The deltoidal hexacontahedron (from “ deltoid ” and other Greek ἑξήκοντα - “sixty”, ἕδρα - “face”) is a semi-correct polyhedron (Catalan body), dual to the rhombo-dodeca-dodecahedron . Made up of 60 identical convex deltoids .
| Deltoidal hexacontahedron | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 ( rotating model , 3D model ) | |||
| Type of | catalan body | ||
| Properties | convex , isohedral | ||
| Combinatorics | |||
| Items |
| ||
| Verge of | deltoids : | ||
| Vertex configuration | 20 (4 3 ) 30 (4 4 ) 12 (4 5 ) | ||
| Face configuration | V3.4.5.4 | ||
| Dual Polyhedron | rhomboikosododecahedron | ||
Scan
| |||
| Classification | |||
| Designations | oD, deD | ||
| Symmetry group | I h (icosahedral) | ||
It has 62 vertices. At 12 vertices (located just as the vertices of the icosahedron ) converge with their smallest angles along 5 faces; at 20 vertices (located just as the vertices of the dodecahedron ) converge with their largest angles on 3 faces; in the remaining 30 vertices (located in the same way as the vertices of the icosododecahedron ) converge with their average largest angles of 4 faces.
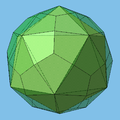
12 vertices are located just like the vertices of the icosahedron
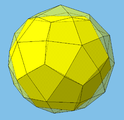
The 20 vertices are located just like the vertices of the dodecahedron

30 vertices are located just like the vertices of the icosododecahedron
It has 120 edges - 60 “long” (together forming something like “bloated” skeleton of icosahedron) and 60 “short” (forming “bloated” skeleton of dodecahedron).
The deltoidal hexacontahedron is one of the six Catalan bodies in which there is no Hamiltonian cycle [1] ; Hamiltonian path for all six also not.
Metric performance and angles
If the “short” edges of the deltoidal hexekontahedron have a length , then its “long” edges have a length
The surface area and volume of the polyhedron are expressed as
The radius of the inscribed sphere (relating to all faces of the polyhedron at their centers of the inscribed circles ) will be equal to
radius of the semi-written sphere (relating to all edges) -
radius of a circle inscribed on the face -
the smaller diagonal of the face (dividing the face into two isosceles triangles ) -
larger diagonal of the face (dividing a face into two equal triangles) -
It is impossible to describe a sphere near the deltoidal hexekontahedron — so that it passes through all the vertices.
The largest angle of the face (between the two "short" sides) is smallest edge angle (between two “long” sides) two medium-sized angles (between the “short” and “long” sides)
The dihedral angle for any edge is the same and equal to
Notes
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W. Catalan body counts (eng.) On the Wolfram MathWorld website.
Links
- Weisstein, Eric W. The deltoidal hexacontahedron (English) on the Wolfram MathWorld website.



