The Battle of Fao is one of the first U.S. military operations during the invasion of Iraq in March 2003 .
| The Battle of Fao | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Main Conflict: Invasion of Iraq | |||
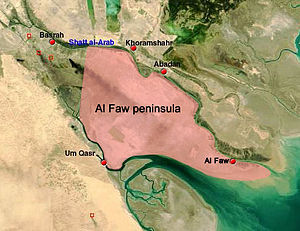 El Fao Peninsula | |||
| date | March 20 - 24, 2003 | ||
| A place | El Fao , Iraq | ||
| Total | Allied victory | ||
| Opponents | |||
| |||
| Forces of the parties | |||
| |||
The purpose of the operation was to capture the oil region of the Fao Peninsula before the oil installations were destroyed by the Iraqi armed forces.
The British 3rd Special Forces Brigade ( 3 Commando Brigade ) also participated in the capture of Umm Qasr , the only deepwater port in Iraq. The 15th expeditionary detachment of the United States Marine Corps took part in the operation.
Content
Battle Progress
March 20
After several days of bad weather, the invasion of the peninsula was scheduled for March 20, 2003 at 22:00 local time. US Air Force helicopters and fighter-bombers attacked enemy positions on the peninsula. 40 American commandos and marines landed from the helicopter, captured three strategic targets without casualties and captured more than 200 Iraqi soldiers.
At the same time, air and sea landing assured control of gas and oil platforms at sea. American and Polish commandos occupied the oil terminals Mina Al-Bakr and Khor Al-Amaya.
At 22-25, the second phase of the operation began. Under the cover of long-range artillery located on Bubiyan Island and the fire of the ships HMS Richmond, HMS Marlborough, HMS Chatham and HMAS Anzac , marines, supported by Bell AH-1 Cobra helicopters, landed north of the city of El Fao and destroyed Iraqi artillery, which could threaten oil platforms.
The landing took place in conditions of poor visibility, exacerbated by fires and sand. The headquarters helicopter Boeing Vertol CH-46 Sea Knight intelligence team of the United States crashed in conditions of loss of horizon, killing 12 officers and soldiers [1] . With a deterioration in visibility, the landing was interrupted and resumed only after 6 hours.
March 21
Early in the morning of March 21, the 15th US expeditionary force crossed the Iraqi-Kuwait border bypassing Umm Qasr and seized the port and began to advance along the western shore of the Abdullah Strait. The British marines landed on the shore, who began to take up positions in the salt marshes south of Basra.
March 22
The Fedains of Saddam Hussein put up stubborn resistance in the Umm Qasr region . Two Navy helicopters Boeing Vertol CH-46 Sea Knight collided, killing 7 people.
March 23
On March 23, Anglo-American troops landed on the peninsula, which refuted the numerous assurances of the American and British military that the peninsula would be under the control of the anti-Iraq coalition two days ago [2] , after which they entered into a fierce battle with Iraqi forces defending the island [3] .
March 24th
The Iraqi tank brigade counterattacked coalition forces near El Fao, but was repelled by special forces with numerous Iraqi losses in armored vehicles [4] .
Only on March 25, the coalition managed to capture the peninsula, after which the clearance of the Umm-Qasr area began. The British 7th Panzer Brigade advanced to Basra, and the US forces launched an attack on Baghdad without the threat of a flank attack by Iraqi forces and their attack on the supply line.
Notes
- ↑ Mark Ormrod, Man Down , Random House, 2009, p. 145
- ↑ A landing party landed on the coast of the Iraqi Peninsula Fao
- ↑ [1] (inaccessible link)
- ↑ Operations In Iraq - First Reflections , British Ministry of Defense, July 7, 2003