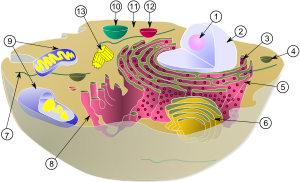
Vacuole ( lat. Vacuus - empty) - a space in the central part of the cell filled with cell juice; single-membrane organelle contained in some eukaryotic cells .
There are digestive and contractile (pulsating) vacuoles that regulate the osmotic pressure and are used to excrete decay products from the body.
Content
Vacuole formation
Vacuoles develop from membrane vesicles - provacuoles . Provacuoles are derivatives of the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi complex , they merge and form vacuoles. Vacuoles and their contents are considered as a compartment isolated from the cytoplasm .
Building
Most mature cells are characterized by a central vacuole. Vacuoles are especially noticeable in many mature plant cells, as they make up more than half the volume of the cell, while they can merge into one. At the same time, the vacuole is so large that it occupies 75 - 90% of the cell volume, so that the protoplast (the living contents of the cell) is located in the form of a very thin wall layer lining the cell membrane.
Vacuoles are found in almost all plant cells. They are cavities in the cell, usually filled with watery contents - cell juice. Cellular juice is, as a rule, an aqueous solution of various substances that are the products of the vital activity of protoplast. The main component is water. Numerous compounds are accumulated in it - mineral or organic. The reaction of cell juice is usually slightly acidic or neutral, less often alkaline (pH 3-5). The substances that make up the cell juice are diverse - these are inorganic substances ( nitrates , phosphates , chlorides , etc.), carbohydrates (sugars and polysaccharides), proteins, organic acids and their salts, alkaloids, glycosides, pigments, tannins, volatile and other water soluble organic compounds.
From the cytoplasm, the cell sap is limited by a selectively permeable vacuolar membrane - the tonoplast (! Not to be confused with the chloroplast tonoplast) (lat. Tonus - voltage; Greek plateau - formed), which performs a barrier and transport function.
Functions
Vacuoles in plant cells form the internal aquatic environment, with their help, water-salt exchange is carried out. They participate in the active transport and accumulation of certain ions in vacuoles. Another important role of vacuoles is to maintain the turgor pressure of the intracellular fluid in the cell. In addition, vacuoles accumulate reserve substances and participate in the “burial” of garbage (end products of metabolism). Sometimes vacuoles destroy toxic or unnecessary substances in the cell. This is usually done with special small vacuoles containing the appropriate enzymes. Such vacuoles are called lysosomal.
Literature
- Kuzevanov V. Ya. , Katkov B. B., R.K. Salyaev General principles for the isolation of vacuoles and vacuolar membranes // Structure and functions of biological plant membranes / Ed. Salyaeva R.K. , Voinikova V.K. - Novosibirsk: Nauka , 1985. - P. 93-107. [one]
- Bilich G.L., Kryzhanovsky V.A. Biology. Full course: In 4 vols. - 5th edition, supplemented and revised. - M.: Onyx Publishing House, 2009. - T. 1. - 864 p. - ISBN 978-5-488-02311-6
- Vasiliev A.E., Voronin N.S., Elenevsky A.G. Serebryakova T.I., Shorina N.I. Botany. Morphology and anatomy of plants. 2nd edition, revised. MOSCOW "EDUCATION" 1988 year. - 480 p. ISBN 5-09-000652-0
- vacuole : Wikimedia Commons thematic media files