(1620) Geographer ( dr. Greek Γεωγράφος ) is a small near-Earth asteroid from the Apollon group, which belongs to the light spectral class S. The asteroid was discovered on September 14, 1951 by American astronomers Rudolph Minkowski and at the Palomar Observatory and is called the Greek word " geographer " in honor of members of the National Geographic Society [1] .
- Orbit of asteroid geographer and his position in the solar system


| (1620) Geographer | |
|---|---|
| Asteroid | |
 Three-dimensional model of an asteroid (1620) Geographer | |
| Opening | |
| Discoverer | R. Minkovsky , AG Wilson |
| Place of discovery | Palomar |
| Discovery date | September 14, 1951 |
| Eponym | NGS |
| Alternative notation | 1951 RA ; 1983 CY 3 |
| Category | NEA ( Apollo ) |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| Age of September 30, 2012 JD 2456200.5 | |
| Eccentricity ( e ) | 0.3355951 |
| Semimajor axis ( a ) | 186.322 million km (1,2454865 AU ) |
| Perihelion ( q ) | 123.793 million km (0.8275073 AU) |
| Aphelion ( Q ) | 248.851 million km (1.6634657 AU) |
| Circulation Period ( P ) | 507.7 days (1.39 g. ) |
| Average orbital speed | 25.919 km / s |
| Inclination ( i ) | 13.33647 ° |
| Longitude node (Ω) | 337.24487 ° |
| Perihelion Argument (ω) | 276.81443 ° |
| Median Anomaly ( M ) | 49.62810 ° |
| physical characteristics | |
| Diameter | 5.0 x 2.0 x 2.1 km |
| Weight | 2.6⋅10 13 kg |
| Density | 2,000 g / cm³ |
| Acceleration of free fall on the surface | 0,0008 m / s² |
| 2nd space speed | 0.0015 km / s |
| Rotation period | 5.22204 h |
| Spectral class | S |
| Apparent magnitude | 16.84 m (current) |
| Absolute magnitude | 16.6 m |
| Albedo | 0.3258 |
| Average surface temperature | 249 K (−24 ° C ) |
| Current distance from the sun | 1,244 a. e. |
| Current distance from earth | 0.408 a. e. |
(1620) The geographer was supposed to be studied by Clementine's spacecraft , but due to engine malfunctions, the probe completed its mission before it managed to get close to the asteroid.
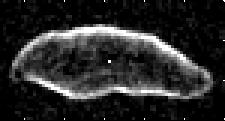
The orbit of this asteroid is characterized by a high eccentricity value (about 0.336), because of which it crosses the orbits of two planets at once: Earth and Mars . In 1994, at the time of the closest approach of the asteroid to the Earth (over 5 million km) over the past two centuries, radar studies of this body were carried out, during which the geographer was able to determine the size of the asteroid (1620) with high accuracy and obtain a series of its images. It turned out that the asteroid has the most elongated shape among all the known bodies of the solar system.
See also
- List of asteroids ( 1601-1700 )
- Classifications of Minor Planets
- List of asteroids crossing the Earth’s orbit
- List of asteroids crossing the orbit of Mars
Notes
- ↑ Schmadel, Lutz D. Dictionary of Minor Planet Names . - Fifth Revised and Enlarged Edition. - B. , Heidelberg, N. Y .: Springer, 2003 .-- P. 128. - ISBN 3-540-00238-3 .

