Demyelinating diseases are any diseases of the nervous system in which the myelin sheath of neurons is damaged. [1] This damage disrupts the signaling of the affected nerves. In turn, a decrease in conductive ability leads to impaired sensitivity, movement, cognitive functions, and other functions, depending on which nerves are affected.
| Demyelinating diseases | |
|---|---|
 | |
| ICD-10 | G 35. - G 37. , G 61.1 |
| ICD-10-KM | |
| ICD-9 | 340 - 341 , 357.0 |
| Mesh | D003711 |
Demyelinating diseases can be caused by genetic factors , pathogens, autoimmune reactions, and other unknown factors. Poisoning with organophosphorus compounds from commercial insecticides, such as sheep bath products, herbicides , and flea anti-pet products, can lead to nerve demyelination. [2] Chronic administration of antipsychotics can also cause demyelination. [3] Vitamin B 12 deficiency can also result from dysmyelination. [4] [5]
Demyelinating diseases are traditionally divided into two types: demyelinating myelinclastic diseases and demyelinating leukodystrophic diseases . In the first group, normal and healthy myelin is destroyed by the action of a toxin or an autoimmune reaction. In the second group, myelin is abnormal and degenerates. [6] The second group is called poser dysmyelinating diseases . [7]
There is evidence that the body’s own immune system is at least partially responsible for the development of the most famous demyelinating disease, multiple sclerosis . It is known that acquired immunity cells, called T-lymphocytes , are present in the lesion foci. Other cells of the immune system called macrophages (and possibly mast cells ) also contribute to damage. [8]
Content
- 1 Classification
- 2 Clinic
- 3 Diagnostics
- 4 In animals
- 5 notes
- 6 References
Classification
Demyelination can be divided into 2 types [9] :
- myelinopathy - the destruction of already formed myelin due to causes associated with a biochemical defect in the structure of myelin, usually genetically determined (for example, Canavan disease );
- myelinlastia - the destruction of normally synthesized myelin under the influence of various influences, both external and internal (for example, Binswanger's disease ).
The division into these two groups is very conditional, since the first clinical manifestations of myelinopathies can be associated with the influence of various external factors, and myelinoplasty is most likely to develop in predisposed individuals [10] .
In addition, demyelinating diseases can be divided into those that affect the central nervous system, and those that damage the peripheral nervous system.
Disorders affecting the central nervous system include:
- multiple sclerosis , Devik's disease , Balo concentric sclerosis , as well as other disorders involving the immune system, called inflammatory demyelinating diseases;
- osmotic demyelination syndrome;
- myelopathy, for example, spinal cord ;
- leukoencephalopathy, for example, PML ;
- leukodystrophy and others.
Demyelinating diseases of the peripheral nervous system include:
- Guillain-Barré syndrome ;
- and others.
Clinic
Clinical signs of demyelination as a pathological process cannot be distinguished. Symptoms depend on the localization of demyelination in the structures of the central or peripheral nervous system.
Diagnostics
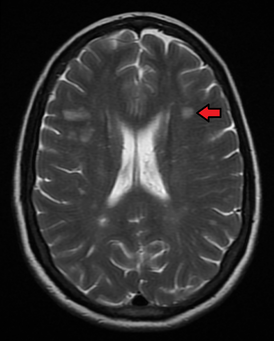
The main diagnostic tool for the demyelinating disease of the central nervous system is MRI , on which foci with a diameter of at least 3 mm are detected.
Diagnosis of a demyelinating disease of the peripheral nervous system is based on electromyography .
In animals
Demyelinating diseases have been found worldwide in various animals. These are mice, pigs, cattle, hamsters, rats, sheep, Siamese cats and a number of dog breeds (including: Chow Chow, Springer Spaniel, Dalmatian, Samoyeds, Golden Retriever, Bernese Mountain Dog, Weimaraner, Australian Silky Terrier and others) [11] [12] . This disease was also found in northern fur seals [13] .
Notes
- ↑ " demyelinating disease " at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ↑ Lotti M., Moretto A. Organophosphate-induced delayed polyneuropathy. ( unspecified ) // Toxicol Rev. - 2005. - T. 24 , No. 1 . - S. 37-49 . - DOI : 10.2165 / 00139709-200524010-00003 . - PMID 16042503 .
- ↑ Konopaske GT; Dorph-Petersen KA; Sweet RA et al. Effect of chronic antipsychotic exposure on astrocyte and oligodendrocyte numbers in macaque monkeys : [ eng. ] // Biol. Psychiatry : journal. - 2008. - T. 63, No. 8 (April). - S. 759-765. - DOI : 10.1016 / j.biopsych.2007.08.08.018 . - PMID 17945195 . - PMC 2386415 .
- ↑ Agadi S., Quach MM, Haneef Z. Vitamin-responsive epileptic encephalopathies in children. : [ eng. ] // Epilepsy Res Treat: journal. - 2013. - T. 2013. - S. 510529. - DOI : 10.1155 / 2013/510529 . - PMID 23984056 . - PMC 3745849 .
- ↑ Yoganathan S., Varman M., Oommen SP, Thomas M. A Tale of Treatable Infantile Neuroregression and Diagnostic Dilemma with Glutaric Aciduria Type I.: [ eng. ] // Journal of Pediatric Neurosciences: journal. - 2017. - T. 12, No. 4. - S. 356-359. - DOI : 10.4103 / jpn.JPN_35_17 . - PMID 29675077 . - PMC 5890558 .
- ↑ Fernández O .; Fernández VE; Guerrero M. Demyelinating diseases of the central nervous system (English) // Medicine: journal. - 2015. - Vol. 11 , no. 77 . - P. 4601-4609 . - DOI : 10.1016 / j.med.2015.04.001 .
- ↑ Poser CM Leukodystrophy and the Concept of Dysmyelination (English) // JAMA : journal. - 1961. - Vol. 4 , no. 3 . - P. 323-332 . - DOI : 10.1001 / archneur.1961.00450090089013 .
- ↑ Laetoli. Demyelination unopened (January 2008). Archived July 28, 2012.
- ↑ Handbook of the formulation of a clinical diagnosis of diseases of the nervous system / Ed. V.N. Stock, O.S. Levin. - M .: Medical Information Agency LLC, 2006. - P. 88–89. - 520 s. - ISBN 5-89481-316-6 .
- ↑ Gusev E.I., Boyko A.N. Demyelinating diseases of the central nervous system // Consilium medicum. - 2002. - T. 2 , No. 2 .
- ↑ Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. The Merck Veterinary Manual - Demyelinating Disorders: Introduction , Merck Veterinary Manual . Date of treatment June 4, 2015.
- ↑ Johnson RT. DEMYELINATING DISEASES. In: Institute of Medicine (US) Forum on Microbial Threats; Knobler SL, O'Connor S, Lemon SM, et al., Editors. The Infectious Etiology of Chronic Diseases: Defining the Relationship, Enhancing the Research, and Mitigating the Effects: Workshop Summary. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US) , NCBI . Date of treatment June 4, 2015.
- ↑ Ziggy Star has a Neurologic Condition . The Marine Mammal Center. Date of treatment 2015-06-04}.
Links
- Demyelinating diseases . Meir Medical Center (2019). - Per. from English N. D. Firsova.
- Multiple sclerosis - Information and educational portal of the Institute of the Human Brain of the Russian Academy of Sciences