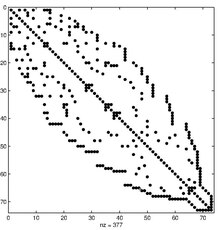
The Cuthill – McKee Algorithm is an algorithm for reducing the width of a tape sparse symmetric matrices . It is named after the developers - Elizabeth Cuthill and James Mackey.
The reverse Cuthill – McKee algorithm ( RCM , reverse Cuthill — McKee ) is the same algorithm with reverse index numbering.
Algorithm
The original symmetric matrix considered as a graph adjacency matrix
. The Cathill – Mackey algorithm renumbers the vertices of the graph so that, as a result of the corresponding permutation of the columns and rows of the original matrix, reduce the width of its ribbon .
The algorithm builds an ordered set of vertices representing the new vertex numbering. For a connected graph, the algorithm is as follows:
- select a peripheral vertex (or a pseudo-peripheral vertex )
for the initial value of the tuple
;
- for
while the condition is satisfied
, perform steps 3-5:
- build an adjacency set
for
where
-
component
, and exclude vertices that are already contained in
, i.e:
;
- sort
ascending degrees of peaks ;
- add
in the result tuple
.
In other words, the algorithm numbers the vertices during the breadth-first search , at which adjacent vertices are dispensed in the order of increasing their degrees .
For a disconnected graph, the algorithm can be applied separately to each connected component [1] .
The temporal computational complexity of the RCM algorithm, provided that sorting by inserts is used for ordering, where
- maximum degree of apex,
- the number of edges of the graph [2] .
Selecting the starting vertex
To get good results, you need to find the peripheral vertex of the graph. . This task is generally quite difficult, therefore, they usually look for a pseudo-peripheral vertex using one of the modifications of the Gibbs heuristic algorithm , etc.
To describe the algorithm, the concept of a root level structure is introduced. For a given vertex level structure with root in will be a split many vertices :
where are the subsets defined as follows:
and
Algorithm for finding a pseudo-peripheral vertex [3] :
- select arbitrary vertex of ;
- build a level structure for the root : ;
- pick the top with the least degree of ;
- build a level structure for the root : ;
- if a then assign and go to step 3;
- vertex is the desired pseudo-peripheral vertex.
Notes
- ↑ George, Liu, 1984 , pp. 65-66.
- ↑ George, Liu, 1984 , p. 68.
- ↑ George, Liu, 1984 , pp. 70-72.
Literature
- E. Cuthill and J. McKee. Reducing the bandwidth of sparse symmetric matrices In Proc. 24th Nat. Conf. ACM , pages 157-172, 1969.
- George A., Liu J. Numerical solution of large sparse systems of equations = Computer Solution of Large Sparse Positive Definite Systems. - M .: Mir, 1984. - 333 p.
Links
- Cuthill-Mackey documentation for Boost C ++ libraries .
- Detailed explanation of the Cuthill-Mackey algorithm .
- A detailed explanation of the Cathill-Mackey algorithm (Russian) (inaccessible link) .
- Python Cuthill-Mackey algorithm implementation (inaccessible link) .