The cervix uteri ( lat. Cervix uteri ) is the lower segment of the uterus of a woman . In the center is the cervical canal, one end of which opens into the uterine cavity, and the other into the vagina . On average, the length of the cervix is 3-4 cm, and the cervical canal is closed.
| Cervix | |
|---|---|
| lat cervix uteri | |
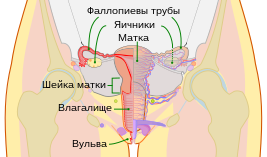 Schematic representation of female reproductive organs. | |
| Blood supply | vaginal, uterine artery |
| Precursor | muller duct |
| Catalogs | |
Anatomy
At the cervix, the vaginal part is distinguished - which can be examined with a mirror. The cervix connects to the vagina through the vaginal arches . Distinguish between the front arch (short), the rear (deeper) and two side. The cervical canal passes through the cervix, which is blocked by mucus. Mucus is normally not permeable to either germs or sperm. But in the middle of the menstrual cycle, the mucus liquefies and becomes permeable to sperm .
Sperm from the vagina rise along the cervical canal and enter the uterine cavity. During childbirth, the cervix opens (up to 10 cm) so that the baby’s head passes through the cervical canal. To examine the external opening of the cervix (as well as the upper parts of the vagina), a colposcope is used - a special optical device. This diagnostic procedure is necessary to exclude diseases of the cervix, including cancer .
1 - fallopian tube ;
2 - fimbria fallopian tube;
3 - bladder ;
4 - pubic bone ;
5 - G-point and U-point ;
6 - urethra ;
7 - clitoris ;
8 - bulb of the vestibule ;
9 - labia minora ;
10 - large labia ;
11 - ovary ;
12 - sigmoid colon ;
13 - the uterus ;
14 - posterior vaginal fornix ;
15 - the cervix ;
16 - the rectum ;
17 - the vagina ;
18 - anus ;
19 - Bartholin glands
Literature
- Cervix // Brockhaus and Efron Encyclopedic Dictionary : in 86 volumes (82 volumes and 4 additional). - SPb. , 1890-1907.
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 Foundational Model of Anatomy