The Cuban Katran [1] [2] , or the Cuban Thorny Shark [2] , or the Cuban Thorny Shark [2] ( lat. Squalus cubensis ) is a species of the thorny shark genus of the family of Katran sharks of the cataract - like order . It lives in the western part of the Atlantic Ocean . It occurs at a depth of 380 m. The maximum recorded size is 110 cm. It is the subject of commercial fishing [3] .
| Cuban Katran |
 |
| Scientific classification |
|---|
| No rank : | Bilateral symmetrical |
|
| International scientific name |
|---|
Squalus cubensis Howell Rivero , 1936 |
| Area |
|---|
|
| Security status |
|---|
Not enough data IUCN Data Deficient : 61416 |
|
The scientific species was first described in 1936 [4] . The holotype is an adult male 52.4 cm long, caught near Havana , Cuba [3] .
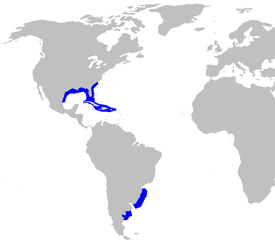
Cuban spiky sharks live in the western Atlantic Ocean from the coast of North Carolina to Florida, off the coast of Cuba, Haiti, in the north of the Gulf of Mexico, off the coast of southern Brazil and Argentina. These sharks are found in warm temperate and tropical waters on the outer border of the continental shelf and in the upper part of the continental slope at a depth of 60 to 380 m. Young sharks prefer to stay in shallow water [3] .
The maximum registered size is 110 cm. The average length does not exceed 75 cm. The body is rather slender. The snout is pointed, wide. The mouth is slightly curved in the form of an arch. The distance from the tip of the snout to the mouth is 1.3-1.4 times the width of the mouth. Large oval eyes are elongated horizontally, have a characteristic incision and are shifted closer to the tip of the muzzle than to the first gill slit. Behind the eyes there are splashes. The nostrils are located much closer to the tip of the snout than the mouth. Long spines are located at the base of the dorsal fins. The base of the first dorsal fin is shifted closer to the pectoral fins. The second dorsal fin is smaller than the first. Anal fin missing. The caudal fin is asymmetric; there is no recess at the edge of a longer upper lobe. On the caudal stem there are lateral carinae and a pronounced precaudal fossa. The pectoral fins are large, the ventral tip is rounded. The body is covered with small lanceolate placoid scales. The color is gray, the belly is lighter, there are no marks [3] .
Cuban spiky sharks breed by egg-born. In the litter up to 10 newborns. Large isopod crustaceans often parasitize in the oral cavity. The diet probably consists of bottom fish and invertebrates [3] .
The view is of little interest for commercial fishing. Meat is rarely eaten; most often, liver fat is used to produce vitamin oils. By-catch is often found in deep-sea fisheries. There is insufficient data to evaluate the conservation status of the species by the International Union for Conservation of Nature [5] .

