Madeira ( port. Madeira - timber) is an archipelago of volcanic origin located in the Atlantic Ocean 680 km west of Morocco and 450 km north of the Canary Islands . On the archipelago is the autonomous region of Portugal - Madeira . The archipelago consists of a central island, Madeira , the island of Porto Santo , a group of three uninhabited protected islands of Ilyas Desertas , as well as several small islands off the coast of Madeira and Porto Santo. The small Selvaženš archipelago (3.6 km²), located 230 km to the south, is part of the autonomous region, but is usually not the archipelago. The area of the archipelago is 797 km², the population is 267,785 [1] people (2011).
| Madeira Archipelago | |
|---|---|
| port. arquipélago da Madeira | |
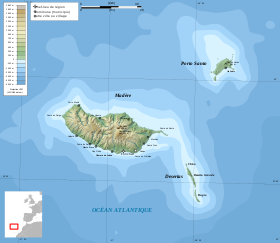 Islands of the archipelago, without the islands of Selvaženš | |
| Specifications | |
| Number of islands | 25 |
| Largest island | Madeira |
| total area | 797 km² |
| Highest point | 1862 m |
| Population | 267 785 people (2011) |
| Population density | 335.99 people / km² |
| Location | |
| Water area | Atlantic Ocean |
| A country |
|
| Region | Madeira |
Content
Madeira Island
Madeira Island is the largest island of the archipelago with an area of 740.7 km² (more than 90% of the total area of the archipelago), it is 57 km long and 22 km wide at its widest point and has a total coast length of 150 km. The longest axis is located between east and west, along which lies a chain of mountains with a height of up to 1220 meters, from which many deep gorges begin, diverging towards the coast. The most famous cliff of the island of Kabu-Zhiran is one of the highest in Europe . The highest point of the island is Piku Ruyu , 1862 meters above sea level. [2]
In the south there are very few relatives of Monteverde , the subtropical forests that used to cover the entire island (the landed Portuguese burned them to farming ) and gave it a name (Madeira in Portuguese means wood). However, in the north, many native forests remained in the valleys , in particular the forests on the northern slopes of Madeira are recognized as UNESCO World Heritage Sites .
Islands of the archipelago
- Madeira (740.7 km²)
- Agostinho (east)
- Sao Lawrence (in the east)
- Moths (in the northwest)
- Porto Santo (42.5 km²)
- Baixu y da Cal (in the south)
- Ferru (in the southwest)
- Senurash (north)
- Fora (North of Senurash)
- Sima (in the east)
- Ilyash-Desertash (14.2 km²)
- Ilya Desert Grandi
- Bujiu
- Shan
Administrative Division
The autonomous region of Madeira consists of 10 municipalities:
- Santa Cruz;
- Kaleta;
- Camara de Lobos;
- Funchal
- Santana
- San Vicente;
- Mashiku;
- Ponta do Sol;
- Porto Manish;
- Ribeira Brava;
- Porto Santo.
Climate
The geographical position of Madeira Island and the mountainous landscape create a very pleasant climate , which differs slightly from north to south and depending on the island of the archipelago. Madeira has a subtropical - Mediterranean climate ( Köppen Climate Classification : Csb ) [3] , which is heavily influenced by the Gulf Stream , which provides the island with one of the mildest climates in the world. The average annual sea temperature is 20 ° C in winter and 23 ° C in summer. The summer season lasts almost year-round, although during the period from December to April the temperature often drops below 20 ° C.
| Climate of Madeira | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indicator | Jan | Feb | March | Apr | May | June | July | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average maximum, ° C | 19.1 | 19.1 | 19.5 | 19.6 | 20.9 | 22.3 | 24.3 | 25.6 | 25.7 | 24.2 | 22.0 | 20,0 | 21.8 |
| Average temperature, ° C | 16.1 | 16,0 | 16.3 | 16.5 | 17.8 | 19,4 | 21,2 | 22.3 | 22.3 | 20.9 | 18.8 | 17.0 | 18.6 |
| Average minimum ° C | 13.1 | 12.8 | 13.0 | 13,4 | 14.6 | 16.5 | 18.0 | 18.9 | 18.9 | 17.6 | 15.6 | 13.9 | 15,5 |
| Precipitation rate, mm | 10.27 | 8.72 | 6.36 | 3.89 | 1.89 | 1.19 | 0.25 | 0.31 | 3.67 | 7.50 | 10.08 | 9.99 | 64.12 |
| Source: World Meteorological Organization ( UN ) [4] . | |||||||||||||
Geological Origin and Volcanism
Madeira Island is the peak of a large thyroid volcano , rising about 6 km above the bottom of the Atlantic Ocean in the underwater mountain range of the Torah, located on the African plate . The volcano formed on a rift in the oceanic crust . Volcano formation began in the Miocene era more than 5 million years ago and ended in the Pleistocene about 700,000 years ago. [5] This was followed by severe erosion , which formed two large circles in the central part of the island.
Later, volcanic activity resumed, forming new peaks and lava flows on top of the old layers. The most recent volcanic eruptions occurred in the west-central part of the island just 6,500 years ago. [five]
Nature
In Madeira there are three species, endemic to birds: Madeira typhoon , Madeira pigeon and Madeira king .
The island is also very important for breeding other seabirds , including Madeira Butterfly and Pied Atlantic Petrels .
Macaronesia is a place of important natural diversity. Forests on the archipelago are very similar to the forests of the Tertiary period , which covered southern Europe and North Africa millions of years ago.
Madeira's enormous biodiversity is phytogeographically associated with the Mediterranean , Africa , America, and Australia . Interest in plant geography has grown recently due to the discovery of new types of epiphytes with very different development.
Madeira has a lot of endemic species, mostly invertebrates , including the extremely rare Madeira Cabbage , as well as some vertebrates , such as some species of lizards and birds mentioned above. Europe 's largest tarantula lives in deserts on Ilyash-Desertash and reaches the size of a human hand. More than 250 species of land mollusks ( snails and slugs ) live on these islands, some with a very unusual pattern and colors of the shell. Most of them are endemic and endangered (such as the snail of the species Boettgeria obesiuscula ).
Notes
- ↑ Population of Portugal (2011) Instituto Nacional de Estatística
- ↑ MadeiraHelp.com unopened (inaccessible link) . Date of treatment July 30, 2010. Archived July 31, 2010.
- ↑ World Map of Climate Classification of Köppen-Geiger . Date of treatment January 8, 2008. Archived August 24, 2011.
- ↑ Weather information in Funchal . Archived August 24, 2011.
- ↑ 1 2 Madeira : [ eng. ] // Global Volcanism Program . - Smithsonian Institution .

