Titin , also known as connectin, is the largest single polypeptide . It plays an important role in the process of contraction of striated muscles [1] [2] . The titin gene contains the largest number of exons.
| Titin | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
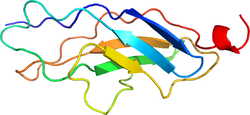 The three-dimensional structure of the module titin type I. PDB is drawn based on 1bpv. | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||
| Symbol | ; CMD1G; CMH9; CMPD4; EOMFC; HMERF; LGMD2J; MYLK5; Tmd | ||||||||||||
| External id | GeneCards : | ||||||||||||
| EC number | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| RNA expression profile | |||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||
| Ortologists | |||||||||||||
| View | Person | Mouse | |||||||||||
| Entrez | |||||||||||||
| Ensembl | |||||||||||||
| UniProt | |||||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |||||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | |||||||||||||
| Locus (UCSC) | |||||||||||||
| PubMed Search | |||||||||||||
Content
Structure
Titin, consisting of 38138 amino acids (titin of the soleus muscle) is the largest known protein . The molecular weight of the protein is approximately 2,993,442.763 a. em. [3] , its theoretical isoelectric point is 6.01 [4] . The empirical chemical formula of this protein is C 132983 H 211861 N 36149 O 40883 S 693 . The theoretical unstable index (II), showing its stability in a test tube, is 39.69. The half-life (the time required for the disappearance of half of the contained protein in the cell after its synthesis) is approximately 30 hours (in animal reticulocytes) [5] . Titin consists mainly of linear modules of two types: type I (type III fibronectin domain) and type II (immunoglobulin-like domain) [6] . These linear blocks are then organized into two sections:
- N-terminal (as part of the I-bands of sarcomere )
- acts as an elastic part of the molecule and consists mainly of type II modules. In particular, Group I consists of two sites of type II tandem immunoglobulin domains on each side of the PEVK site, rich in proline , glutamic acid , valine and lysine . Located between myosin and Z-disk [7] .
- C-terminal (composed of A-bands)
- performs the control function and probably has a protein kinase activity. A-bands consist of alternating type I and type II modules.
Functions
Titin is a large striated muscle protein. The N-terminal region of the Z-disk and the C-terminal region of the M-line are connected, respectively, with the Z-disk and M-line of the sarcomere , so that a single titin molecule stretches along half its length. Titin also contains binding sites for the attachment of muscle proteins, so that it serves as a matrix for the proper assembly of the proteins that make up the sarcomere. It was found that it is also included as a structural protein in the composition of chromosomes . Significant variability is characteristic of titin molecule sites located in the I-band, M-line, and Z-disk. Variability in the I-band region determines the differences in the elasticity of different titin isoforms, and, consequently, the differences in the elasticity of different types of muscles. Of the many known variants of titin, only five of them fully decoded the amino acid sequence [2] [8] .
Titin interacts with many sarcomeric proteins, including: [9]
- Z-linear segment: teletonin and α-actinin-1
- Plot I-band: calpain-3 and obscure
- M-linear region: myosin-binding protein C, calmodulin 1, calpein-3 and Ubiquitin ligase .
Role in medicine
Mutations in the titin gene are associated with hereditary hypertrophic cardiomyopathy [10] [11] and progressive Myosi distal muscular dystrophy [12] . Anti-titin autoantibodies are produced in patients with autoimmune scleroderma [13] .
Meaning in linguistics
Like the biggest known protein, titin has the longest nomenclature name IUPAC . The full chemical name, starting with methionyl ... and ending with ... isoleucine , includes (in English) 189,819 letters, recognized as the longest word not only in English, but also in any other [14] . However, professional compilers of dictionaries consider the names of chemical compounds rather as verbal chemical formulas, rather than as words of the commonly used language [15] .
Notes
- ↑ OMIM 188840
- 2 1 2 Entrez Gene: TTN titin Neopr .
- ↑ Result of Molecular Weight Calculation
- ↑ ExPASy-calculated pI for titin Neopr . The appeal date is August 26, 2007. Archived on April 13, 2012.
- ↑ Swiss-Prot Protein knowledgebase, main entry . The appeal date is May 4, 2006. Archived April 13, 2012.
- ↑ Labeit S., Kolmerer B. Titins: giant proteins in muscle ultrastructure and elasticity (eng.) // Science: journal. - 1995. - October ( vol. 270 , no. 5234 ). - P. 293-296 . - PMID 7569978 .
- ↑ Wang, K., McCarter, R., Wright, J., Beverly, J., Ramirez-Mitchell, R., Regulation tit tit tit of the United States of America : journal. - 1991. - August ( vol. 88 , no. 16 ). - P. 7101-7105 . - PMID 1714586 .
- ↑ Labeit S., Barlow DP, Gautel M., Gibson T., Holt J., Hsieh CL, Francke U., Leonard K., Wardale J., Whiting A., Trinick J. A regular pattern of two types of 100 -residue motif in the sequence of titin (eng.) // Nature: journal. - 1990. - May ( vol. 345 , no. 6272 ). - P. 273-276 . - DOI : 10.1038 / 26926a0 . - PMID 2129545 .
- ML Bang ML, Centner T., Fornoff F., Geach AJ, Gotthardt M., McNabb M., Witt CC, Labeit D., Gregorio CC, Granzier H., Labeit S. Observe approximately 700-kDa titin isoform, and identify it to the I-band linking system ( Circ. ) . Res. : journal. - 2001. - November ( vol. 89 , no. 11 ). - P. 1065-1072 . - DOI : 10.1161 / hh2301.100981 . - PMID 11717165 .
- ↑ Siu BL, Niimura H., Osborne JA, Fatkin D., MacRae C., Solomon S., Benson DW, Seidman JG, Seidman CE Familial dilated cardiomyopathy locus maps to chromosome 2q31 (English) // Circulation : journal. - Lippincott Williams & Wilkins , 1999. - March ( vol. 99 , no. 8 ). - P. 1022-1026 . - PMID 10051295 .
- ↑ Itoh-Satoh M., Hayashi T., Nishi H., Koga Y., Arimura T., Koyanagi T., Takahashi M., Hohda S., Ueda K., Nouchi T., Hiroe M., Marumo F. , Imaizumi T., Yasunami M., Kimura A. Titin mutations of cardiomyopathy (English) // Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. : journal. - 2002. - February ( vol. 291 , no. 2 ). - p . 385–393 . - DOI : 10.1006 / bbrc.2002.6448 . - PMID 11846417 .
- ↑ Hackman P., Vihola A., Haravuori H., Marchand S., Sarparanta J., De Seze J., Labeit S., Witt C., Peltonen L., Richard I., Udd B. Tibial muscular dystrophy is a titinopathy caused by mutations in TTN, the skeletal-muscle protein titin, the gene encoding the giant (Eng.) // Am. J. Hum. Genet. : journal. - 2002. - September ( vol. 71 , no. 3 ). - P. 492—500 . - DOI : 10.1086 / 342380 . - PMID 12145747 .
- Ado Machado C., Sunkel CE, Andrew DJ Human autoantibodies reveal titin as a chromosomal protein (Eng.) // J. Cell Biol. : journal. - 1998. - April ( vol. 141 , no. 2 ). - P. 321-333 . - DOI : 10.1083 / jcb.141.2.321 . - PMID 9548712 .
- What is the longest word in the English language? CliffsNotes.com . The date of circulation is January 24, 2016.
- ↑ Oxford Word and Language Service team. Ask the experts - What is the longest English word? AskOxford.com / Oxford University Press . The date of circulation is January 13, 2008. Archived April 13, 2012.