Cynognathus [1] ( lat. Cynognathus , from other Greek κύνεος γνάθος - canine jaws) is a genus of relatively large predatory cynodonts from the infraorder Procynosuchia , living during the Triassic period ( Anisian - Carnian century) [2] . Fossil remains of cynognates are today found in South Africa, South America, China and Antarctica. Many species are described, but most of them are synonyms of the type species - Cynognathus crateronotus .
| † Cynognath |
|---|

Skull of Cynognathus crateronotus |
|
| No rank : | Bilateral symmetrical |
| Infrastructure : | † Procynosuchia |
|
|
Cynognathus Seeley , 1895 |
|
- † Cynognathus crateronotus
Seeley, 1895 - † Cynognathus seeleyi Broom
|
|
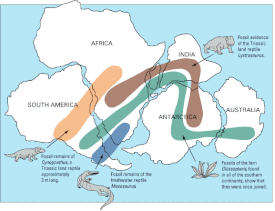 - area of cynognates |
|
Several different names have been given over the years. In addition, Cistecynodon , Cynidiognathus , Cynogomphius , Karoomys , Lycaenognathus , Lycochampsa and Lycognathus were known . There are different opinions as to whether all residues belong to the same species.
Species-level synonyms from Cynognathus crateronotus include Cistecynodon parvus, Cynidiognathus broomi, Cynidiognathus longiceps, Cynidiognathus merenskyi, Cynognathus beeryi, Cynognathus minor, Cynognomathomymi phius berius platyceps, Cynogomymi phymphius berius
The genera Karoomys and Cistecynodon are known only from the remains of young individuals.
The cynognathus was a formidable animal, with an elongated body, more than 2 meters long. He had a large head, 30 cm long, with wide jaws and sharp teeth. His hind limbs were placed directly under the body, and the front legs are slightly apart. This form of double gait is also observed in some primitive mammals living today. The oral cavity, equipped with a system of differentiated teeth, could effectively process food before swallowing. The presence of a secondary palate in the oral cavity proves that the cinnamon was able to breathe and swallow at the same time.
The absence of ribs in the abdomen suggests the presence of a diaphragm (an important muscle for mammalian breathing). Pits and canals on the front surface of the skull indicate the concentration of nerves and blood vessels. In mammals, such structures are associated with vibrissae, which are used as sense organs.
Fossils were found in Karu, in the Puesto Viejo Formation and the Fremouw Formation in South Africa (Lesotho), in Argentina; in Antarctica and in China.
Cynognathus crateronotus was a meter-long predator, and was distributed almost throughout the world. Fossils have been found in South Africa, South America, China and Antarctica.

