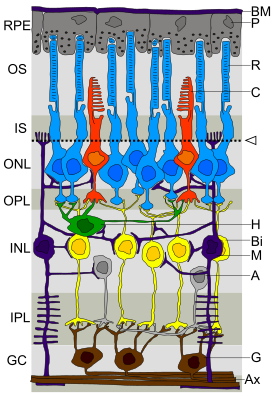
The ganglion layer ( English ganglion cell layer, GCL ) is one of ten layers of the vertebral retina , contains the bodies of ganglion cells and one type of amacrine cells .
| Ganglion layer | |
|---|---|
| lat stratum ganglionicum retinae | |
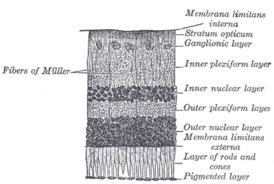 Section of the retina (ganglion layer is indicated on the right, the third on top). | |
| |
| Catalogs | |
|
The dendrites of the ganglion cells extend from the inner reticular layer , where they receive impulses from bipolar and amacrine cells. The axons of the ganglion cells are sent to the layer of nerve fibers , where they are collected in bundles and subsequently form the optic nerve , which carries several information processed by the retinal tissue into the central nervous system .
In addition to ganglion cells, this layer also contains another type of amacrine cells - displaced amacrine cells ( English displaced amacrine cells ) and neuroglia cells.
The number of cells of the ganglionic layer over the entire area is not constant; on the periphery of the retina, this layer contains one row of pericarions , and several layers in the central and middle parts. The layer thickness is about 20-30 microns.
Notes
Literature
- O. D. Lutsik, A. I. Ivanova, K. S. Kabak, Yu. B. Tchaikovsky Human histology . - K .: Book Plus, 2003 - ISBN 966-7619-39-7
- Histology : Textbook / Ed. By Yu. I. Afanasyev, N. A. Yurina - M.: Medicine, 2002 - ISBN 5-225-04523-5
Links
- Boston University Histology Learning System: 07902loa