Currant kidney tick [1] ( lat. Cecidophyopsis ribis ) is a type of microscopic four-legged tick of the genus Cecidophyopsis from the family Eriophyidae ( Trombidiformes ). Europe , Australia , Oriental region [2] .
| Currant kidney mite |
 |
| Scientific classification |
|---|
| No rank : | Bilateral symmetrical |
| Squadron : | Acariform ticks |
| Superfamily : | Four-legged ticks |
|
| International scientific name |
|---|
Cecidophyopsis ribis ( Westwood , 1869) |
| Synonyms |
|---|
- Acarus ribis Westwood, 1869
- Phytoptus ribis Nalepa, 1893
|
|
Content
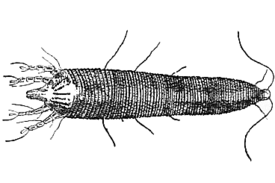
Length about 0.2 mm, body white, vermiform with 4 legs [3] . Sternum shortened. Dorsal setae on scutellum absent. The female genitalia are close to the bases of the coxae of the legs [1] .
A currant bud mite is a pest of gooseberries and black currants [1] (sometimes it damages red and white currants). Wintering and further development of ticks occurs inside the kidneys (up to 3-8 thousand individuals can be in one kidney). After colonization by mites, the kidneys become rounded and become larger by fall. At the beginning of next year, the kidneys swell to the size of a pea (deformed leaves protrude outward through the scales), and gradually take the form of a small bursting cabbage cabbage. Settled both with planting material, and with the help of wind, birds, insects (most of them die). There are five generations a year: two spring and three summer-autumn [3] . They are a carrier of terry (reversion) of black currant [4] .
To control pests, it is necessary to pluck the kidneys and destroy the tick-infected branches, observe the rules of agricultural technology and use acaricides [3] .
