Amphilinids ( lat.Amphilinidea ) - a detachment of parasitic flatworms from the class of cestodes ( Cestoda ). There are 8 species sporadically found on all continents. Adult worms parasitize in the body cavity of marine and freshwater bone fish ; an exception is Gigantolina elongata , using Australian snake-necked turtles ( Chelodina ) as the final host [2] [3] . Currently, amphilinid is considered as a sister group in relation to tapeworms ( Eucestoda ), contrasting the third group of cestodes - gyrocotyloids ( Gyrocotyloidea ) [4] .
| Amphilinides |

Gigantolina elongata in the body cavity of an Australian tortoise |
| Scientific classification |
|---|
| No rank : | Bilateral symmetrical |
|
| International scientific name |
|---|
Amphilinidea Poche , 1922 |
| Childbirth and species [1] |
|---|
- Amphilina
- Amphilina foliacea
- Amphilina japonica
- Gigantolina
- Gigantolina elongata
- Gigantolina magna
- Schizochoerus
- Schizochoerus janickii
- Schizochoerus africanus
- Schizochoerus liguliodes
- Schizochoerus paragonopora
|
|
Amphilina foliacea ,
sturgeon parasite
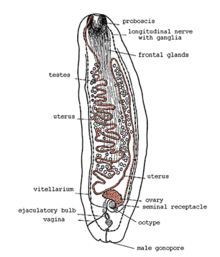
The body length of sexually mature individuals is 2.5–38 cm [3] . The form varies from leaf to belt-like, the color is white or light cream [3] . Due to the habitat in the body cavity, amphilinids do not have developed attachment organs characteristic of tapeworms and gyrocotylids, which are forced to withstand the intestinal motility of the host [3] . A proboscis is located on the front end of the body - a muscular retraction capable of eversion, where the ducts of numerous glands open [3] .
The intestine is absent, food is absorbed through the integument. Amphilinids possess a hermaphroditic reproductive system [3] . A long convoluted uterus opens near the proboscis: for the release of eggs into the water, the worms expose the front end of the body to the outside - either through the host product or destroying the body wall [3] .
The development cycle of worms is characterized by a change of owners: amphipods and decapod cancers act as an intermediate host, and water vertebrates are the final ones [3] .
From the eggs swallowed by the crustacean, the ciliary larva - lycophore emerges [3] . At the posterior end of the lycophore, there are 5 pairs of movable actin hooks, which serve to penetrate the crustacean body through the intestinal wall [3] . After the introduction of the lycophore, it undergoes metamorphosis, acquiring structural features of an adult [3] . Unlike the lycophore gyrocotilides, which also have 5 pairs of hooks, the extreme pairs of hook lyophore amphilinids differ from the central ones and have a different structure than similar structures in other cestodes and monogenetic flukes ( Monogenoidea ) [3] .
To close the life cycle, the crustacean must be eaten by the final host, from the intestines of which the worm moves to the body cavity, where it continues to grow and reaches puberty [3] . According to the hypothesis of the neotenic origin of the group, adult amphilinids correspond to the plerocercoid stage in the Eucestoda life cycle.

