Fly ( born Fly River ) is a river on the island of New Guinea . Most of the river flows through the territory of the Western province of Papua New Guinea (Fly is the second longest river, after Sepik , in this country); only a small part of the river serves as the state border with Indonesia .
| Fly | |
|---|---|
| English Fly river | |
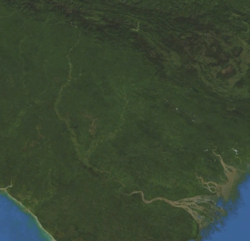 Space image of the river Space image of the river | |
| Characteristic | |
| Length | 1120 km |
| Pool | 76,000 km² |
| Water consumption | 6000 m³ / s |
| Watercourse | |
| Source | |
| • Location | Mountains Star (mountains) |
| • Height | 3000 m |
| • Coordinates | |
| Mouth | Papua |
| • Height | 0 m |
| • Coordinates | |
| Location | |
| Water system | Coral sea |
| A country |
|
| Region | Papua |
| Area | Western province |
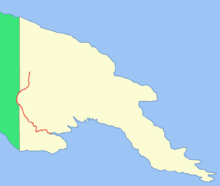

The source of the river is in the Star Mountains at an altitude of about 3,000 m. It flows in a south, and then in a southeast direction, flowing into the Gulf of Papua . The upper reaches of the river are in highlands; in the middle and lower parts, the Fly flows through the vast New Guinean plains . The river is navigable up to the city of Kiunga , which is located about 800 km from the mouth of the river [1] . A large estuary 56 km wide is formed at the mouth. The total area of the delta is 7100 km² with an average depth of 8 m [2] . Due to the fact that a large amount of soil and other sediments carried by the river are washed away into the bay, a large number of islands are located in the estuary, the largest of which are Kivai , Purutu , Wabuda , Aibinio , Mibu and Domori .
The main tributaries of the Fly are the Strickland and Oak Tedi rivers . The total length of the river is about 1120 km, and the basin area is 76,000 km² [3] . Climatic conditions (primarily rainfall) vary greatly throughout the course of the Fly. In the upper reaches of the river, the climate is very humid: up to 10,000 mm of rain falls here, with no rain and drought seasons. In the middle and lower parts, the amount of precipitation depends on monsoons and trade winds , so they are unstable. In general, at least 3500 mm of precipitation falls in this region [3] .
The European captain of the river was the British captain of the Fly, Francis Price Blackwood , who explored the west coast of Papua Bay in 1842 [4] . It was in honor of his ship that the river got its modern name [5] . In 1876, the river was explored by the Italian traveler Luigi Maria d'Albertis , who moved inland New Guinea about 900 km on his ship "Neva" [6] .
See also
- Oceania River List
- Murray (lake)
Notes
- ↑ Papua New Guinea. Dept. of Environment and Conservation, International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources, IUCN Environmental Assessment Service. The Fly River catchment, Papua New Guinea: a regional enviromental assessment. - IUCN, 1995. - P. 1. - 86 p. - ISBN 2831702364 .
- ↑ Papua New Guinea. Dept. of Environment and Conservation, International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources, IUCN Environmental Assessment Service. The Fly River catchment, Papua New Guinea: a regional enviromental assessment. - IUCN, 1995 .-- P. 10 .-- 86 p. - ISBN 2831702364 .
- ↑ 1 2 Papua New Guinea. Dept. of Environment and Conservation, International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources, IUCN Environmental Assessment Service. The Fly River catchment, Papua New Guinea: a regional enviromental assessment. - IUCN, 1995 .-- P. 7 .-- 86 p. - ISBN 2831702364 .
- ↑ Mozley, Ann. Blackwood, Francis Price (1809 - 1854 ) . Australian Dictionary of Biography. Date of treatment January 24, 2010. Archived on April 18, 2012.
- ↑ Fly River . Encyclopædia Britannica. Date of treatment April 2, 2010. Archived April 18, 2012.
- ↑ Lightbody, Mark. Papua New Guinea: a travel survival guide. - 3rd edition. - Lonely Planet, 1985. - P. 172. - ISBN 0-908086-59-8 .
