Shul - a cave on Mount Carmel in Israel . It is located 20 km south of the city of Haifa and 3 km from the shores of the Mediterranean Sea .
| Schul | |
|---|---|
| Location | |
| A country |
|
| Region | Haifa District |
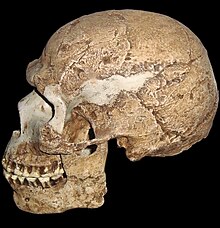
The prehistoric site was first excavated by Dorothy Garrod in the summer of 1928 [1] .
In the cave of Shul, Neanderthals alternately settled (up to 130 and 65–47 thousand years ago), then a reasonable person (130–80 and after 47 thousand years ago) [2] . The cave was inhabited during the Middle Paleolithic , 200–45 thousand years ago [3] .
Fourteen skeletons were discovered in the Shul Cave, most of which were found by Theodore D. McCown in 1932. Neanderthals from Schul belong to the more progressive group of Middle Eastern hominids Schul-Kafzeh , which differ markedly from more primitive and similar to European Neanderthals local finds from the caves of Tabun , Amud and Kebar [4] .
The remains found in the Shul cave, along with those found in other caves in the Nahal-Mearot (Wadi al-Mugara) reserve and in the cave, were classified in 1939 by and Theodore Mac -Coon as a species of Palaeoanthropus palestinensis is a descendant of the Heidelberg man ( Homo heidelbergensis ) [5] [6] [7] .
The 100-thousand-year-old ankle bone of Schul IV has a morphological resemblance to the talus (adrenal) bone of a hominid from the Siberian Baigara , 43 thousand years old [8] [9] . The occipital bone, found on Merovsky Island in the Saratov Region , is similar to the archaic sapiens of Schul V [10] .
Notes
- ↑ Dorothy Garrod : Excavations in the Mugharet el-Wad, near Athlit, April-June 1929. Quarterly Statement of the Palestine Exploration Fund 61, S. 220–222
- ↑ Three perforated shells make you take a fresh look at the origin of human culture
- ↑ Olson, S. Mapping Human History. Houghton Mifflin, New York (2003). p. 74-75.
- ↑ Cro-Magnons, ancient man, fossil man
- ↑ The Palaeolithic Origins of Human Burial , Paul Pettitt, 2013, p. 59
- ↑ Human Adaptation in the Asian Palaeolithic: Hominin Dispersal and Behavior during the Late Quaternary , Ryan J. Rabett, 2012, p90
- ↑ The stone age of Mount Carmel: report of the Joint Expedition of the British School of Archeology in Jerusalem and the American School of Prehistoric Research, 1929-1934 , p. 18
- ↑ Drobyshevsky S.V. New data on human evolution
- ↑ Razhev D.I. , Kosintsev P.A. , Kuzmin Ya. V. Pleistocene talus ( os talus ) of a person from the location of Baigar (center of Western Siberia)
- ↑ Kharitonov V. M. Findings of fossil hominids in Eastern Europe and adjacent regions of Asia (Part 2)
