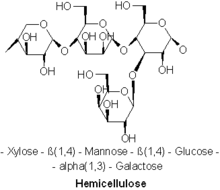
Hemicelluloses (HMCs) are plant homo- and heteropoly saccharides with a molecular weight lower than that of cellulose (10,000-40000), consisting of residues of various pentoses and hexoses . The main components of hemicelluloses are glucans, xylans, mannans, galactans, fructosans, arabinogalactans, etc. Most of the plants contain xylans . There are a lot of GMCs in seeds , seeds, straw , sunflower husk, husk of cotton seeds, corn cob. On average, about 25% (by weight) of the organic matter of annual plants is represented by hemicelluloses.
Hydrolysis of HMC gives a diverse set of compounds: D-fructose, D-xylose, D-galactose, D-mannose, L-arabinose, L-ramnose, D-glucose, D-galacturonic and 4-O-methyl-D-glucuronic acid which are present as lateral branches. Monosaccharides are part of HMC in furanose and pyranose forms, uronic acids in pyranose form. Individual monosaccharides in the HMC are linked by β-1 → 2-, β-1 → 3-, β-1 → 4 and β-1 → 6-bonds.
HMC polysaccharides are an indispensable component of plant cell walls [1] ; they perform mainly constructive functions by encrusting cellulose. In some cases, along with starch, HMC polysaccharides are reserve nutrients. They are also part of the cell walls of various microorganisms .
In contrast to cellulose, HMCs are easily hydrolyzable polysaccharides . They are extracted from crushed fat-free and non-tarred tissues or delignified raw materials with aqueous solutions of alkalis, dimethyl sulfoxide . From the obtained solutions, HMC is precipitated with alcohol , acetone , Feling reagent , salts, separated by centrifugation , washed and lyophilized.
Content
Composition
HMC polysaccharides are distinguished by various properties, which is due to the different arrangement of units in the polymer chain, the type of bond between monosaccharide residues, the degree and nature of branching units, the molecular weight and the content of various functional groups.
Arabinans are polysaccharides associated with pectin in plant tissues. Isolated from various types of raw materials ( sugar beet roots, peanuts , apples , citrus fruits ). They are soluble in water , easily hydrolyzed .
Xylans are the most common polysaccharides in the hemicellulose group. Their molecular weight is approximately 40,000 Da. The macromolecules are branched, the main longest chain is formed from D-xylopyranose residues connected by a β-bond at the site of 1 → 4 carbon atoms. The composition of the side, less branched chains found: L-arabinose, D-xylose, glucuronic acid , and its methyl ester , less often D-glucose, and D-galactose. Different types of plants and their anatomical parts are characterized by polysaccharides that are different in composition of side chains, which also affects the quality of food products.
Galactans - their amounts range from 1 to 16%, they form the cell walls of various plants. The structure of galactan macromolecules depends on the type of plant material. Sulphonated galactans released from algae have significant gelling properties and are widely used in confectionery production. They are divided into two groups of agar and carrageenan. Agar is a mixture of two polysaccharides - agarose and agropectin. Carrageenans are built from sulfonated galactose and 3,6-anhydrogalactose units. Sulphonated polysaccharides are widely used in the confectionery industry in the production of jelly , marmalade , jelly and other food products.
Mannans - form the cell walls of coniferous wood , yeast , algae and other raw materials. They are built from the remains of D-mannapyranoses connected by 1 → 4 or 1 → 6 bonds. These include galactomannan, glucomannan, galactoglucoman. Molecules can be linear or branched, side chains are connected to the main chain by bonds 1 → 4 or 1 → 3.
Fructans - found in grain of wheat , barley and other angiosperms, in Jerusalem artichoke , herbs , bacteria . Fructans are built from residues of fructose connected at the site of 2 → 1 or 2 → 6 carbon atoms . These include inulin , asparagosin and other substances.
The role of hemicelluloses in human nutrition is diverse. They are harmless to the human body and are digested depending on the structure by 69% - 95%. HMCs serve as a source of energy, affect lipid metabolism, play the role of enterosorbents , lower cholesterol , sorb microflora , salts of heavy metals.
Functions
Hemicelluloses provide non-covalent crosslinking of individual cellulose fibrils. In this connection, it is proposed to use a functional term in modern plant biology: cross-linking glycans. [2]
Systematics
Wood , in addition to cellulose, contains other polysaccharide substances, which include hemicelluloses. They are less resistant to diluted acids, which they hydrolyze and, unlike cellulose, dissolve in dilute alkali. Since hemicelluloses are substances representing all polysaccharides and their derivatives present in wood in addition to cellulose and starch, many criteria have been proposed for their classification.
- Division due to ease of hydrolysis :
The most common is the division into hemicelluloses, which are easily and difficult to hydrolyze. In contrast to cellulose, hemicellulose macromolecules consist not only of glucose residues, but also of other simple sugars, such as xylose , mannose and galactose . Hemicelluloses have a lower degree of polymerization (SP <300) than cellulose, a lower regularity of the structure and a degree of ordering of the structure, which makes them less resistant to degradation. A characteristic feature of all hemicelluloses is their good solubility in dilute alkali . The name hemicellulose was introduced by Schulze in 1891 for the non-cellulose portion of carbohydrates found in plants. Rogwin introduced the generally accepted concept of hemicellulose separation. As a criterion for the separation of hemicelluloses, he adopted the design of their basic units and macromolecules.
- Chemical structure separation
Based on the chemical structure of hemicellulose, it can be divided into:
- homogeneous:
consisting of the remainder of the same simple sugars
- consisting of polyuronic acids
- heterogeneous:
consisting of residues of various simple sugars
- consisting of residues of various simple sugars and uronic acids.
Schulze division:
- Cellulosates - they include relatively short chain polysaccharides (SP 150-200) and are divided into pentosans and
hexosanes with general formulas:
- pentosans - (C 5 H 8 O 4) n
- hexosanes - (C 6 H 10 O 5) n
In the presence of inorganic acids, pentosans are hydrolyzed to pentoses:
(C 5 H 8 O 4) n + nH 2 O → n C 5 H 10 O 5 and hexosans under the same conditions are hydrolyzed to hexoses:
(C 6 H 10 O 5) n + nH 2 O → n C 6 H 12 O 6 Hexosans and pentosans are polymers consisting of glycoside residues bound to pentose or hexose. Cellulosates are part of hemicelluloses that are more difficult to hydrolyze. They consist mainly of xylan and mannan. They may also be present in the form of mixed celluloses, for example, arabogalactan, galactomannan, galactomannoxylate.
- Polyuronides are amorphous substances containing significant amounts of hexauronic acids, some methoxy groups, acetyl groups and free carboxyl groups. Hydrolysis of polyuronides leads to the formation of uronic acids. The most common uronic acids include β-D-glucuronic acid, β-D-mannuronic acid, and α-D-galacturonic acid. The most important reactions of uronic acids are decarboxylation , which occurs when heated with inorganic acids. Then the corresponding pentoses arise.
Notes
- ↑ Scheller HV, Ulvskov P., Hemicelluloses. // Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2010; 61: 263-89. doi: 10.1146 / annurev-arplant-042809-112315 .
- ↑ N.D. Alekhine, Yu.V. Balnokin, V.F. Gavrilenko, T.V. Zhigalova, N.R. Meychik, A.M. Nosov, O.G. Polesskaya, E.V. Kharitonashvili, V.V. Forelock. Plant Physiology / I. Ermakov. - 1. - 5: Academy, 2005. - S. 273, 463. - 640 p. - ISBN 5-7695-1669-0 .
Links
- Structure and Properties of Hemicellulose / David Wang's Wood Chemistry Class
Ivanova L.A., Voyno L.I., Ivanova I.S. Food biotechnology. Prince 2. Processing of plant materials / Ed. I. M. Gracheva. - M .: KolosS, 2008.472 s.: 212-214.