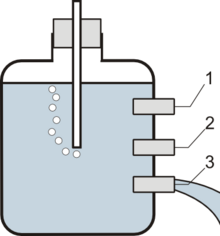
Mariotte siphon ( siphon of Mariotte [1] ) is a device that allows to achieve a uniform flow of a liquid stream due to constant pressure. It was invented by the French physicist of the 17th century Edmie Marriott (1620-1644).
Principle of Operation
The Mariotte siphon is a hermetically sealed vessel, into the cover of which a tube is opened that is open at both ends, immersed in liquid at one end and communicating with the other at the other.
Initially, when all the valves and the atmosphere-related opening in the tube are closed, the liquid level in the tube coincides with the liquid level in the vessel. If the vessel is not completely filled with liquid, there will be a certain amount of air above its surface, and pressure at the bottom of the tube is calculated by the formula:
- where:
- - fluid density ;
- - acceleration of gravity ;
- - the distance between the surface of the liquid and the lower part of the tube;
- - pressure in space above water ( atmospheric pressure ).
If you open valve 3, then the tube, displacing the liquid in it, will fill the air, and the pressure above the surface will become equal . At the end of the tube, atmospheric pressure . The liquid from the hole will start to flow out only under the pressure of the liquid column between valves 2 and 3 (in the figure), which will remain constant all the time, while the end of the tube remains immersed in the liquid. Air will flow through the tube to the top of the vessel.
The fluid flow rate can be determined using the Torricelli formula [2] :
- where - the distance between the lower end of the tube and the valve (or between valves 2 and 3 in the figure).
If, with the valve 3 open, open valve 2 located at the lower end of the tube, liquid will not flow out of it due to equal pressure on both sides of the valve. If valve 1 is opened with valve 3 open, liquid will also not flow out of it - instead, air will enter the vessel through valve 1, and pressure at the level of valve 3 and the flow rate of the jet will increase from it.
Application
The main property of a Marriott vessel is that it allows you to adjust the fluid flow rate . This is used in continuous ink supply systems (CISS) [3] , for dosing liquids in laboratory conditions [4] , in fuel tanks for fuel oil burners of the evaporative type (in small boiler rooms).
See also
- Hydrostatics
- Marriott, Edm
- Hydrostatic pressure
Notes
- ↑ Science Network >> Continuum Mechanics
- ↑ Kosmodemyansky A. A. “The course of theoretical mechanics. Part 2"
- ↑ CISS (Continuous Ink Supply Systems) for inkjet printers Epson, Canon, HP, CISS RDM | CISS RDM, CISS IST | CISS IST | CISS Ink-System, CISS Chernil.net
- ↑ Chemical catalog >> Laboratory workshop on the technology of basic organic synthesis page 68