Crater Vargentin ( lat. Wargentin ) - a large lava- flooded impact crater in the southern hemisphere of the visible side of the moon . The name was given in honor of the Swedish astronomer and demographer Per Wilhelm Vargentin (1717-1783) and approved by the International Astronomical Union in 1935. The formation of the crater belongs to the nectar period [1] .
| Vargentin | |
|---|---|
| lat Wargentin | |
 Shot of the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter probe. | |
| Characteristics | |
| Diameter | 84.7 km |
| Deepest | 300 m |
| Title | |
| Eponym | Per Wilhelm Vargentin (1717-1783) - Swedish astronomer and demographer. |
| Location | |
| Heavenly body | Moon |

Content
- 1 Crater Description
- 2 Satellite Craters
- 3 See also
- 4 notes
- 5 Links
Crater Description
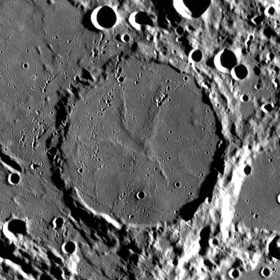
The closest neighbors of the crater are the Ingirs crater in the west; the huge Shikkard crater in the northeast, the Nesmith crater adjacent to it in the east, and the large Fokilid crater in the southeast [2] . Selenographic coordinates of the center of the crater , diameter 84.7 km [3] , depth 0.3 km [4] .
Crater Vargentin is an unusual crater, the bottom of its bowl is significantly elevated above the surrounding area, the bowl of the crater is completely flooded with basalt lava , so the crater is a raised plateau, resembling an inverted shallow plate in shape. When filling the crater with lava, something blocked the return of lava flows to the equilibrium state and the crater was filled almost to the edge of the shaft. Over time, rocks accumulated on top of the lava field ejected during impacts that formed adjacent craters, and today the albedo of the crater bowl is significantly higher than that of typical basalt deposits.
The crater shaft is significantly destroyed and streaked with many small craters. The shaft height above the surrounding area is 1380 m [1] , the volume of the crater is approximately 6600 km³ [1] . The bottom of the crater’s bowl is relatively flat, with the exception of a few low ridges emanating from a point close to the center of the crater, resembling a bird’s paw.
Owing to its southern location, the shape of the crater upon observation from the Earth seems oval due to perspective distortions.
Satellite Craters
| Vargentin [3] | Coordinates | Diameter, km |
|---|---|---|
| A | 20.7 | |
| B | 17.0 | |
| C | 12.5 | |
| D | 16.1 | |
| E | 16,0 | |
| F | 19.8 | |
| H | 9.7 | |
| K | 8.3 | |
| L | 11.5 | |
| M | 6.7 | |
| P | 9.3 |
See also
- List of Craters on the Moon
- Lunar crater
- Morphological catalog of Moon Craters
- Planetary nomenclature
- Selenography
- Mineralogy of the Moon
- Geology of the moon
- Late heavy bombardment
Notes
- ↑ 1 2 3 Lunar Impact Crater Database . Losiak A., Kohout T., O'Sulllivan K., Thaisen K., Weider S. (Lunar and Planetary Institute, Lunar Exploration Intern Program, 2009); updated by Öhman T. in 2011. Archived page .
- ↑ Crater Vargentin on the map LAC-124
- ↑ 1 2 Handbook of the International Astronomical Union
- ↑ John E. Westfall's Atlas of the Lunar Terminator, Cambridge Univ. Press (2000)
