Potassium chlorate ( bertolet salt [1] , potassium chloride ) is potassium salt of chloric acid .
| Potassium chlorate | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
 | |
| Are common | |
| Systematic name | Potassium chlorate |
| Traditional names | Bertoletov salt |
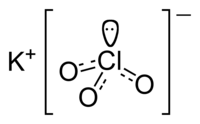
| Chem. formula | KClO 3 |
| Physical properties | |
| condition | Colorless crystals |
| Molar mass | 122.55 g / mol |
| Density | 2.32 g / cm³ |
| Thermal properties | |
| T. melt. | 356 ° C |
| T. | ~ 400 |
| Education enthalpy | -391,204 kJ / mol |
| Chemical properties | |
| Water solubility at 0 ° C | 3.25 g / 100 ml |
| Solubility in water at 20 ° C | 7.3 g / 100 ml |
| Solubility in water at 100 ° C | 56.2 g / 100 ml |
| Solubility in water at 104.2 ° C | 61.5 g / 100 ml |
| Classification | |
| Reg. CAS number | [3811-04-9] |
| Pubchem | |
| Reg. EINECS number | |
| SMILES | |
| Inchi | |
| RTECS | |
| UN number | |
| Chemspider | |
Content
History
First obtained by Claude Berthollet (hence the name Bertoletov or Berthollet salt) in 1786 by passing chlorine through a hot concentrated solution of potassium hydroxide :
Getting
Industrial production of chlorates in general (and potassium chlorate in particular) is based on the disproportionation reaction of hypochlorites , in turn, produced by the interaction of chlorine with alkali solutions:
Technological design of the process can be different: since the most large-scale product is calcium hypochlorite (part of the bleach), the most common process is to conduct an exchange reaction between calcium chlorate (obtained from calcium hypochlorite when heated) and potassium chloride, which, by virtue of low solubility, crystallizes from the mother liquor.
Potassium chlorate is also produced using a modified Bertholl method with electrolyzer- free potassium chloride, chlorine formed during electrolysis reacts in situ (at the moment of isolation, "in situ") with potassium hydroxide to form potassium hypochlorite, which further disproportionates to potassium chlorate and initial potassium chloride . When using graphite anodes, a more convenient method is the electrolysis of sodium chloride to produce sodium chlorate and exchange reaction with potassium chloride. This allows you to clear from the anode sludge solution of sodium chlorate, which has a much greater solubility than potassium chlorate, and, thus, easier to filter.
Chemical Properties
- At a temperature of ~ 400 ° C decomposes with the release of oxygen with the intermediate formation of potassium perchlorate :
- In the presence of catalysts ( MnO 2 , Fe 2 O 3 , CuO , etc.), the decomposition temperature significantly decreases (up to ~ 200 ° C).
- Reacts with ammonium sulfate in a water-alcohol solution with the formation of ammonium chlorate :
Application
Explosives
Mixtures of potassium chlorate with reducing agents ( phosphorus , sulfur , aluminum, organic compounds ) are explosive and sensitive to friction and shocks, sensitivity increases in the presence of bromates and ammonium salts.
Due to the high sensitivity of the compounds with bertolet salt, they are practically not used for the production of industrial and military explosives.
It is sometimes used in pyrotechnics as a source of chlorine for color-flame compositions, it is included in the composition of the combustible substance of a match head, and extremely rarely as initiating explosives (chlorate powder - sais, detonating cord, torsional composition of hand-grenades of Wehrmacht).
In medicine
Potassium chlorate solutions have been used for some time as a weak antiseptic , external medicine for gargling.
To get oxygen
At the beginning of the 20th century it was used for the laboratory production of oxygen, but due to the low availability, it was no longer used.
For chlorine dioxide
The reduction reaction of potassium chlorate with oxalic acid by adding sulfuric acid is used to obtain chlorine dioxide in the laboratory:
Potassium chlorate can react with oxalic acid without the presence of sulfuric acid, but this reaction is not used for the preparative production of chlorine dioxide:
Toxicity
Toxic. The lethal dose of potassium chlorate is 1 g / kg [2] .
Notes
- ↑ Bertoletov salt // Brockhaus and Efron Encyclopedic Dictionary : 86 t. (82 t. And 4 add.). - SPb. , 1890-1907.
- ↑ New guide chemist and technologist. Radioactive substances. Harmful substances. Hygienic standards / Redkol .: Moskvin A.V. and others. - SPb. : ANO NPO Professional, 2004. - 1142 p.
Literature
- Vukolov, S.P. , Mendeleev, D.I. ,. Chloric salts // Brockhaus and Efron Encyclopedic Dictionary : 86 tons (82 tons and 4 extra). - SPb. , 1890-1907.