
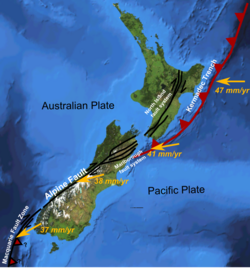
The Marlboro Span system is a collection of four large right-sided shifts and associated geological structures in the northern part of the South Island of New Zealand . This is a system of transform faults extending from the Alpine fault to the Kermadek trench , along the convergent boundaries of which the relative movement of the Australian and Pacific lithospheric plates occurs [1] .
Geometry
The Marlborough fault system consists of four major shear faults, along which almost the entire displacement is transmitted, associated with the boundaries of the lithospheric plates located here. Other, smaller faults were formed as a result of the interaction of these four faults or transfer deformations of the earth's crust between them, such as the Newton and Hur faults in the western part of the Hope fault and the overthrust Jordan, forming the ridge . Right-sided shift in this area also arose due to the rotation of the wings of faults approximately 20 ° clockwise from the times of the Pliocene [2] .
Development
The Marlborough fault system was formed about 5 million years ago, during the early Pliocene , due to changes in the movement of lithospheric plates. Due to the Alpine fault, the lithospheric plates mainly began to interact tangentially, increasing the power of convergence. The system of shear faults was formed as a result of this change, taking on most of the shear components of the plate movement [3] .
Faults
There are four main faults in the system, despite the fact that many other smaller faults or thrusts have been studied in this area.
Hope Rift
Hope Hole is located in the southernmost part of the Marlborough fault system. The calculated sliding speed during the Holocene was 20–25 mm / year, more than half of the total plate displacement in the region of the convergent boundary. In the north-eastern part of the fault Hope connects with the thrust Jordan and most of the displacement is transmitted to it. The fault got its name from , which flows along one of the central fault segments [1] .
Clarence Rift
Main article:
Clarence Rift begins at the Alpine Rift and ends 10 km west of , where it suddenly ends. The sliding speed in the Holocene, calculated for this fault, is 3.5–5.0 mm / year. On the surface, the shear looks almost horizontal, but the continuous uplift of the nearby Inner Kaikoura Range mountain range during the same period leads to the conclusion that some components of the shear in the depth of the fault cause the formation of thrusts or thrusts under the mountain range [4] . An additional 10 ° clockwise rotation was detected in a block located at the northeast tip of the Clarence Fault [2] . The fault was named after the , which flows along the fault line in its north-eastern part.
Break Avatere
Main article:
The Avatere fault consists of two main segments: the Molesworth in the southwest and the East section in the northeast. The calculated slip velocity in the Molesworth segment is 4.4 mm / year [5] . The fault was named after the , whose valley follows a fault for some of its length.
Weirau Rift
Main article:
Wairau fault is sometimes regarded as a direct continuation of the Alpine fault. It can be called the Alps-Waira Fault. It was named after , which flows along a fault along its length. The calculated slip velocity in the fault is 3.5 mm / year [6] .
Seismicity
All components of the Marlborough fault system are seismically active. Since the founding of a European settlement in New Zealand, earthquakes have occurred in the Hoep and Avatere faults, in the small Poulter fault. The study of geomorphology and research have revealed many earthquakes that occurred in the Holocene in many places of the Marlborough fault system [1] [4] [5] [6] . Hope, which has the highest sliding speed, is characterized by the shortest earthquake repetition interval.
Notes
- ↑ 1 2 3 Langridge, R .; Campbell, J., Hill, N., Pere, V., Pope, J., Pettinga, J., Estrada, B., & Berryman, C. & Pope's Future at Greenburn Stream, South Island, New Zealand (eng .) // Annals of Geophysics: journal. - 2003. - Vol. 46 , no. 5
- 2 1 2 Roberts, AP , Fect System, New Zealand (Eng.) // Geophysical Research Letters : journal. - 1995. - Vol. 22 , no. 3 - P. 187-190 . - DOI : 10.1029 / 94GL02582 . - .
- ↑ Musgrave, the RJ The Early to Middle Miocene Pacific-Australia plate boundary in the New Zealand: an alternative transcurrent-fault occurred system // Evolution and Dynamics of the the Australian plate : [ eng ] / Hillis RR & Muller RD. - Geological Society of America. - Vol. 22. - P. 333–341. - ISBN 978-0-8137-2372-3 .
- ↑ 1 2 Nicol, A .; Claire Fault, New Zealand (Eng.) // Journal of Structural Geology : journal. - 2002. - Vol. 24 , no. 9 - P. 1521-1535 . - DOI : 10.1016 / S0191-8141 (01) 00141-9 . - .
- ↑ 1 2 Mason, DPM; Quarter fluvial terrace formation at Saxton River, Awatere fault, New Zealand (Eng.) // Geological Society of America Bulletin : journal. - 2006. - Vol. 118 , no. 11–12 . P. 1431-1446 . - DOI : 10.1130 / B25961.1 .
- ↑ 1 2 Zachariasen, J .; Berryman, K., Langridge, R., Prentice, C., Rymer, M., Striling, M. & Villamor . Geophysics: journal. - 2006. - Vol. 49 , no. 1 . - P. 159-174 . (inaccessible link)