Intervertebral hernia (herniated disc) is a protrusion of the nucleus of the intervertebral disc into the spinal canal as a result of the integrity of the annulus.
| Intervertebral hernia | |
|---|---|
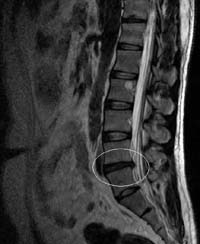 MRI is an image of an intervertebral hernia in the L4 — L5 segment. | |
| ICD-10 | M 51.2 |
| ICD-9 | 722.0 - 722.2 |
| OMIM | 603932 |
| DiseasesDB | 6861 |
| MedlinePlus | 000442 |
| eMedicine | orthoped / 138 radio / 219 |
| Mesh | D007405 |

The most common hernias of the intervertebral discs of the lumbar - sacral spine (150 cases per 100,000 population per year), hernias in the cervical spine are much less common, the rarest of them are the most rare - in the thoracic region .
Hernias relatively rarely require surgery, however, more than 200 thousand are performed annually in the United States , and 20 thousand in Germany. In 48% of cases, hernias are localized at the L5-S1 level of the lumbosacral region, in 46% of cases - at the L4-L5 level, the remaining 6% - at other levels or at several levels of the lumbosacral.
Reasons to
The provoking factors of disc degeneration and further herniation are not fully understood. Obviously, this process is due to multifactor etiology. Among the many causes of genetic, hereditary factor is of paramount importance. Genetic influence is the most important factor in the early onset of disk degeneration.
However, not only genetic endogenous factors, but also exogenous influences determine the nature and rate of degenerative changes in the disk. Of particular interest are biomechanical aspects leading to the introduction of a part of the disk into the spinal canal. Physical activity in the form of weight lifting, torsion loads, that is, weight lifting in combination with twisting, or "golfing", driving a car is defined as the main risk factors for disk degeneration and subsequent hernia formation.
Clinical manifestations
Herniated discs mostly occur in people of working age. They are often accompanied by neurological disorders caused by compression of the spinal root. The formation of a herniated disc is usually preceded by episodes of lumbar pain, often associated with physical exertion. During neurological examination, one can presumably orient in relation to the localization of the compressing process along the length and diameter of the spinal canal, assessing the well-known topic of neurological disorders. The following is a clinical topographic orientation during compression of the roots of the cervical and lumbar spine:
- L4 spine syndrome (L3-L4 disc) - irradiation of pain in the anterior inner thigh, lower leg and inner ankle, hypesthesia on the anterior surface of the thigh, weakness of the quadriceps muscle, reduction or loss of the knee jerk;
- L5 spine syndrome (L4-L5 disc) - irradiation of pain from the upper gluteal region to the outer parts of the thigh and lower leg, sometimes spreading to the rear of the foot, to I-III fingers, hypesthesia in the same zone; weakness of the peroneal muscle group, hypotrophy possible, weakness of the extensor of the first toe (spurling symptom);
- S1 spine syndrome (L5-S1 disc) - irradiation of pain from the middle gluteal region to the external or posterior thigh, lower leg, heel with transition to the outer edge of the foot and IV — V toes, hypoesthesia in the external posterior of the lower leg and external foot; hypotrophy of the gluteus maximus and gastrocnemius muscles, calf muscle weakness, reduction or absence of Achilles and plantar reflexes. The following syndromes of compression of the roots of the cervical spinal nerves, which are usually compressed in the intervertebral foramen above the vertebra of the same name, are noted.
Compression syndrome root C4 manifests pain in the shoulder girdle, may be accompanied by amyotrophy trapezius, supraspinatus, and even the pectoralis major muscle. C5 root compression syndrome - projection pain and sensory disorders are localized in the deltoid muscle zone, may be accompanied with its weakness and hypotrophy, and a lowering of the scapular reflex.
C6 root compression syndrome - projection pain and sensitive disorders are localized in a strip on the outer edge of the arm, up to the first finger of the hand. The strength of muscles flexing the forearm decreases, the reflex from the biceps muscle is disturbed.
C7 root compression syndrome - projection pain and sensitive disorders are localized in a strip on the back of the hand, especially in the three middle fingers. Tricipital reflex is usually reduced or absent. There may be vegetative-trophic disorders in the hand.
C8 root compression syndrome is very rarely diagnosed, mainly in post-traumatic osteochondrosis with the formation of a hernia or “osteophyte” in the intervertebral orifice of C7 — Th1. The projection of pain and sensory disorders corresponds to the ulnar margin of the arm, including the fourth and fifth fingers. Can be reduced carporadial reflex.
Survey
The method of choice for diagnosing herniated intervertebral discs is currently magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or multispiral computed tomography (MSCT). If necessary, non-invasive MR myelography or invasive CT myelography is performed.
Treatment
In most cases, the symptoms of intervertebral hernia subside within six weeks after their appearance, remission occurs and surgery is not required. A study by Vroomen et al. (2002) showed that in 73% of patients, a marked improvement occurred without surgical intervention within 12 weeks after the onset of symptoms.
However, the fact of relief, in the presence of a hernia, does not exclude the fact of the formation of consequences of the type of radicular syndrome (injury and inflammation of the nerve roots of the spinal cord)
Surgical treatment of intervertebral hernia should be considered only as a last resort and only after unsuccessful attempts at conservative treatment, which could not control pain syndrome.
The main method of conservative treatment of intervertebral hernia is systemic anti-inflammatory therapy using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs ( NSAIDs ). In some cases, local corticosteroid administration was effective.
In addition to the main treatment is also used physical therapy. It is also recommended to sleep on a hard surface or on the floor. [one]
Traction therapy shows good results. At the same time, under the action of a vacuum created inside the disk, the pulpal nucleus is drawn inward and the size of the hernia decreases.
However, there are opinions of doctors that the hernia cannot be drawn in any way. This opinion is based on the fact that the hernia itself (it’s the pulpal nucleus) cannot be drawn in with any external influence (except for surgical removal), but can only “dry out” - dehydrate, become stiff and shrink like a foreign body over time. . In this case, it is believed that the pain is caused by muscles that are disturbed due to changes in the height of the intervertebral disc or other muscle disorders. Common in this approach with the traditional opinion is to limit the axial load on the spine and strengthen the muscular framework of the spine. Private is the method of anesthesia - manual techniques aimed at stretching spastic muscles (acupressure (Tibetan) massage), effects on the muscles themselves in order to relax them, and many others. It should also be noted that some experts believe that muscle disorders can contribute to the development of a hernia (spasm of the back muscles, causing constant pressure on the intervertebral disk) along with lifting weights.
Indications for the surgical treatment of herniated disc
There are three disease states in the surgical incision section: 1. No indications; 2. Relative indications; 3. Absolute indications.
- Indications in surgical intervention are absent if the pain syndrome is susceptible to conservative treatment.
- Relative indications are available in case of ineffectiveness of conservative treatment, or in order to achieve recovery in the shortest possible time.
- Absolute indications are available for critical disorders associated with compression of the roots and nerves, causing incontinence of urine and feces, impaired potency and others. A certain role is played by the time from the appearance of the clamping itself to the operation, in connection with possible violations of the functionality of the clamped nerve in the future.
This separation is partly conditional, as each case is individual and requires an individual approach to treatment.
Types of surgical treatment
Until recently, the removal of a herniated disc by a laminectomy of the appropriate level was used. With the advent of the surgical microscope, it became possible to reduce the trauma of the operative access and to remove the disc herniation through a smaller trephination window, this is how the intralaminar microsurgical disc herniation was removed, which is still used today, being the “gold standard” for the surgical treatment of herniated intervertebral discs. Further development of the methods follows the path of reducing surgical trauma, and this development is inseparably linked with the development of medical technology and optics. Currently, microsurgical removal is widely used, and there are many options for the endoscopic removal of the hernial protrusion.
Transfaceous removal of intervertebral hernia of the lumbar spine using tubular retractors and percutaneous semi-smooth transpedicular stabilization on the PEEK-rods
Modern minimally invasive method of neurosurgical treatment of intervertebral hernia. The operation removes the hernia and stabilizes the operated segment with a system consisting of four titanium screws and two PEEK (PIK) rods. The operation uses a tubular retractor (retractor), which allows you to perform the operation through a small incision without damaging the back muscles (like endoscopic operations).
At the first stage of the operation, the area in which the operation will be performed is marked with intraoperative x-rays. Then a small incision is made of the skin (about 2 cm long) and the retractor is set. A part of the joint is removed through a retractor using an operating microscope, after which the surgeon can see the hernia, which puts pressure on the nerve root. Then the intervertebral hernia is removed. It should be noted that, in contrast to endoscopic surgery, through the use of a tubular retractor and an operating neurosurgical microscope, a doctor can see a 3D image instead of a 2D image, and also has more freedom in using various surgical instruments. Ultimately, this significantly affects the quality of the operation.
After removal of the intervertebral hernia, percutaneous transpedicular stabilization is performed with the PEEK rods of the middle and posterior support column. All stabilizing implants are installed under the control of an image intensifier (electron-optical converter, X-ray).
As a result of this operation, the mechanical cause - intervertebral hernia is eliminated. The operated segment is reliably strengthened, taking into account the preservation of the biomechanics of the spine. The very next day after surgery, the patient can become more active (get up, sit down, walk). Three days after the operation, the patient can leave the hospital and return to the usual way of life. Then, during the implant implantation period, which lasts for 3-4 months, extreme axial loads on the spine are not recommended (but not prohibited). Special rehabilitation after surgery is not required.
Microsurgical removal of herniated intervertebral disc
Microsurgical removal of a herniated disc ( microdiscectomy ) is an operation that is an effective method of surgical treatment. This method is performed under high magnification using an operating headlamp or using an operating microscope. The main advantage of this method is the ability to remove a herniated intervertebral disk of any density and any location. The paravertebral muscles are separated from the vertebral arches, an economical resection of the arches of the adjacent vertebrae, part of the intervertebral joint, is performed. The large magnification makes it possible to precisely and delicately manipulate in the spinal canal, to remove any possible hernias of intervertebral discs with a minimal probability of damage to the nerve structures of the spinal canal. The operation is performed under general anesthesia in the position of the patient on the abdomen, with a skin incision of 3-4 cm. The risk of postoperative complications is minimal. Modern neurosurgery involves the early activation of the patient the next day. The average length of stay in the hospital is 5-7 days. The patient can begin non-physical work in 7-14 days, and physical work in 2-4 weeks. It is usually recommended to restrain sitting positions for a month. To maintain posture and minimize possible complications, it is recommended to wear a semi-rigid lumbar corset for 1-2 months.
Endoscopic hernia repair
The endoscopic method of surgical treatment of hernias of intervertebral discs is a fairly new direction and, as such, is exposed to a mass of criticism and comparisons. To date, there is an extensive arsenal of endoscopic methods for the treatment of hernias of intervertebral discs. First of all, they should be divided according to the section of the spine on which they are applied.
In the treatment of hernias of intervertebral disks of the cervical spine , three methods are most widely used:
- HD Jho, or antero-lateral endoscopic method;
- PECD (percutaneous endoscopic cervical discectomy) - anterior cervical endoscopic disc ectomy ;
- posterior endoscopic discectomy.
In the treatment of hernias of intervertebral discs of the thoracic spine , the anterior or thoracoscopic method is used.
For the treatment of hernias of intervertebral discs of the lumbosacral spine , a group of lateral posterior endoscopic approaches is used.
The use of the endoscope can significantly reduce the operating injury, but has more limited conditions of use (size, location of the herniated disk). The size of the incision and the total access are reduced to 1–2.5 cm, the risk of postoperative complications is less. The patient can walk on the day of surgery or the next day, is discharged from the hospital for 3-4 days after surgery. This type of intervention provides faster rehabilitation and resumption of previous work activities.
ENDOSPINE by Dr.Destandau
Endoscopic surgery
Notes
- ↑ Is it good to sleep on the floor - the opinion of doctors (December 14, 2018). The appeal date is December 15, 2018.
Literature
- Biktimirov R. G., Kedrov A. V., Kiselev AM, Kachkov I. A. Spine Osteochondrosis (rus.) // Almanac of Clinical Medicine: scientific article. - Moscow Regional Research Clinical Institute. Mf Vladimirsky, 2004. - № 7 . - pp . 328–337 . - ISSN 2072-0505 .
- Krotenkov P.V., Kiselev AM, Sherman L.A. MRI tomography in the diagnosis and treatment of hernias of the thoracic intervertebral disks. (Rus.) // Herald of radiology and radiology: a scientific article. - Beam Diagnostics, 2007. - № 4 . - pp . 53—57 . - ISSN 0042-4676 .
- Shchurova Ye. N. Investigation of stabilometric parameters before and after the removal of interstitial hernia in the lumbar spine. (Rus.) // Neurosurgery: scientific article. - Non-profit partnership in organizing and assisting in the publication of the journal “Neurosurgery”. - № 1 . - pp . 23-29 . - ISSN 1683-3295 .
- Bubnovsky S. M. Hernia of the spine - not a sentence! - M .: Eksmo, 2010. - ISBN 978-5-699-41232-7 .
- Kaplan L. Hernia of the lumbar disc . Per. from English ND Firsova (2017).
- Gallyamova A.F. Diagnosis and features of clinical manifestations of dystrophic diseases of the spine among refinery workers. (Rus.) // Neurosurgery: scientific article. - Ufa: Non-profit partnership in organizing and assisting in the publication of the journal Neurosurgery, 1999.