov island (landscape, 361 ha; total area of the island 530 ha) [4] , islands of Olzhin and Kozachy (470 ha), Birch guy , Belaya Dibrova , Rybnoe (all three - Darnitsky LPH), oz. Verbnoye ( Obolon ), Bobrovnya tract ( Muromets Island , Muromets Park), Mezhigorskoye (Svyatoshinsky LPH GKO Kyivzelenstroy, Mezhigorsk Forestry); Pushcha-Voditsky Forest Park (360 ha; the total forest area is approximately 8 thousand ha).
see. Category: Protected areas of the Kiev region
Climate
The climate is temperate continental , with mild winters and warm summers. The average January temperature in the north of the region is −6 ° C, in the southwest −5 ° C; July, respectively +17 and +19 ° C; absolute minimums of temperatures reach −34, −36 ° C; absolute maximums - +39, +40 ° C. The average annual air temperature in the north of the region is +6.5 ° C, in the south +7.5 ° C. The average annual rainfall is about 550 mm (in the north of the region 600 mm, in the south - 500 mm per year), maximum in summer. The period with temperatures of +10 ° C is over 155-175 days.
History
Historical area - Kiev region . The Kiev region was formed on February 27, 1932 as part of the Ukrainian SSR , among the first five regions of the republic. The administrative center of the region was the city of Kiev .
October 15, 1932 from the eastern regions of the region formed the Chernihiv region .
September 22, 1937 from the western regions of the region formed the Zhytomyr region .
On January 7, 1954, Cherkasy region was formed from the southern regions of the region, and the region received modern borders.
Population
| Settlements with a population of over 10 thousand as of January 1, 2015 [5] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The population of the region according to the State Statistics Committee as of July 1, 2013 amounted to 1,722,875 people (which is 588 more than June 1), including the urban population of 1,066,812 people (61.92%), the rural population of 656,063 people (38.08%). The permanent population is 1,717,096 people, including the urban population of 1,055,762 people (61.48%), the rural population 661,334 people (38.52%).
About 558 thousand people (32% of the region’s population) work in Kiev [6] .
National composition
According to the 2001 Census (total: 1 814 280), peoples over 1 thousand people are shown:
- Ukrainians - 1 684 803
- Russian - 109 322
- Belarusians - 8698
- Poles - 2846
- Armenians - 2341
- Moldavians - 1515
- Non-nationality - 1350
- Jews - 1270
- Tatars - 1102
- Azerbaijanis - 1033
Administrative-territorial structure
Kiev region consists of 25 districts and 11 cities of regional subordination:
The Kiev region has two exclaves - the city of Slavutich , surrounded by the territory of the Chernihiv region and the village of Kotsyubinskoye , surrounded by the territory of the city of Kiev .
The number of administrative units, councils and settlements of the region:
- districts - 25;
- settlements - 1184, including:
- rural - 1127;
- urban - 55, including:
- urban-type settlements - 30;
- 25 cities, including:
- cities of regional significance - 12;
- cities of regional significance - 13;
- village councils - 606.
Neighborhoods
In the Kiev region 25 districts:
- Baryshevsky district
- Belotserkovsky district
- Boguslavsky district
- Borispol district
- Borodyansky district
- Brovarsky district
- Vasilkovsky district
- Volodarsky district
- Vyshgorod district
- Zgurovsky district
- Ivankovo district
- Kagarlyk district
- Kiev Svyatoshinsky district [7]
- Makarovsky district
- Mironovsky district
- Obukhov district
- Pereyaslav-Khmelnitsky district
- Polessky district
- Rakitnyansky district
- Skvirsky district
- Stavishchensky district
- Tarashchansky district
- Tetievsky district
- Fastovsky district
- Yagotinsky district
Cities
Cities of regional significance:
- White church
- Berezan
- Borispol
- Brovary
- Butch
- Vasilkov
- Irpin
- Obukhov
- Pereyaslav-Khmelnitsky
- Rzhischev
- Slavutich
- Fastov
Cities of district significance
- Bohuslav
- Boyar
- Vyshhorod
- Cherry
- Kagarlyk
- Mironovka
- Squira
- Gibberish
- Tetiev
- Uzin
- Ukrainian
- Chernobyl
- Yagotin
Non-residential cities:
- Pripyat (former city of regional significance)
Authorities
Local self-government in the region is carried out by the Kiev Regional Council, the executive branch is the regional state administration. The head of the region (the governor) is the chairman of the regional state administration, in order to appoint the chairman of the regional state administration, a submission of the Cabinet of Ministers is required, which must be signed by the President of Ukraine .
Kiev Regional Council (2006-2010).
Leadership: Head - V. Maybozhenko, O. S. Kachny (from 05.2010), Deputy Heads: K. A. Bondarev, O. S. Kachny, S. I. Dorotich , L. M. Piotrovich, O. Kalenik. I., Babenko N.V.
Only 120 deputies
- Yulia Tymoshenko Bloc - 66 mandates
- Our Ukraine - 16 seats
- Socialist Party of Ukraine - 14 seats
- Party of Regions - 11 seats
- Litvin Bloc - 7 mandates
- Ukrainian People’s Bloc Kostenko and Ivy - 6 seats
Kiev Regional Council (since 2010).
Leadership: Chapter - O. S. Kachny, Deputy Heads: Yu. A. Pavlov, I. Shkyrta
Kiev Regional Council (since 2014).
Leadership: Chapter - N.V. Babenko, Deputy Heads: Y. V. Dobriansky, Yu. M. Noah
A total of 148 deputies
- Party of Regions - 97 seats
- Front Zmіn - 16 seats
- "BLOW" - 11 mandates
- Strong Ukraine - 10 seats
- Freedom - 5 seats
- People's Party - 3 seats
- “Justice” - 2 mandates
- European Party of Ukraine - 1 mandate
- Our Ukraine - 1 mandate
- " Third Force " - 1 mandate
- Socialist Party of Ukraine - 1 mandate
Economics
| No. | indicator | units | value, year 2014 |
|---|---|---|---|
| one | Export of goods | million US dollars | 1852.4 [10] |
| 2 | Specific weight in the all-Ukrainian | % | 3.4 |
| 3 | Import of goods | million US dollars | 3756.9 [10] |
| four | Specific weight in the all-Ukrainian | % | 6.9 |
| five | Balance export - import | million US dollars | −1904.5 [10] |
| 6 | Capital investment | million hryvnias | 18264.1 [11] |
| 7 | Average salary | UAH | 7200 [12] |
| eight | Average salary [13] | US dollars | 180 [14] |
According to the materials of the Committee of Statistics of Ukraine (Ukrainian) and the Main Department of Statistics in the Kiev region (Ukrainian)
Industry
The industries that determine scientific and technological progress (mechanical engineering and metalworking, including instrument making, electronic, electric power, powder metallurgy, chemistry and petrochemistry), as well as new areas of production - microbiological and paperboard are developing rapidly. In the village of Proliski , on the eastern outskirts of Kiev, the Borispol Bus Plant operates. The plant produces 1700 buses a year of various modifications. The plant is actively collaborating with the Etalon Research Institute of Automotive Engineering.
Resort and recreation resources
Resort resources of the Kiev region Along with a mild climate conducive to climate therapy, mineral waters are brought to the surface by drilling. Radon waters of low salinity and various chemical composition (sulfate-chloride calcium-sodium, hydrocarbonate magnesium-calcium) found in a number of regions of the region — near the town of Mironovka (health resort area, hydropathic in Mironovka), and in the village are of the greatest balneological importance. Vladislavovka Mironovsky district , in the resort of Bila Tserkva, in the resort area Koncha-Zaspa. Sodium chloride waters were brought to the surface near Brovary (in the region there are numerous children's health camps (school camps for schoolchildren), including on the basis of sources - in particular, Zhuravochka in Brovary ).
A number of mines are being bottled. bottled water as table water under the names “Kievskaya” (low-salinity calcium-magnesium hydrocarbonate, used primarily as a table drink for metabolic disorders), “Borispolskaya”, “Chernobyl” (in the recent past), “Resort”, “Berezanskaya”, as well as “Obolonskaya” (“Obolon”), “Calypso” (“Orlan”), “Sofia Kievskaya” (“Rosinka”), and others. Spa and therapeutic resources supplement peat mud , deposits of which are located in the north Kiev. areas (floodplains of the Desna, Pripyat, Zdvizh rivers).
There are resorts Bila Tserkva , Mironovka , Boyarka , Vorzel (there is a House of Composers, a pump room of min. Water), Pushcha-Voditsa ; there are a number of resort areas: Koncha-Zaspa , Svyatoshino , Irpen (known for the Writers' House), Bucha (some long-distance passenger trains stop at Bucha station), Klavdievo-Tarasovo (including (children’s) camp near the village of Poroskoten , at Lysaya Gora ), Pirnovo (recreation center on the Desna and Dnieper (Kiev Sea)), Lutezh , recreation area Feofania ;
34 sanatoriums (5200 places), including 3 trade union (1420 places); 16 rest houses, numerous pensions and recreation centers belonging to various institutions and departments (Potievka (on the outskirts of Fastov ), Plesetskoye , Kovalevka , Kotsyubinskoye , and others - promising resort (resort and recreational) areas). In Kiev, there is an office (branch) of the Mirgorod resort.
Attractions
In the Kiev region there are many architectural and historical monuments and cultural monuments. Kiev is especially rich in them - the oldest city, the center of Kievan Rus . Here, the remains of city fortifications - the Golden Gate ( XI century ), St. Sophia Cathedral (founded in 1017-1037) - the main public and religious building [metropolitan temple] of Kievan Rus, the ensemble of Kiev-Pechersk Lavra (founded in the middle of the XI century , from 1926) historical and cultural museum-reserve), the Church of the Savior on Berestov (1113-1125) and Kirillovskaya ( XII century ), the monumental churches of St. Nicholas of Prisysk (Nikolsko-Prisitskaya) and Ilyinskaya (XVII century); the XVII — XVIII centuries include buildings mainly in the Ukrainian Baroque style — the Sofia ensembles (“Sophia of Kiev” founded by P. Mogila), the Vydubetsk (XI — XVIII century) and Frolovsky (Pritisko-Nikolskaya St., 5) monasteries, Pokrovskaya (in Bekhterevsky Lane, 15) and St. Andrew's Church (1749-1753), Mariinsky (1747-1755) and Klovsky Palaces, the Great Bell Tower of the Kiev Pechersk Lavra (1745), the Brahma Zaborovsky in Kiev [the narrow (solemn) gates of the Sofia Monastery], the Collegium ( 1753-1757) in Pereyaslav and others.
At the end of the 18th - 1st half of the 19th centuries, large civil buildings were erected in cities in the classicist style (shopping arcades on Bazarnaya Square (1809–1814), warehouses, a post office (ensemble of structures, 1825–1831), Winter Palace (1796), house “Public meetings” (the House of the Noble Assembly) and the building of the gymnasium in the White Church; the Institute of Noble Maidens and the University of Kiev and others], in the countryside - landowner palaces with parks; the famous Alexandria dendrological park near the White Church (architect Muffo and Dominic Botany, as well as A. Ens; there is a museum arboretum).
There are many monuments in the capital city, including Prince Vladimir (1853), Princess Olga (1911, rebuilded 1996) and Bogdan Khmelnitsky (1881-1888), Magdeburg Law (1802-1808); on the territory of the Holy Dormition Kiev-Pechersk Lavra (near the Refectory Church) the body of P.A. Stolypin rests, and also (in the lower part of the Lavra, near and distant caves) the relics of the chronicler Nestor, the healer Agapit, monk Elijah Pechersky are buried.
Also interesting are the modern architecture of the 20th century (Palaces of Sports (1958-60) and pioneers (Kiev Palace of Children and Youth), the airport terminal in Borispol; Palace of Culture "Ukraine" (1970, reconstructed 1997-98) and others) and Kiev museums - Ukrainian House (exhibition center, palace of arts), historical, Ukrainian fine arts (national art museum), Western and Eastern art (Bogdan and Varvara Khanenko Museum of Art), history of medicine (37 B. Khmelnitsky Street), museum-pharmacy, folk architecture and life ( Pirogovo , 150 ha; 1969) and others (more than 15 museums in total).
In Pereyaslav-Khmelnitsky excavations, the remains of buildings of the 11th-12th centuries (the Episcopal Palace, the Church of St. Michael and others) were discovered, the Mikhailovsky Church (1646-1666, erected on the ruins of the Mikhailovsky Church (1090)) and the ensemble of the Ascension Monastery (1695-1700); there are museums - historical, memorial, Ukrainian philosopher, poet and teacher of the XVIII century G. S. Skovoroda, folk architecture and life (about 20 museums); There is also a museum of local lore in the Bila Tserkva (since 1924).
The Bila Tserkva operates the regional drama theater named after P.K. Saksagansky (1933); house of organ and chamber music. In one of the oldest Russian cities, Vasilkov , the Cathedral of St. Anthony and Theodosius (1756-1758 years) and St. Nicholas Church (1792). There is a beer museum in Fastov .
Archaeological excavations (the first half of the 20th century) in Vyshgorod opened the detinets and the Olzhin Grad handicraft and trading post, where a part of an ancient street with the remains of ground and half-earth dwellings of metal finishing and pottery workshops, the remains of fortifications, tools, dishes, decorations, the foundation of Borisoglebskaya churches and other finds belonging to the X — XIII centuries (ancient Russian settlement of the IX — XIII centuries). In the vicinity of Vyshgorod there was the Mezhigorsk Spaso-Preobrazhensky Monastery (988-1930s).
Near the village Tripoli revealed settlements (sites) of the Stone Age, near the village. Trakhtemirova - a settlement of the Scythian period ; in the region of Boryspil , in the village of Sofievka , - the Sofievsky burial ground (late stage of Trypillian culture ) and others.
In the Kiev region there was a specific folk icon-painting style, formed under the influence of the old icon-painting tradition of the Kiev-Pechersk Lavra . The saints were depicted on a dark purple or black background in the decoration of dark tones with dark blue, dark green or even black nimbuses , outlined by a dotted dotted white outline. The collection of home icons of the Kyiv region is part of the exposition of the Museum of Ukrainian Home Icon in the historical and cultural complex “ Radomysl Castle ” [15] .
Famous People
Born in the area
- Vovchenko, Ivan Antonovich (1905-1976) - Soviet military leader, major general of tank troops (1943).
- Kozlovsky, Ivan Semenovich (1900-1993) - singer, People's Artist of the USSR (1940).
- Короленко, Иосиф Федосеевич (1902—1978) — советский военный деятель, генерал-майор артиллерии ( 1944 год ).
- Сердюк, Александр Иванович (1900—1988) — актёр, режиссёр театра и кино, народный артист СССР (1951).
- Сидоренко, Пётр Иванович (1907—1985) — советский военный деятель, генерал-лейтенант артиллерии . Hero of the Soviet Union .
- Малышко, Андрей Самойлович (1912—1970) — советский украинский писатель и переводчик.
See also
- Главы Киевской области
Notes
- ↑ Статистичний збірник «Регіони України» 2016. Частина І / За редакцією І. М. Жук. Відповідальний за випуск М. Б. Тімоніна. — К. : Державна служба статистики України , 2016. — С. 261. (укр.)
- ↑ Грамота
Президиум Верховного Совета СССР
за успехи, достигнутые в деле увеличения производства и заготовки зерна, мяса, молока, яиц, сахарной свеклы, льна-долгунца и других сельскохозяйственных продуктов, указом от 26.II .58 наградил Киевскую область Украинской ССР
орденом Ленина.
Москва — Кремль. 4 марта 1958. - ↑ Природно-заповідний фонд Києва. Довідник / Редкол. М. М. Мовчан та ін. — К. : «Арктур-А», 2001. — 64 с. — ISBN 966-7572-05-6 . (Ukrainian)
- ↑ Первым действительно заповедным объектом Киевщины можно считать озёра Конча-Заспы (вместе с островами Жуковым, Ольжиным и Казачьим), взятые под охрану Киевским отделом Российского Императорского общества рыбоводства и рыболовства в 1893 году .
- ↑ Государственный комитет статистики Украины. Сборник: Численность наличного населения Украины на 1 января 2015 года. Киев 2015. Ответственная за выпуск Тимошенко Г. М. (doc) (укр.)
- ↑ Сергиенко А., Ткачук А. Киев в оковах окраин, или Как развиваться украинским мегаполисам? // Зеркало недели. 13 января 2017.
- ↑ В составе района, или даже отдельно (отделённо) от него, существует Ирпенский район-регион (26-й в области) — со своей администрацией [ незалежной от Боярки-Вишнёвого], своей центральной районной больницей, центральной районной аптекой, почтой-телеграфом (свой ирпенский телефонный код), центральным районным рынком, рай.библиотекой и т. п. По существу города Ирпень, Буча, посёлки Коцюбинское, Гостомель, Ворзель (имеющие один Ирпенский тел. код (0)4597) к Киево-Святошинскому району (тел. код (0)4598) не имеют никакого отношения, хотя формально это нигде и не закреплено. При этом в Ирпенском регионе (за ним) существует тоже своеобразный анклав — сёла Горенка, Мощун и Мироцкое не относятся к Ирпенскому р-ну, не относятся они также к Вышгородскому р-ну (что было бы тоже логично), а в адм.-терр. отношении отнесены к Киево-Святошинскому р-ну — все районные структуры (паспортный стол, БТИ, ЦРБ , ЦРА и т. д. и т. п.) находятся в гор. Вишнёвое — Боярка, и частью в Киеве.
- ↑ В Київську облраду пройшли шість політсил
- ↑ Избирательный список БЮТ насчитывал только 65 кандидатов, соотв. облсовет имеет в наличии 119 мандатов.
- ↑ 1 2 3 Географическая структура внешней торговли товарами Киевской области за 2014 год (укр.)
- ↑ Капитальные инвестиции по видам активов за 2014 год (укр.)
- ↑ Среднемесячная заработная плата штатных работников по городам и районам Киевской области за январь — декабрь 2014 года (укр.)
- ↑ Официальный курс гривны НБУ (средний за период) (укр.)
- ↑ Курс 11,8867 за 2014 г.
- ↑ Богомолець О. Замок-музей Радомисль на Шляху Королів Via Regia. — Київ, 2013
Literature
- Київська область // Украинская Советская (Радянська) Энциклопедия, в 12 томах = Українська Радянська Енциклопедія. — 2-е видання. — К. : Головна редакція Української Радянської енциклопедії, 1980 . — Т. 5. — С. 128–131, 144. (укр.) , там же см. схему «Основные памятки и памятные места Киевской области» на стр. 130.
- «Київська область» (с. Войкове) // История городов и сел Украинской ССР = Історія міст і сіл Української РСР: у 26 томах / Редкол.: П. Т. Тронько (голова редкол.) та ін.. — К. : Головна редакція Української Радянської енциклопедії АН УРСР, 1971 . — Т. <<Київська область>>. — С. 94; 12 (схема). (укр.) (рус.)

