
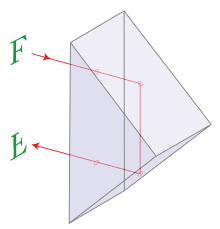

Prism Malafeev - Porro ( Malafeev-Porro wrapping system) - prism BR-180 °, located in the configuration in which the image is turned over (turned around) [1] . Invented by Russian optician O. N. Malafeev in 1827 [2] . Named after Ignazio Porro , who later rediscovered it in Italy in the 1850s. Used in optical instruments (mainly binoculars and monoculars) to change the orientation (flipping) of an image.
Content
Device
It is a product of glass or other transparent optical material in the form of a direct prism with an isosceles right-angled triangle at the base. In normal use, the beam enters from the wide rectangular side of the prism, experiences total internal reflection from the small rectangular sides twice, and exits through the wide rectangular side. Since light enters and leaves the prism approximately perpendicular to the surface, the prism is not dispersive - the path of light in it does not depend on the wavelength.
An image passing through a prism is reflected specularly with respect to a plane of symmetry perpendicular to the base. The direction of the beam changes by 180 °.
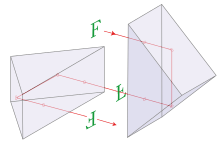
Porro prisms are often used in pairs, forming a prismatic system of the first or second kind [3] . In the system of the first kind, two identical Porro prisms are used. The second prism, rotated 90 ° relative to the first, is set so that the beam hits it after exiting the first prism. In this case, the image, which is twice reflected specularly relative to two perpendicular planes, is ultimately turned 180 ° relative to the original.
The Porro double prism is often used in binoculars to flip the image, increase the optical distance between the lens and the eyepiece while maintaining external dimensions, as well as some increase in stereo base.
Double Porro prism can be made in the form of a single block or gluing.
The prismatic system of Porro of the second kind was called the Abbe prism - Porro . There are as many reflecting faces as in a prism of the first kind, but the entire system is made of one piece of glass [3] .
It is also possible to use the Porro prism, similar to using the pentaprism , for example, in the periscope . In this case, light enters and leaves through small rectangular faces, and is reflected from a wide rectangular face. This use is not as widespread as described above.
See also
- Pentaprism
- Pentazerkalo
- Prism Abbe - Porro
Notes
- ↑ Theory of Optical Systems, 1992 , p. 73.
- ↑ Theory of Optical Instruments, 1966 , p. 31.
- ↑ 1 2 Theory of optical systems, 1992 , p. 74.
Literature
- N.P. Zakaznov, S.I. Kiryushin, V.I. Kuzichev. Chapter V. Details of optical systems // Theory of optical systems / T.V. Abivova. - M .: "Mechanical Engineering", 1992. - S. 53–91. - 448 p. - 2300 copies. - ISBN 5-217-01995-6 .
- V.N. Churilovsky . Chapter I. Geometric optics // Theory of optical instruments / A. P. Grammatin. - M .: "Engineering", 1966. - S. 28-35. - 274 p. - 150 copies, copies. - ISBN 5-7577-0077-7 .
Links
- Hecht, Eugene. Optics (4th ed.). - Pearson Education, 2001. - ISBN ISBN 0-8053-8566-5 .