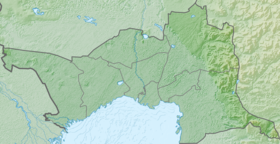
Indre (also Inder Lake ) is a rather large self-landing , drainless, salt lake in the northern part of the Atyrau region of Kazakhstan . It is located in the northern part of the Caspian lowland , 10 km east of the Ural River . The mirror area is about 110 km². The catchment area is 425 km².
| Lake | |
| Inder | |
|---|---|
| kaz. Inder | |
| Morphometry | |
| Dimensions | 13 × 11 km |
| Square | 110 km² |
| Coastline | 40 km |
| Average depth | 0.7 m |
| Hydrology | |
| Type of mineralization | bitter salty |
| Pool | |
| Pool area | 425 km² |
| Location | |
| A country |
|
| Region | Atyrau region |
| Area | Inder District |
The shape of the lake is round, slightly elongated from the northwest to the southeast. The diameter of the lake is from 10 to 13.5 km. Rivers do not flow into the lake; food is mainly underground: salty springs confined to clay deposits, which are abundant along the coast; also melt and rainwater in spring.
The northern and northeastern shores of the lake border the Inder Mountains .
Content
Usage
The waters of the lake contain high-quality salts containing potassium , bromine and boron [1] . Salt is being mined. The thickness of the salt layer in some places reaches 10-15 m (according to the CNE , up to 56 m). Back in the 19th century, Russian geologists showed increased interest in the study of the lake and its environs. The closest settlement to the lake is the urban-type Inderborsk settlement , the center of the Inder district of the Atyrau region , located 10 km to the north-west [2] .
Up to 1.5 million tons of salts (mainly edible salt ) are precipitated in the lake per year. Clays of the lake are used for medicinal purposes.
Flora
Near the Inder Lake in the Caspian Lowland in the 19th century, Russian researchers first discovered the Inderus eremurus plant. Inder's onion , despite its name, does not grow by the lake.
Notes
- ↑ Inder // Great Soviet Encyclopedia : [in 30 vol.] / Ch. ed. A.M. Prokhorov . - 3rd ed. - M .: Soviet Encyclopedia, 1969-1978.
- ↑ Russia, Murmansk Oblast, Inder Lake - Yandex. Cards
Literature
- Inder // Kazakhstan. National Encyclopedia . - Almaty: Kazakh encyclopedias , 2005. - T. II. - ISBN 9965-9746-3-2 .
- Valyashko M. G. Study of the physicochemical regime of Lake Inder and the preparation of salts from its brines (dissertation), 1943.
- Inder self-landing lake // Brockhaus and Efron Encyclopedic Dictionary : 86 tons (82 tons and 4 additional). - SPb. , 1890-1907.