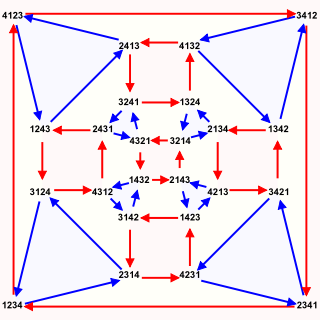

( permutation matrix multiplication table )
The following six matrix positions are available:
 The table is asymmetric with respect to the main diagonal, i.e. the group is not abelian.
The table is asymmetric with respect to the main diagonal, i.e. the group is not abelian.Symmetric group - the group of all permutations of a given set (i.e. bijection ) relative to the operation of the composition .
The symmetric group of the set usually indicated , if then also denoted by . Since for equipotent sets ( ) their permutation groups ( ), therefore, for a finite group of order the group of its permutations is identified with .
The neutral element in the symmetric group is the identity permutation .
Content
- 1 permutation groups
- 2 Properties
- 3 views
- 4 notes
- 5 Literature
Permutation Groups
Although usually the group of permutations (or permutations) is called the symmetric group itself, sometimes, especially in English literature, permutation groups of the set called subgroups of a symmetric group [1] . The degree of the group in this case is called the power .
Each end group isomorphic to some subgroup of the group ( Cayley's theorem ).
Properties
The number of elements of the symmetric group for a finite set is equal to the number of permutations of the elements, that is, the power factorial : . At symmetric group non-commutative.
Symmetric group allows the following task :
- .
We can assume that rearranges and . Maximum order of group elements - Landau function .
Groups solvable when symmetric group is insoluble .
A symmetric group is perfect (that is, the conjugation map is an isomorphism) if and only if its order is different from 2 and 6 ( Hölder's theorem ). When Group has another . By virtue of this and the previous property, for all automorphisms are internal, that is, every automorphism has the form for some .
The number of classes of conjugate elements of a symmetric group equal to the number of partitions [2] . Many transpositions is the generating set . On the other hand, all these transpositions are generated by just two permutations so that the minimum number of generators of a symmetric group is two.
The center of the symmetric group is trivial for . Commutant is an alternating group ; with Is the only nontrivial normal subgroup , but has another normal subgroup - the Klein quadruple group .
Views
Any subgroup permutation groups representable by a group of matrices from , with each permutation there corresponds a permutation matrix (a matrix in which all elements in cells equal to 1, and other elements are equal to zero); e.g. permutation represented by the following matrix :
A subgroup of such a group, composed of matrices with determinant equal to 1, is isomorphic to an alternating group .
There are other representations of symmetric groups, for example, the symmetry group (consisting of rotations and reflections) of the dodecahedron is isomorphic , and the rotation group of the cube is isomorphic .
Notes
- ↑ Aigner M. Combinatorial Theory. M .: Mir, 1982.- 561 p.
- ↑ sequence A000041 in OEIS
Literature
- Vinberg E. B. The course of algebra. - M .: Factorial Press, 2001.
- Kargapolov M. I, Merzlyakov Yu.I. Fundamentals of group theory. - M .: Science, Fizmatlit, 1982.
- Kostrikin A. I. Introduction to Algebra. Part III. The main structure. - M. publishing house = Fizmatlit, 2004.
- Kurosh A.G. Group Theory. - M .: Science, Fizmatlit, 1967.
- Postnikov M.M. Galois Theory. - M .: Fizmatlit, 1963.








