Tjavzino ( Swede. Teusina , Fin. Täyssinä ) - a disappeared village located in the XIV - XVI centuries in the Ivangorodsky Suburbs of the Shelonsky Pyatina on the River Narva , now in the territory of Ivangorod .
| Disappeared village | |
| Tyavzino | |
|---|---|
| A country | |
| Region | Leningradskaya |
| Area | Kingisepp |
| Urban settlement | Ivangorod |
| History and Geography | |
| Timezone | UTC + 3 |
It was first mentioned in the Census Book of Shelonsky Pyatina of 1498 , as the village of Tyavzino in the Ivangorodsky Okologorodye - 3 obzhi [1] (5 ½ obezh [2] ).
Then, as the village of Täysina by - 2 lodge in the Swedish scribe books of 1618 - 1623 [3] .
"Ivan has a city near the village posad for the Ivano-Gorod residents.
D. Tyavzino: dv. Vasco Izheryanin, his son Ignat, dv. Grichno Ostashov, dv. Yakhno Fedkov, his son Senka, dv. Fedko Belaya [...], dv. Isak da Michal Bragin, dv. Zahar Fomin, dv. Filya Fomin, arable land 12 baskets, hay 100 kopen, 3 livestock. "
In 1581, during the Livonian War , Tyavzino was occupied by Swedish troops; in 1590 , at the beginning of the Russian-Swedish war (1590-1595) , - returned to Russia.
On January 20, 1593, a two-year truce was signed in the village of Tyavzino between Russia and Sweden , and on May 18, 1595, the Tyavzinsky peace treaty ("eternal peace").
Academician P.I. Köppen assumed that the village of Tyavzino was located on the site of the modern village of Izvoz (Teesuu, Tiesuu, Tiensuun) by the river Luga , however, in the scribe books of 1571 , in the Yamsky Okrugorodgorod this village is referred to as Vzvoz, and in Ivangorodsky - Tyavzino village (2 courtyards, 5 ½ trees) [4] .
“For Mikhail, for Dmitriev’s son Tatyanin.
[...]
In the village of Tyavzin, the lodge was empty, and that lodge was for a pentathlete after Istom for Maximov’s son Gulidov, and Istoma didn’t, and that lodge was assigned to the tsar of the sovereign Grand Duke, arable land was in the fourth quarter, and two in the same hay 6 kopen, no forest.
[...]
In the Shelonsky Pyatina in the Yvanegorodsky okrugorody for Fedor, for the son of Zakharyin Grigoryev, there are 3 burns in the villages in Tyavzin, about half to 3 are empty, half of the lives are half-fed, Fedor himself lives in arable land, 4 quarters, 5 kopens of hay, and sowing and cutting were half-dead same.
In the Shelonsky pyatiny in the Yvanegorodsky okrugorody for Nechay, the son of Morozov was behind Nechayev, and Nechay did not become a fad in the summer of 7080, his son Lark remained. In the villages in Tyavzin on Nerovo, half-2 are obzhi, the obzhi is empty, and on the living half-obzhi: dv. his son Lark, arable land in the field of 2 quarters, and in two for the same, hay 3 heaps, the sowing and obstruction on the empty land was the same; and the lands catch all kinds of seine fish in the rivers in Nerovo, but there is no forest. ”
Seltso Tyavzino is also mentioned in the death book of 1572 (5 with a third obzhi) [5] .
“Ivanyagorod near the village posad and village for the Ivano-Gorod residents.
The village of Tyavzino on the river on Narova, two plows without a third and a third obzhi, from it three rubles from Moscow are in arrears, five altyns from the arrears. And then, according to the sovereign’s letter, Seltso was handed over to Falki Grigoryev’s son Zakharyev, and to him from that village of davat, and service to him from those servants from Yerevan served, dues and duties were taken. Yes, I will accept 4 rubles 23 altyns and a half-2 de., For bread 3 altyns and a half-4 de., Writing diyachi 2 de., For city affairs 8 altyns and half-6 de., For clerks 2 altyns without money, for help 8 altyn 5 de. "
Later, Tyavzino was marked on the map of the St. Petersburg province of J. F. Schmitt in 1770 at some distance from the Narva River, under the name Tevziko [6] .
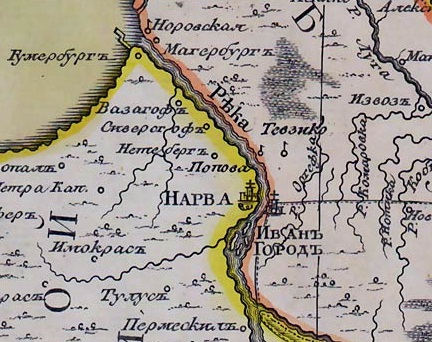
Tyavzino (Tevziko) on the map of 1770.
Then, in these places appeared: Novoivanovskaya Manor (Lilienbach), brick factory and Sloboda Brick Factory (Telliskivi) [7] .
Currently, this territory is part of Ivangorod.
Notes
- ↑ Novgorod scribe books. t. IV. Census obrochnye books Shelonsky pyatiny. 1498, 1539, 1552-1553, St. Petersburg, 1886, p. 230
- ↑ Andriyashev A. M. Materials on the historical geography of Novgorod land. Shelonskaya pyatina according to the scribe books of 1498-1576 I. Lists of villages. Typography of G. Lissner and D., 1912, p. 446 Archived December 3, 2013.
- ↑ Andriyashev A. M. Materials on the historical geography of Novgorod land. Shelonskaya pyatina according to the scribe books of 1498-1576 I. Lists of villages. Typography of G. Lissner and D., 1912, p. 446, 456 Archived December 3, 2013.
- ↑ A fragment is cited from the publication: “Novgorod scribe books published by the Archaeographic Commission. T.V. Editor Epiphany S.K. St. Petersburg. 1905. "
- ↑ A fragment is cited from the publication: “Scribe books of Novgorod land. T.6. Compiled by K.V. Baranov. M.2009. ”
- ↑ Map of the St. Petersburg province containing Ingermanland part of the Novgorod and Vyborg province sochi. J.F. Schmitt 1770.
- ↑ O-35-21-Cd
