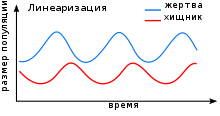
Model Loti - Volterra (spread the wrong [1] name - Lotka-Volterra model [2] ) - a model of the interaction of two species of the “predator-prey” type, named after its authors ( Lotka , 1925 ; Volterra 1926 ), who proposed model equations independently of each other.
Such equations can be used to simulate the predator – prey , parasite – host systems , competition, and other types of interaction between two species [3] .
In mathematical form, the proposed system has the following form:
- ,
- ,
Where - number of victims, - number of predators, - time - coefficients reflecting interactions between species.
Content
- 1 Solution of the system of equations
- 1.1 statement of the problem
- 1.2 solution of the problem
- 1.2.1 Finding a stationary position of the system
- 1.2.2 Defining a deviation in the system
- 2 See also
- 3 notes
- 4 References
Solution of a system of equations
Statement of the Problem
A closed range is considered, in which two species live - herbivores ("prey") and predators. It is assumed that animals do not immigrate and do not emigrate , and that there is an abundance of food for herbivores. Then the equation for changing the number of victims (excluding predators) takes the form:
- ,
Where - the birth rate of victims, - the size of the population of victims, - the growth rate of the victim population.
While predators do not hunt, they die out, therefore, the equation for the number of predators (excluding the number of victims) takes the form:
- ,
Where - coefficient of predator attrition, - the size of the predator population, - the growth rate of the predator population.
At meetings of predators and victims (the frequency of which is directly proportional to ) victims are killed with a coefficient , well-fed predators are capable of reproduction with a coefficient of . With this in mind, the system of equations of the model is as follows:
- .
Problem
Finding a Stationary System Position
For stationary position the change in population is zero. Hence:
- ,
- ,
from which it follows that the stationary point of the system around which oscillations occur is determined as follows:
- ,
- .
Deflection in the system
When introduced into the oscillation system and , due to their small size by their squares, cubes and subsequent degrees ( ) can be neglected. Thus populations and with small deviations are described by the following expressions:
- ,
- .
Applying them to the equations of the model, it follows:
Differentiation of one of these equations and substitution into another gives the following result:
- ,
- .
The resulting expression is a proportional equation of a harmonic oscillator with a period .
See also
- Biological systems modeling
- Kleiber's Law
Notes
- ↑ All surnames ending in unstressed and after consonants are declined according to the first declension: Ribera - Ribera, Ribera, Ribera, Ribera, Seneca - Seneca , etc .; Kafka, Spinoza, Smetana, Petrarch, Kurosawa, Glinka, Deineka, Gulyg, Olesha, Nagnibeda, Okudzhava and others are also inclined. All such names, regardless of origin, are morphologically distinct in Russian, that is, the ending is highlighted in them Oh . [one]
- ↑ P.V. Turchin. Lecture 14. Population dynamics
- ↑ Odum, 1986





