
City block distance is a metric introduced by German Minkowski . According to this metric, the distance between two points is equal to the sum of the absolute values of the differences of their coordinates.
This metric has many names. City block distance is also known as Manhattan distance , a rectangular city metric, L1 metric or norm (see space L p ), city block metric, taxi metric, Manhattan metric , rectangular metric , right angle metric ; on it is called the grid metric and the 4-metric [1] [2] [3] .
The name "Manhattan distance" is associated with the street layout of Manhattan [4] .
Formal Definition
City blocks distance between two vectors
in an n- dimensional real vector space with a given coordinate system , the sum of the lengths of the projections of the segment between points on the coordinate axis. More formally,
Where
-
and
- vectors .
For example, on a plane, the distance of city blocks between and
equally
Properties
The Manhattan distance depends on the rotation of the coordinate system, but does not depend on reflection relative to the coordinate axis or transport . In the geometry based on the Manhattan distance, all Hilbert's axioms are fulfilled , except for the axiom of congruent triangles.
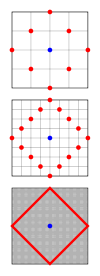
For three-dimensional space, the ball in this metric has the shape of an octahedron , whose vertices lie on the coordinate axes.
Examples
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
| eight | eight | ||||||||
| 7 | 7 | ||||||||
| 6 | 6 | ||||||||
| five | five | ||||||||
| four | four | ||||||||
| 3 | 3 | ||||||||
| 2 | 2 | ||||||||
| one | one | ||||||||
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
Chess Distances
The distance between the fields of the checkerboard for the vizier (or rook , if the distance is counted in cells) is equal to the Manhattan distance; the king uses the Chebyshev distance , and the elephant uses the Manhattan distance on the board rotated 45 °.
Fifteen
The sum of the Manhattan distances between the knuckles and the positions in which they are located in the solved “ Fifteen ” puzzle is used as a heuristic function to find the optimal solution [5] .
Cellular Automata
The set of cells on a two-dimensional square parquet , the Manhattan distance to which from this cell does not exceed r , is called the von Neumann neighborhood of the range (radius) r [6] .
See also
- Normalized Vector Space
- Metrics
- Hamming Distance
- Chebyshev distance
- French railway metric
- Game at 15
- Random walk
- Distance matrix
Notes
- ↑ Elena Deza, Michelle Marie Desa. Chapter 19. Distances on the real and digital planes. 19.1. Metrics on the Real Plane // Encyclopedic Dictionary of Distances = Dictionary of Distances. - M: Nauka, 2008 .-- S. 276. - ISBN 978-5-02-036043-3 .
- ↑ Cluster Analysis: Distance Measures
- ↑ Manhattan distance
- ↑ City Block Distance. Spotfire Technology Network.
- ↑ Computer History: Heuristic Functions
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W. von Neumann Neighborhood on Wolfram MathWorld .
Literature
- Eugene F. Krause. Taxicab Geometry. - Dover, 1987 .-- ISBN 0-486-25202-7 .
Links
- city-block metric on PlanetMath
- Weisstein, Eric W. Taxicab Metric ( Wolfram ) at Wolfram MathWorld .
- Manhattan distance . Paul E. Black, Dictionary of Algorithms and Data Structures , NIST
- Taxi! - AMS column about Taxicab geometry
- TaxicabGeometry.net - a website dedicated to taxicab geometry research and information

