Trimebutin is a drug that has an antispasmodic effect.
| Trimebutin | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Chemical compound | |
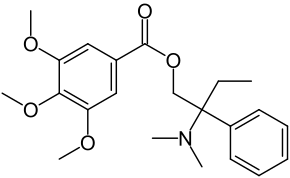
| IUPAC | 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoic acid 2- (dimethylamino) -2-phenylbutyl ether |
| Gross formula | C 22 H 29 NO 5 |
| Cas | |
| PubChem | |
| Drugbank | |
| Classification | |
| Farmakol. Group | antispasmodic |
| ATX | |
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Bioavailable | 4-6% |
| Plasma Protein Binding | around 5% |
| Metabolism | excreted by the liver |
| The half-life. | about 12 hours |
| Excretion | with urine, mainly in the form of metabolites (approximately 70% during the first 24 hours) |
| Dosage Forms | |
| pills | |
| Other names | |
| Trimedat® | |
Content
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Trimebutin, acting on the intestinal enkephaling system, is a regulator of its peristalsis . Having an affinity for the receptors of excitation and suppression, it has a stimulating effect in hypokinetic states of smooth muscles of the intestine and antispasmodic in hyperkinetic. The drug acts throughout the gastrointestinal tract, reduces the pressure of the sphincter of the esophagus , promotes emptying of the stomach and enhances intestinal motility, and also contributes to the response of smooth muscles of the colon in various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract associated with impaired motility.
Pharmacokinetics
After ingestion, it is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, the maximum concentration in blood plasma is reached after 1-2 hours. To a small extent penetrates the hematoplacental barrier .
Indications for use
General
- Motor disorders in functional diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, gastroesophageal reflux disease , dyspeptic disorders in gastroduodenal diseases (abdominal pain, digestive disorders, nausea , vomiting ), irritable bowel syndrome .
- Postoperative paralytic intestinal obstruction , preparation for x-ray and endoscopic examination.
In children
Diseptic disorders associated with impaired motility of the gastrointestinal tract.
Contraindications
General
Hypersensitivity to the components that make up the drug. Children's age up to three years (for this dosage form).
Pregnancy and lactation
- It is not recommended to use the drug in the first trimester of pregnancy .
- It is not recommended to prescribe trimebutin during lactation, due to the lack of reliable clinical data confirming the safety of the drug during this period.
- In experimental studies, no data were found on teratogenicity (increasing the likelihood of malformations) and embryotoxicity of the drug.
Dosage and administration
Inside. Adults and children from 12 years: 100-200 mg 3 times a day. Children 3-5 years: 25 mg 3 times a day. Children 5-12 years: 50 mg 3 times a day.
Side effect
Rarely : skin reactions
Overdose
There are currently no cases of overdose.
Release Form
100 mg tablets, 200 mg. On 10 tablets in a blister strip packaging from a film of polyvinyl chloride and aluminum foil printed varnished. On 1, 2 or 3 blister strip packagings together with the instruction are placed in a pack from a cardboard box.
Interaction
Not described.
Holidays from pharmacies
Over the counter.